Pal Halvorsen
Medical Imaging AI Competitions Lack Fairness
Dec 19, 2025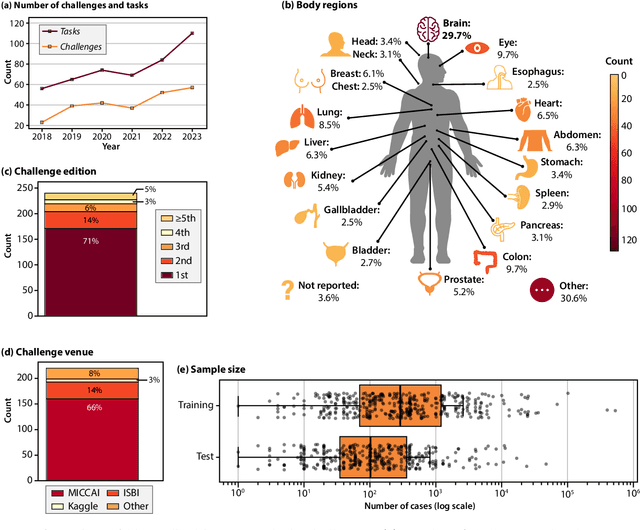
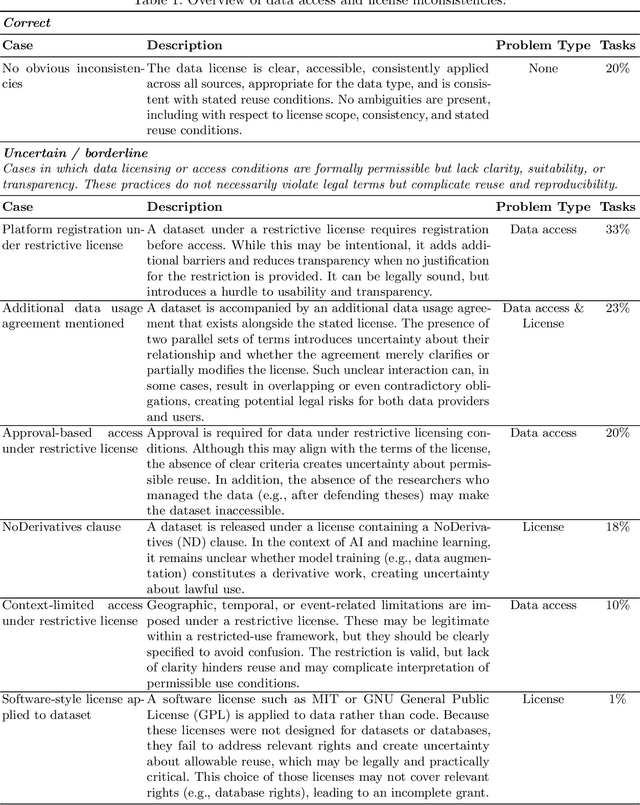
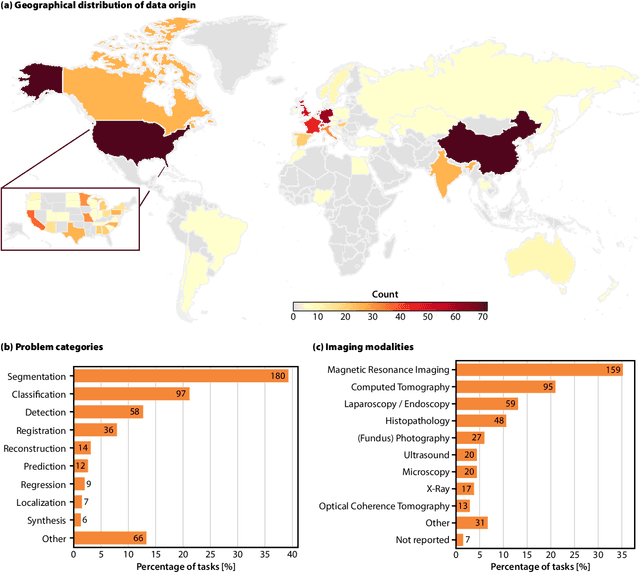
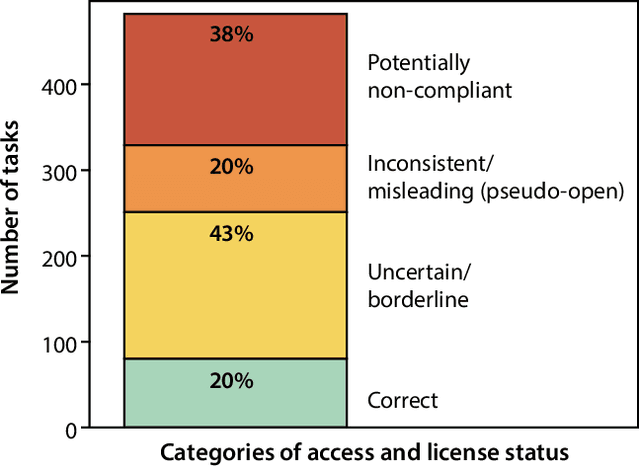
Abstract:Benchmarking competitions are central to the development of artificial intelligence (AI) in medical imaging, defining performance standards and shaping methodological progress. However, it remains unclear whether these benchmarks provide data that are sufficiently representative, accessible, and reusable to support clinically meaningful AI. In this work, we assess fairness along two complementary dimensions: (1) whether challenge datasets are representative of real-world clinical diversity, and (2) whether they are accessible and legally reusable in line with the FAIR principles. To address this question, we conducted a large-scale systematic study of 241 biomedical image analysis challenges comprising 458 tasks across 19 imaging modalities. Our findings show substantial biases in dataset composition, including geographic location, modality-, and problem type-related biases, indicating that current benchmarks do not adequately reflect real-world clinical diversity. Despite their widespread influence, challenge datasets were frequently constrained by restrictive or ambiguous access conditions, inconsistent or non-compliant licensing practices, and incomplete documentation, limiting reproducibility and long-term reuse. Together, these shortcomings expose foundational fairness limitations in our benchmarking ecosystem and highlight a disconnect between leaderboard success and clinical relevance.
Explainability of Machine Learning Models under Missing Data
Jun 29, 2024



Abstract:Missing data is a prevalent issue that can significantly impair model performance and interpretability. This paper briefly summarizes the development of the field of missing data with respect to Explainable Artificial Intelligence and experimentally investigates the effects of various imputation methods on the calculation of Shapley values, a popular technique for interpreting complex machine learning models. We compare different imputation strategies and assess their impact on feature importance and interaction as determined by Shapley values. Moreover, we also theoretically analyze the effects of missing values on Shapley values. Importantly, our findings reveal that the choice of imputation method can introduce biases that could lead to changes in the Shapley values, thereby affecting the interpretability of the model. Moreover, and that a lower test prediction mean square error (MSE) may not imply a lower MSE in Shapley values and vice versa. Also, while Xgboost is a method that could handle missing data directly, using Xgboost directly on missing data can seriously affect interpretability compared to imputing the data before training Xgboost. This study provides a comprehensive evaluation of imputation methods in the context of model interpretation, offering practical guidance for selecting appropriate techniques based on dataset characteristics and analysis objectives. The results underscore the importance of considering imputation effects to ensure robust and reliable insights from machine learning models.
2020 CATARACTS Semantic Segmentation Challenge
Oct 21, 2021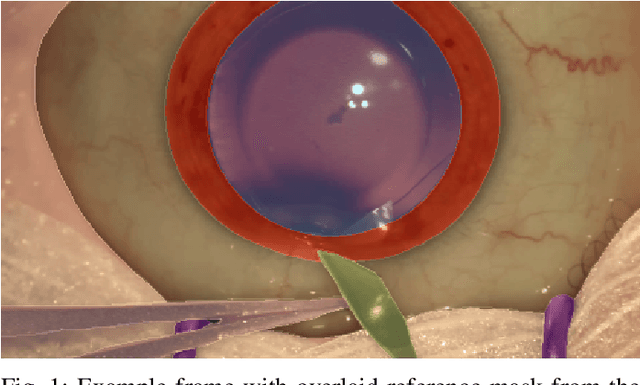
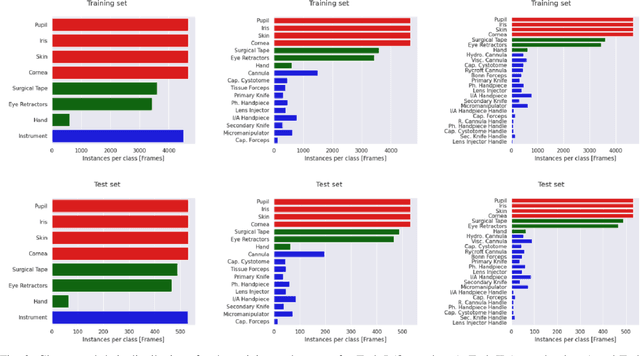
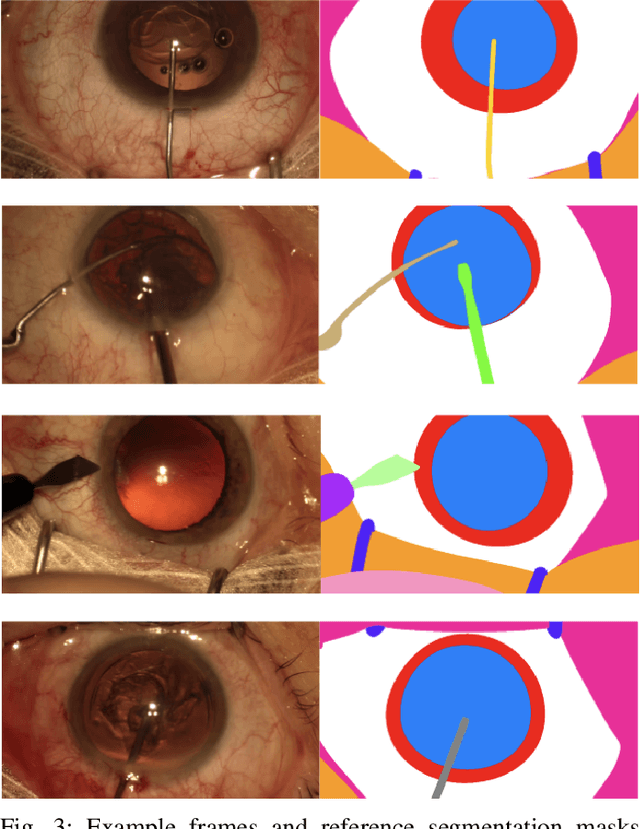
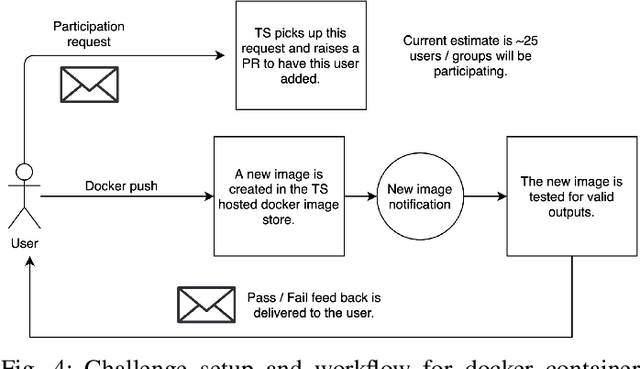
Abstract:Surgical scene segmentation is essential for anatomy and instrument localization which can be further used to assess tissue-instrument interactions during a surgical procedure. In 2017, the Challenge on Automatic Tool Annotation for cataRACT Surgery (CATARACTS) released 50 cataract surgery videos accompanied by instrument usage annotations. These annotations included frame-level instrument presence information. In 2020, we released pixel-wise semantic annotations for anatomy and instruments for 4670 images sampled from 25 videos of the CATARACTS training set. The 2020 CATARACTS Semantic Segmentation Challenge, which was a sub-challenge of the 2020 MICCAI Endoscopic Vision (EndoVis) Challenge, presented three sub-tasks to assess participating solutions on anatomical structure and instrument segmentation. Their performance was assessed on a hidden test set of 531 images from 10 videos of the CATARACTS test set.
ResUNet++: An Advanced Architecture for Medical Image Segmentation
Nov 16, 2019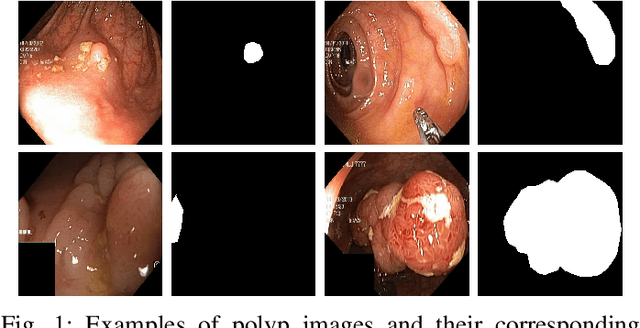



Abstract:Accurate computer-aided polyp detection and segmentation during colonoscopy examinations can help endoscopists resect abnormal tissue and thereby decrease chances of polyps growing into cancer. Towards developing a fully automated model for pixel-wise polyp segmentation, we propose ResUNet++, which is an improved ResUNet architecture for colonoscopic image segmentation. Our experimental evaluations show that the suggested architecture produces good segmentation results on publicly available datasets. Furthermore, ResUNet++ significantly outperforms U-Net and ResUNet, two key state-of-the-art deep learning architectures, by achieving high evaluation scores with a dice coefficient of 81.33%, and a mean Intersection over Union (mIoU) of 79.27% for the Kvasir-SEG dataset and a dice coefficient of 79.55%, and a mIoU of 79.62% with CVC-612 dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge