Nur Al Hasan Haldar
Dynamic watermarks in images generated by diffusion models
Feb 13, 2025



Abstract:High-fidelity text-to-image diffusion models have revolutionized visual content generation, but their widespread use raises significant ethical concerns, including intellectual property protection and the misuse of synthetic media. To address these challenges, we propose a novel multi-stage watermarking framework for diffusion models, designed to establish copyright and trace generated images back to their source. Our multi-stage watermarking technique involves embedding: (i) a fixed watermark that is localized in the diffusion model's learned noise distribution and, (ii) a human-imperceptible, dynamic watermark in generates images, leveraging a fine-tuned decoder. By leveraging the Structural Similarity Index Measure (SSIM) and cosine similarity, we adapt the watermark's shape and color to the generated content while maintaining robustness. We demonstrate that our method enables reliable source verification through watermark classification, even when the dynamic watermark is adjusted for content-specific variations. Source model verification is enabled through watermark classification. o support further research, we generate a dataset of watermarked images and introduce a methodology to evaluate the statistical impact of watermarking on generated content.Additionally, we rigorously test our framework against various attack scenarios, demonstrating its robustness and minimal impact on image quality. Our work advances the field of AI-generated content security by providing a scalable solution for model ownership verification and misuse prevention.
Deepfake Detection with Spatio-Temporal Consistency and Attention
Feb 12, 2025Abstract:Deepfake videos are causing growing concerns among communities due to their ever-increasing realism. Naturally, automated detection of forged Deepfake videos is attracting a proportional amount of interest of researchers. Current methods for detecting forged videos mainly rely on global frame features and under-utilize the spatio-temporal inconsistencies found in the manipulated videos. Moreover, they fail to attend to manipulation-specific subtle and well-localized pattern variations along both spatial and temporal dimensions. Addressing these gaps, we propose a neural Deepfake detector that focuses on the localized manipulative signatures of the forged videos at individual frame level as well as frame sequence level. Using a ResNet backbone, it strengthens the shallow frame-level feature learning with a spatial attention mechanism. The spatial stream of the model is further helped by fusing texture enhanced shallow features with the deeper features. Simultaneously, the model processes frame sequences with a distance attention mechanism that further allows fusion of temporal attention maps with the learned features at the deeper layers. The overall model is trained to detect forged content as a classifier. We evaluate our method on two popular large data sets and achieve significant performance over the state-of-the-art methods.Moreover, our technique also provides memory and computational advantages over the competitive techniques.
On quantifying and improving realism of images generated with diffusion
Sep 26, 2023



Abstract:Recent advances in diffusion models have led to a quantum leap in the quality of generative visual content. However, quantification of realism of the content is still challenging. Existing evaluation metrics, such as Inception Score and Fr\'echet inception distance, fall short on benchmarking diffusion models due to the versatility of the generated images. Moreover, they are not designed to quantify realism of an individual image. This restricts their application in forensic image analysis, which is becoming increasingly important in the emerging era of generative models. To address that, we first propose a metric, called Image Realism Score (IRS), computed from five statistical measures of a given image. This non-learning based metric not only efficiently quantifies realism of the generated images, it is readily usable as a measure to classify a given image as real or fake. We experimentally establish the model- and data-agnostic nature of the proposed IRS by successfully detecting fake images generated by Stable Diffusion Model (SDM), Dalle2, Midjourney and BigGAN. We further leverage this attribute of our metric to minimize an IRS-augmented generative loss of SDM, and demonstrate a convenient yet considerable quality improvement of the SDM-generated content with our modification. Our efforts have also led to Gen-100 dataset, which provides 1,000 samples for 100 classes generated by four high-quality models. We will release the dataset and code.
Text-image guided Diffusion Model for generating Deepfake celebrity interactions
Sep 26, 2023



Abstract:Deepfake images are fast becoming a serious concern due to their realism. Diffusion models have recently demonstrated highly realistic visual content generation, which makes them an excellent potential tool for Deepfake generation. To curb their exploitation for Deepfakes, it is imperative to first explore the extent to which diffusion models can be used to generate realistic content that is controllable with convenient prompts. This paper devises and explores a novel method in that regard. Our technique alters the popular stable diffusion model to generate a controllable high-quality Deepfake image with text and image prompts. In addition, the original stable model lacks severely in generating quality images that contain multiple persons. The modified diffusion model is able to address this problem, it add input anchor image's latent at the beginning of inferencing rather than Gaussian random latent as input. Hence, we focus on generating forged content for celebrity interactions, which may be used to spread rumors. We also apply Dreambooth to enhance the realism of our fake images. Dreambooth trains the pairing of center words and specific features to produce more refined and personalized output images. Our results show that with the devised scheme, it is possible to create fake visual content with alarming realism, such that the content can serve as believable evidence of meetings between powerful political figures.
Reinforced Meta-path Selection for Recommendation on Heterogeneous Information Networks
Dec 28, 2021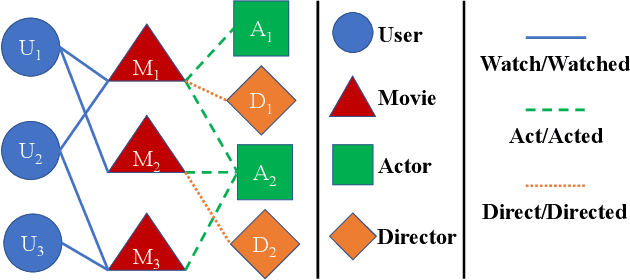
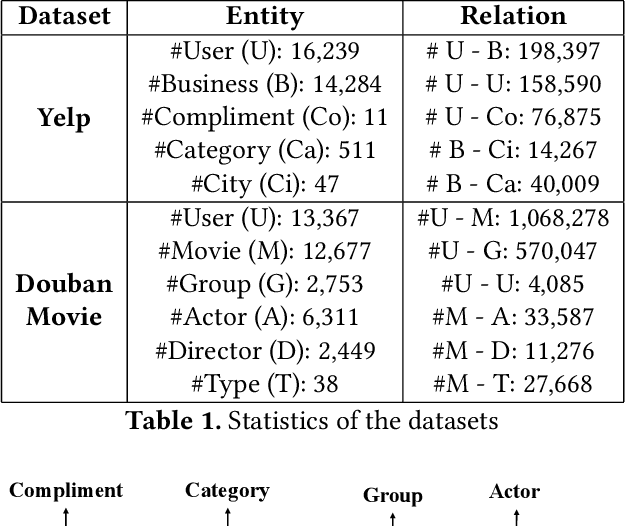
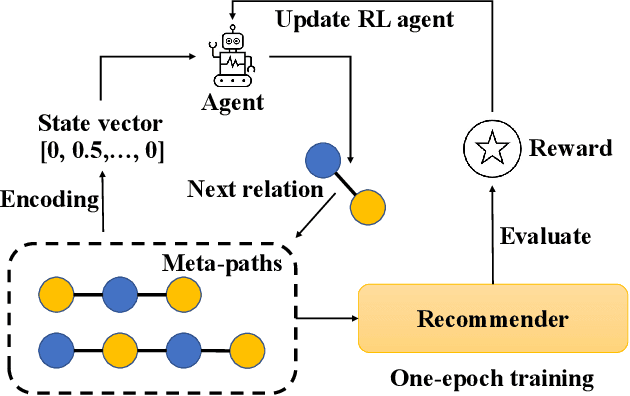
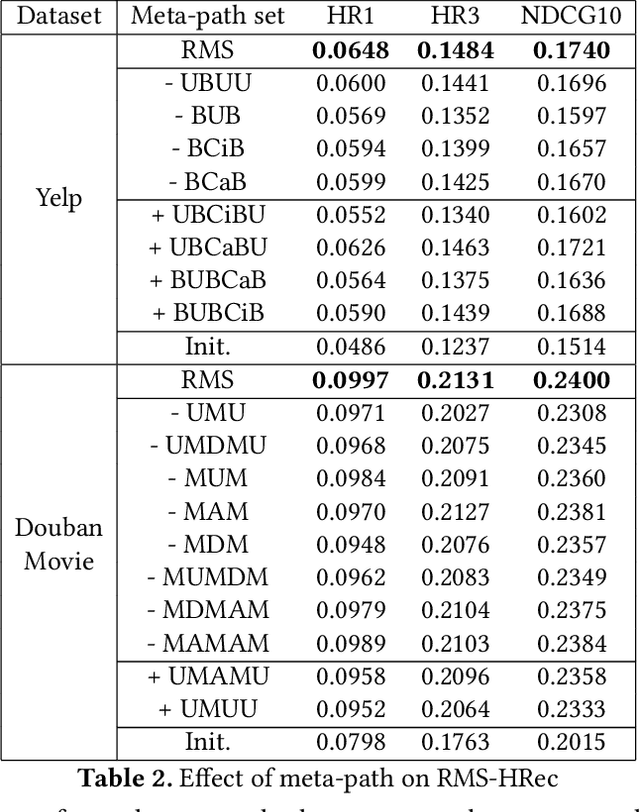
Abstract:Heterogeneous Information Networks (HINs) capture complex relations among entities of various kinds and have been used extensively to improve the effectiveness of various data mining tasks, such as in recommender systems. Many existing HIN-based recommendation algorithms utilize hand-crafted meta-paths to extract semantic information from the networks. These algorithms rely on extensive domain knowledge with which the best set of meta-paths can be selected. For applications where the HINs are highly complex with numerous node and link types, the approach of hand-crafting a meta-path set is too tedious and error-prone. To tackle this problem, we propose the Reinforcement learning-based Meta-path Selection (RMS) framework to select effective meta-paths and to incorporate them into existing meta-path-based recommenders. To identify high-quality meta-paths, RMS trains a reinforcement learning (RL) based policy network(agent), which gets rewards from the performance on the downstream recommendation tasks. We design a HIN-based recommendation model, HRec, that effectively uses the meta-path information. We further integrate HRec with RMS and derive our recommendation solution, RMS-HRec, that automatically utilizes the effective meta-paths. Experiments on real datasets show that our algorithm can significantly improve the performance of recommendation models by capturing important meta-paths automatically.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge