Paul-Alexis Dray
NL-Augmenter: A Framework for Task-Sensitive Natural Language Augmentation
Dec 06, 2021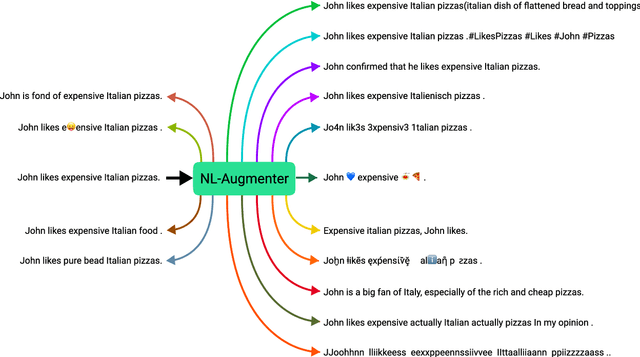
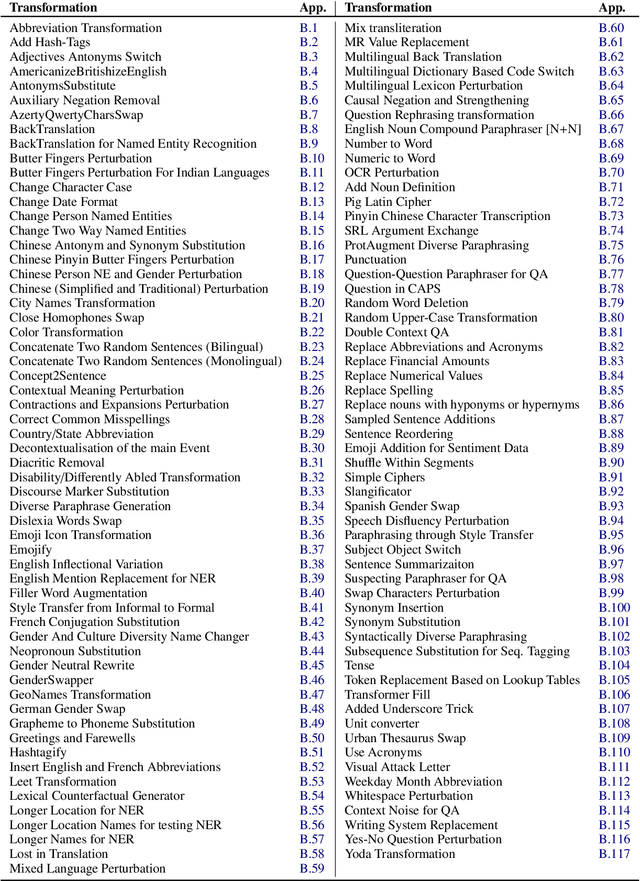
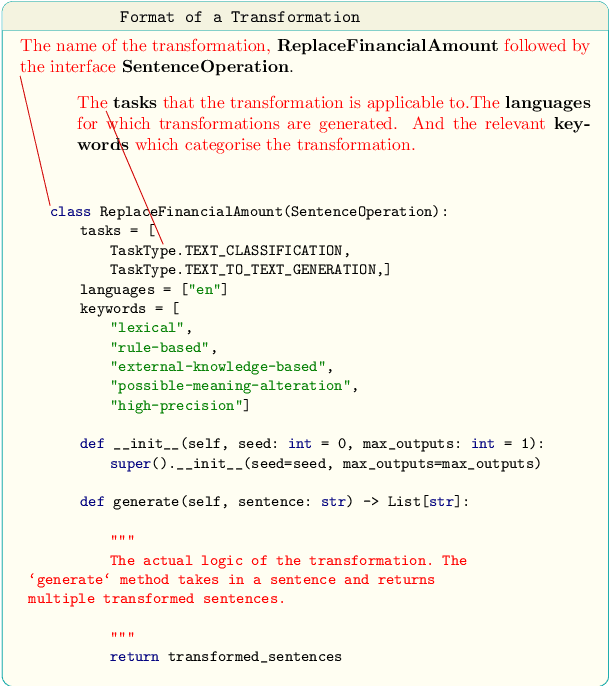
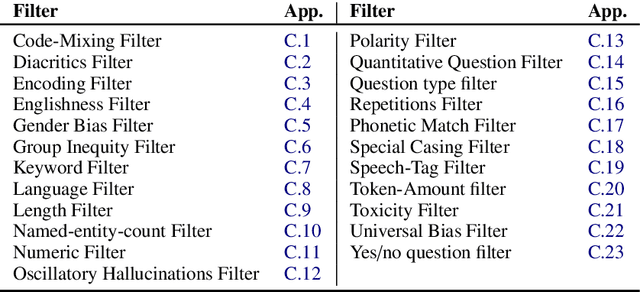
Abstract:Data augmentation is an important component in the robustness evaluation of models in natural language processing (NLP) and in enhancing the diversity of the data they are trained on. In this paper, we present NL-Augmenter, a new participatory Python-based natural language augmentation framework which supports the creation of both transformations (modifications to the data) and filters (data splits according to specific features). We describe the framework and an initial set of 117 transformations and 23 filters for a variety of natural language tasks. We demonstrate the efficacy of NL-Augmenter by using several of its transformations to analyze the robustness of popular natural language models. The infrastructure, datacards and robustness analysis results are available publicly on the NL-Augmenter repository (\url{https://github.com/GEM-benchmark/NL-Augmenter}).
To Beam Or Not To Beam: That is a Question of Cooperation for Language GANs
Jun 11, 2021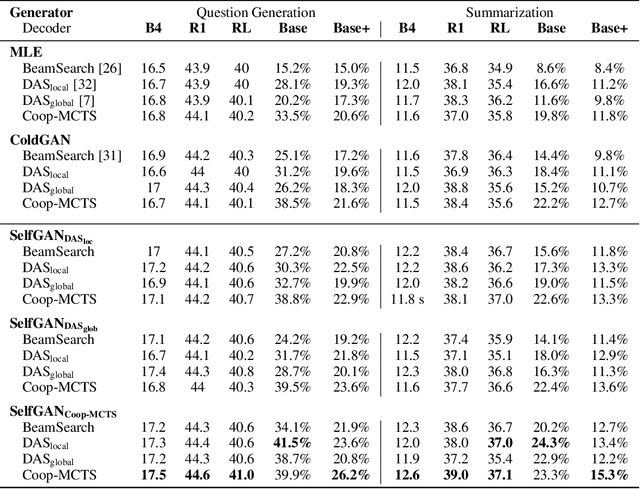
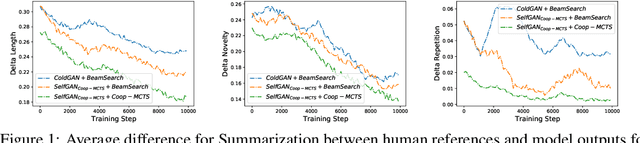
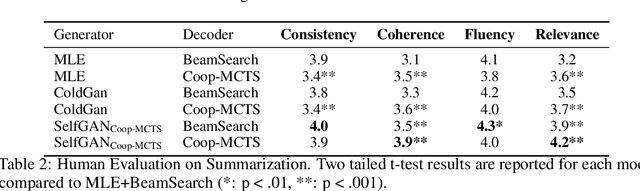
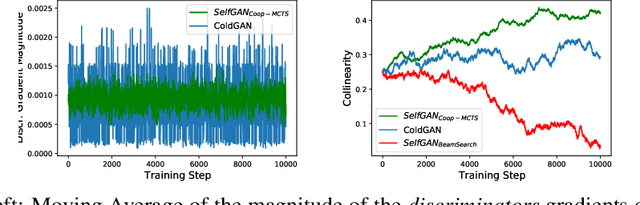
Abstract:Due to the discrete nature of words, language GANs require to be optimized from rewards provided by discriminator networks, via reinforcement learning methods. This is a much harder setting than for continuous tasks, which enjoy gradient flows from discriminators to generators, usually leading to dramatic learning instabilities. However, we claim that this can be solved by making discriminator and generator networks cooperate to produce output sequences during training. These cooperative outputs, inherently built to obtain higher discrimination scores, not only provide denser rewards for training, but also form a more compact artificial set for discriminator training, hence improving its accuracy and stability. In this paper, we show that our SelfGAN framework, built on this cooperative principle, outperforms Teacher Forcing and obtains state-of-the-art results on two challenging tasks, Summarization and Question Generation.
QuestEval: Summarization Asks for Fact-based Evaluation
Apr 09, 2021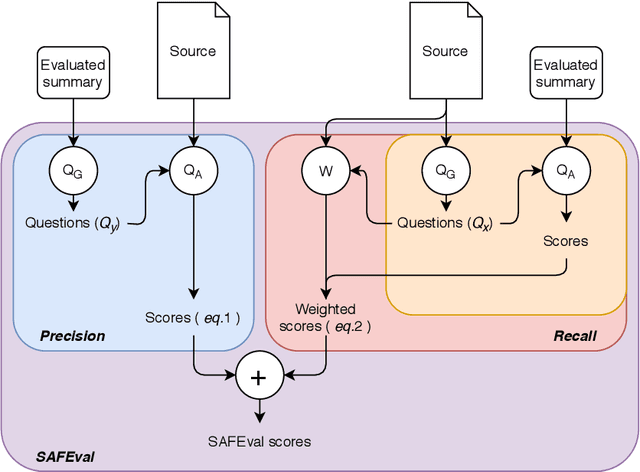
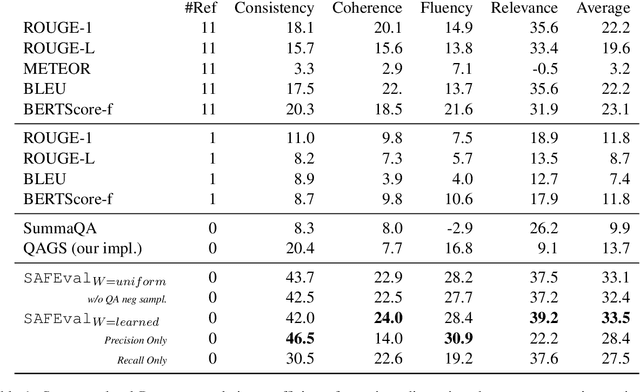
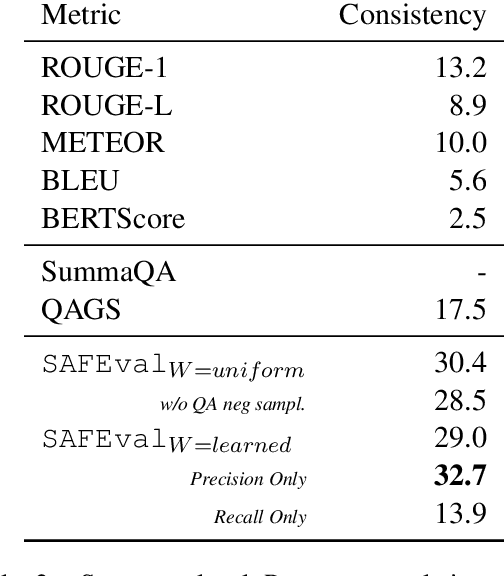
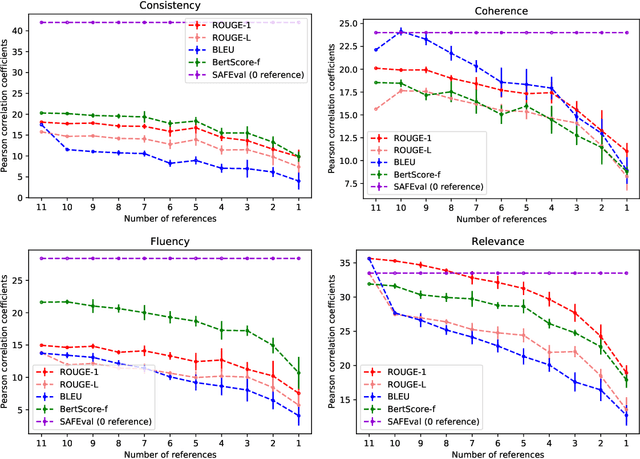
Abstract:Summarization evaluation remains an open research problem: current metrics such as ROUGE are known to be limited and to correlate poorly with human judgments. To alleviate this issue, recent work has proposed evaluation metrics which rely on question answering models to assess whether a summary contains all the relevant information in its source document. Though promising, the proposed approaches have so far failed to correlate better than ROUGE with human judgments. In this paper, we extend previous approaches and propose a unified framework, named QuestEval. In contrast to established metrics such as ROUGE or BERTScore, QuestEval does not require any ground-truth reference. Nonetheless, QuestEval substantially improves the correlation with human judgments over four evaluation dimensions (consistency, coherence, fluency, and relevance), as shown in the extensive experiments we report.
ColdGANs: Taming Language GANs with Cautious Sampling Strategies
Jun 08, 2020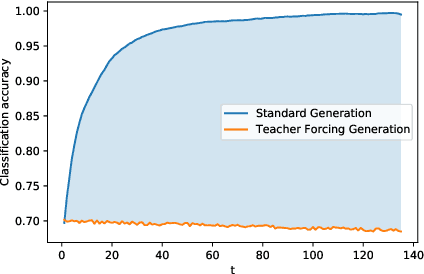
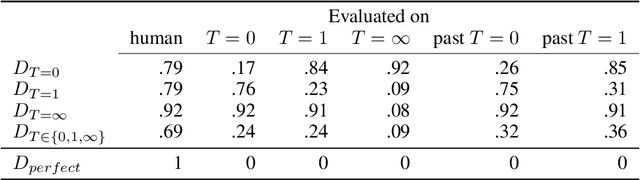
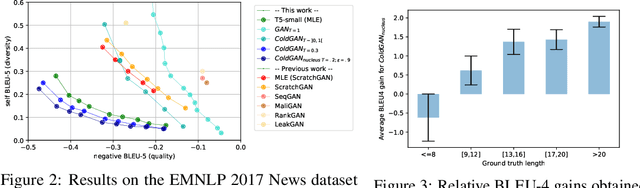
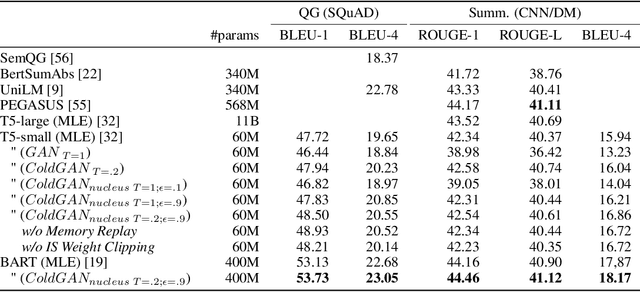
Abstract:Training regimes based on Maximum Likelihood Estimation (MLE) suffer from known limitations, often leading to poorly generated text sequences. At the root of these limitations is the mismatch between training and inference, i.e. the so-called exposure bias, exacerbated by considering only the reference texts as correct, while in practice several alternative formulations could be as good. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) can mitigate those limitations but the discrete nature of text has hindered their application to language generation: the approaches proposed so far, based on Reinforcement Learning, have been shown to underperform MLE. Departing from previous works, we analyze the exploration step in GANs applied to text generation, and show how classical sampling results in unstable training. We propose to consider alternative exploration strategies in a GAN framework that we name ColdGANs, where we force the sampling to be close to the distribution modes to get smoother learning dynamics. For the first time, to the best of our knowledge, the proposed language GANs compare favorably to MLE, and obtain improvements over the state-of-the-art on three generative tasks, namely unconditional text generation, question generation, and abstractive summarization.
MLSUM: The Multilingual Summarization Corpus
Apr 30, 2020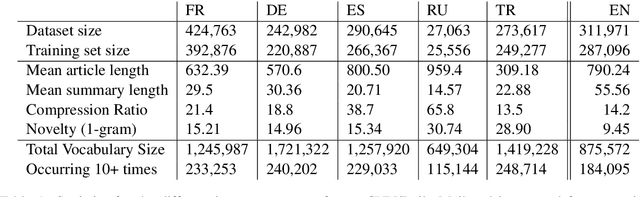
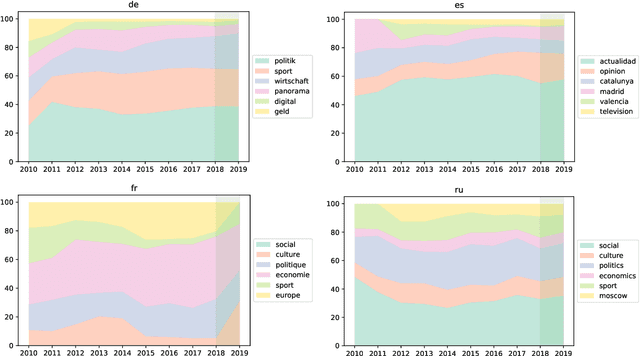
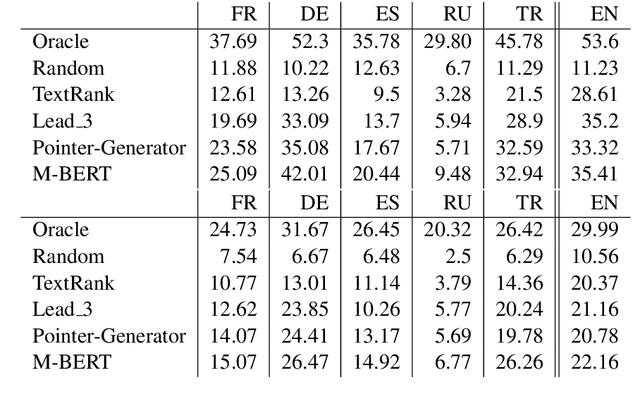
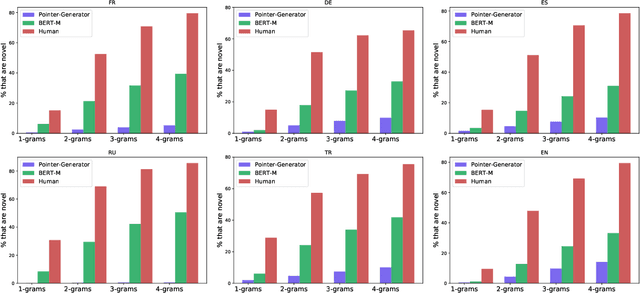
Abstract:We present MLSUM, the first large-scale MultiLingual SUMmarization dataset. Obtained from online newspapers, it contains 1.5M+ article/summary pairs in five different languages -- namely, French, German, Spanish, Russian, Turkish. Together with English newspapers from the popular CNN/Daily mail dataset, the collected data form a large scale multilingual dataset which can enable new research directions for the text summarization community. We report cross-lingual comparative analyses based on state-of-the-art systems. These highlight existing biases which motivate the use of a multi-lingual dataset.
BERT Can See Out of the Box: On the Cross-modal Transferability of Text Representations
Feb 25, 2020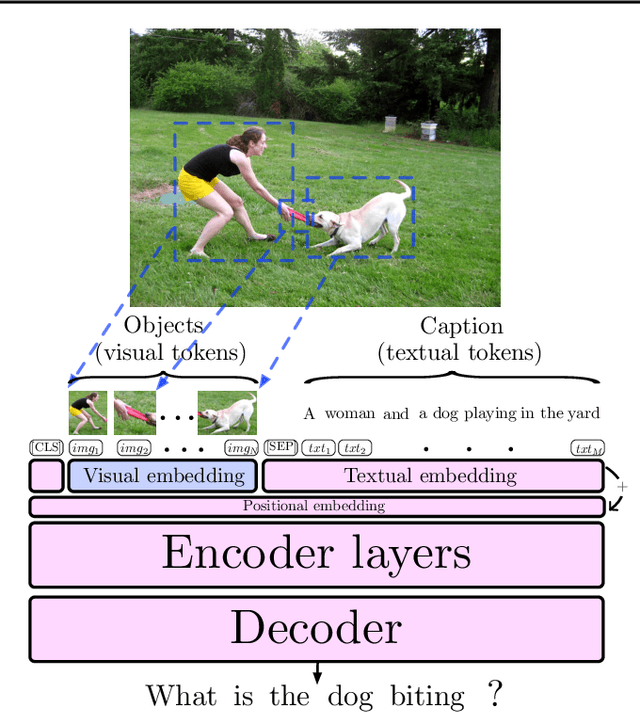
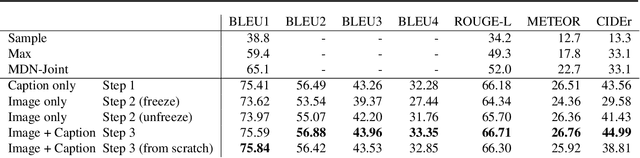
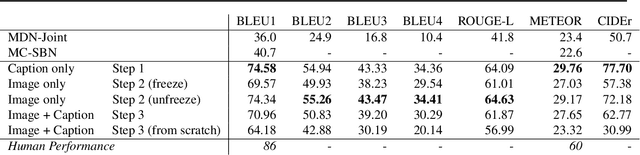
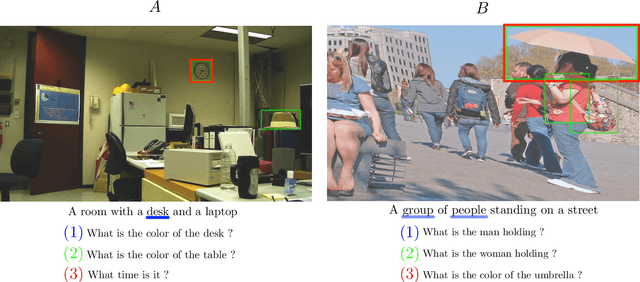
Abstract:Pre-trained language models such as BERT have recently contributed to significant advances in Natural Language Processing tasks. Interestingly, while multilingual BERT models have demonstrated impressive results, recent works have shown how monolingual BERT can also be competitive in zero-shot cross-lingual settings. This suggests that the abstractions learned by these models can transfer across languages, even when trained on monolingual data. In this paper, we investigate whether such generalization potential applies to other modalities, such as vision: does BERT contain abstractions that generalize beyond text? We introduce BERT-gen, an architecture for text generation based on BERT, able to leverage on either mono- or multi- modal representations. The results reported under different configurations indicate a positive answer to our research question, and the proposed model obtains substantial improvements over the state-of-the-art on two established Visual Question Generation datasets.
Discriminative Adversarial Search for Abstractive Summarization
Feb 24, 2020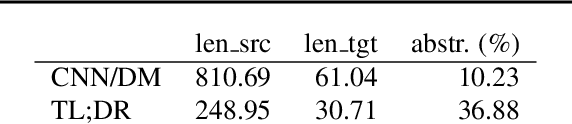
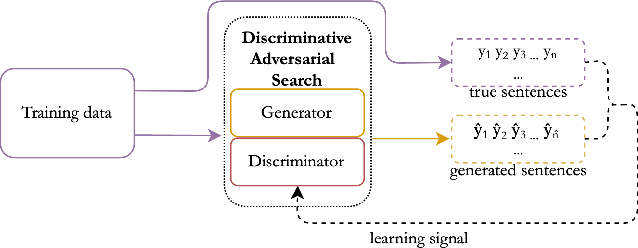
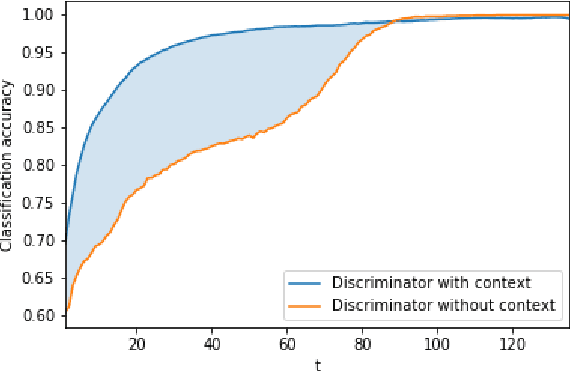
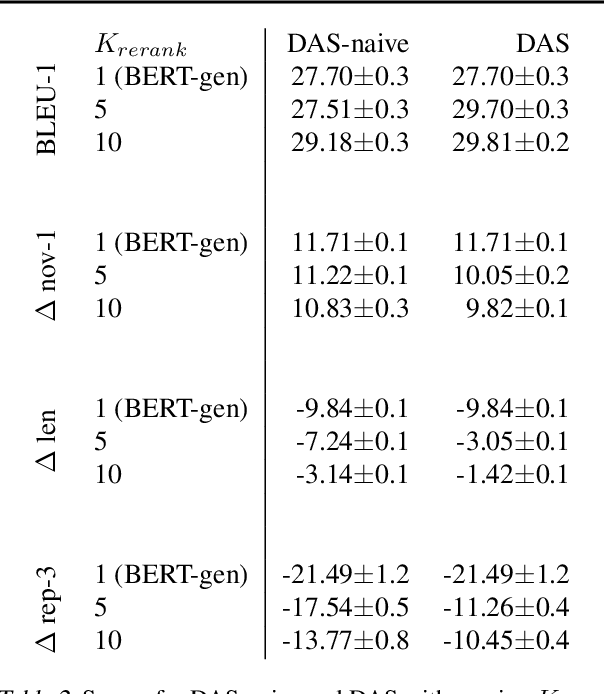
Abstract:We introduce a novel approach for sequence decoding, Discriminative Adversarial Search (DAS), which has the desirable properties of alleviating the effects of exposure bias without requiring external metrics. Inspired by Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), wherein a discriminator is used to improve the generator, our method differs from GANs in that the generator parameters are not updated at training time and the discriminator is only used to drive sequence generation at inference time. We investigate the effectiveness of the proposed approach on the task of Abstractive Summarization: the results obtained show that a naive application of DAS improves over the state-of-the-art methods, with further gains obtained via discriminator retraining. Moreover, we show how DAS can be effective for cross-domain adaptation. Finally, all results reported are obtained without additional rule-based filtering strategies, commonly used by the best performing systems available: this indicates that DAS can effectively be deployed without relying on post-hoc modifications of the generated outputs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge