Peiyi Zhang
Beyond Translation: Cross-Cultural Meme Transcreation with Vision-Language Models
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:Memes are a pervasive form of online communication, yet their cultural specificity poses significant challenges for cross-cultural adaptation. We study cross-cultural meme transcreation, a multimodal generation task that aims to preserve communicative intent and humor while adapting culture-specific references. We propose a hybrid transcreation framework based on vision-language models and introduce a large-scale bidirectional dataset of Chinese and US memes. Using both human judgments and automated evaluation, we analyze 6,315 meme pairs and assess transcreation quality across cultural directions. Our results show that current vision-language models can perform cross-cultural meme transcreation to a limited extent, but exhibit clear directional asymmetries: US-Chinese transcreation consistently achieves higher quality than Chinese-US. We further identify which aspects of humor and visual-textual design transfer across cultures and which remain challenging, and propose an evaluation framework for assessing cross-cultural multimodal generation. Our code and dataset are publicly available at https://github.com/AIM-SCU/MemeXGen.
M3KE: A Massive Multi-Level Multi-Subject Knowledge Evaluation Benchmark for Chinese Large Language Models
May 21, 2023



Abstract:Large language models have recently made tremendous progress in a variety of aspects, e.g., cross-task generalization, instruction following. Comprehensively evaluating the capability of large language models in multiple tasks is of great importance. In this paper, we propose M3KE, a Massive Multi-Level Multi-Subject Knowledge Evaluation benchmark, which is developed to measure knowledge acquired by Chinese large language models by testing their multitask accuracy in zero- and few-shot settings. We have collected 20,477 questions from 71 tasks. Our selection covers all major levels of Chinese education system, ranging from the primary school to college, as well as a wide variety of subjects, including humanities, history, politics, law, education, psychology, science, technology, art and religion. All questions are multiple-choice questions with four options, hence guaranteeing a standardized and unified assessment process. We've assessed a number of state-of-the-art open-source Chinese large language models on the proposed benchmark. The size of these models varies from 335M to 130B parameters. Experiment results demonstrate that they perform significantly worse than GPT-3.5 that reaches an accuracy of ~ 48% on M3KE. The dataset is available at https://github.com/tjunlp-lab/M3KE.
Self-supervised learning for fast and scalable time series hyper-parameter tuning
Feb 10, 2021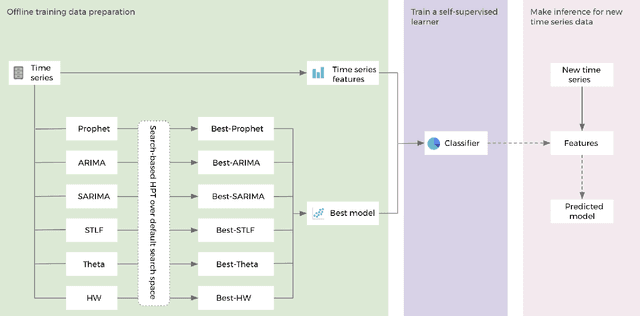
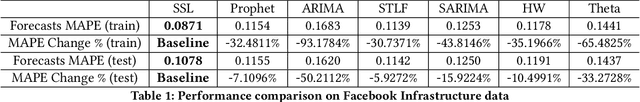
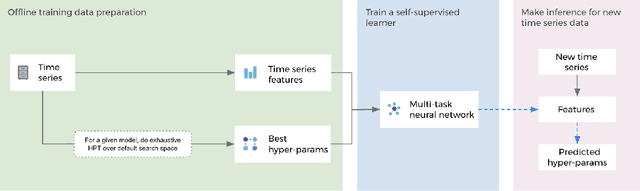
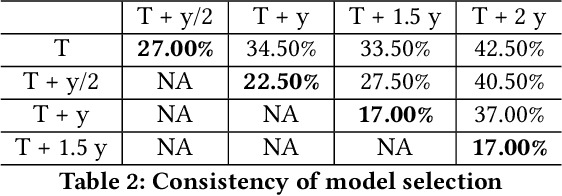
Abstract:Hyper-parameters of time series models play an important role in time series analysis. Slight differences in hyper-parameters might lead to very different forecast results for a given model, and therefore, selecting good hyper-parameter values is indispensable. Most of the existing generic hyper-parameter tuning methods, such as Grid Search, Random Search, Bayesian Optimal Search, are based on one key component - search, and thus they are computationally expensive and cannot be applied to fast and scalable time-series hyper-parameter tuning (HPT). We propose a self-supervised learning framework for HPT (SSL-HPT), which uses time series features as inputs and produces optimal hyper-parameters. SSL-HPT algorithm is 6-20x faster at getting hyper-parameters compared to other search based algorithms while producing comparable accurate forecasting results in various applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge