Nicola Toschi
Hyperbolic Graph Neural Networks Under the Microscope: The Role of Geometry-Task Alignment
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Many complex networks exhibit hyperbolic structural properties, making hyperbolic space a natural candidate for representing hierarchical and tree-like graphs with low distortion. Based on this observation, Hyperbolic Graph Neural Networks (HGNNs) have been widely adopted as a principled choice for representation learning on tree-like graphs. In this work, we question this paradigm by proposing an additional condition of geometry-task alignment, i.e., whether the metric structure of the target follows that of the input graph. We theoretically and empirically demonstrate the capability of HGNNs to recover low-distortion representations on two synthetic regression problems, and show that their geometric inductive bias becomes helpful when the problem requires preserving metric structure. Additionally, we evaluate HGNNs on the tasks of link prediction and node classification by jointly analyzing predictive performance and embedding distortion, revealing that only link prediction is geometry-aligned. Overall, our findings shift the focus from only asking "Is the graph hyperbolic?" to also questioning "Is the task aligned with hyperbolic geometry?", showing that HGNNs consistently outperform Euclidean models under such alignment, while their advantage vanishes otherwise.
Simple Models, Rich Representations: Visual Decoding from Primate Intracortical Neural Signals
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:Understanding how neural activity gives rise to perception is a central challenge in neuroscience. We address the problem of decoding visual information from high-density intracortical recordings in primates, using the THINGS Ventral Stream Spiking Dataset. We systematically evaluate the effects of model architecture, training objectives, and data scaling on decoding performance. Results show that decoding accuracy is mainly driven by modeling temporal dynamics in neural signals, rather than architectural complexity. A simple model combining temporal attention with a shallow MLP achieves up to 70% top-1 image retrieval accuracy, outperforming linear baselines as well as recurrent and convolutional approaches. Scaling analyses reveal predictable diminishing returns with increasing input dimensionality and dataset size. Building on these findings, we design a modular generative decoding pipeline that combines low-resolution latent reconstruction with semantically conditioned diffusion, generating plausible images from 200 ms of brain activity. This framework provides principles for brain-computer interfaces and semantic neural decoding.
Training Neural Networks by Optimizing Neuron Positions
Jun 16, 2025Abstract:The high computational complexity and increasing parameter counts of deep neural networks pose significant challenges for deployment in resource-constrained environments, such as edge devices or real-time systems. To address this, we propose a parameter-efficient neural architecture where neurons are embedded in Euclidean space. During training, their positions are optimized and synaptic weights are determined as the inverse of the spatial distance between connected neurons. These distance-dependent wiring rules replace traditional learnable weight matrices and significantly reduce the number of parameters while introducing a biologically inspired inductive bias: connection strength decreases with spatial distance, reflecting the brain's embedding in three-dimensional space where connections tend to minimize wiring length. We validate this approach for both multi-layer perceptrons and spiking neural networks. Through a series of experiments, we demonstrate that these spatially embedded neural networks achieve a performance competitive with conventional architectures on the MNIST dataset. Additionally, the models maintain performance even at pruning rates exceeding 80% sparsity, outperforming traditional networks with the same number of parameters under similar conditions. Finally, the spatial embedding framework offers an intuitive visualization of the network structure.
Transforming Multimodal Models into Action Models for Radiotherapy
Feb 06, 2025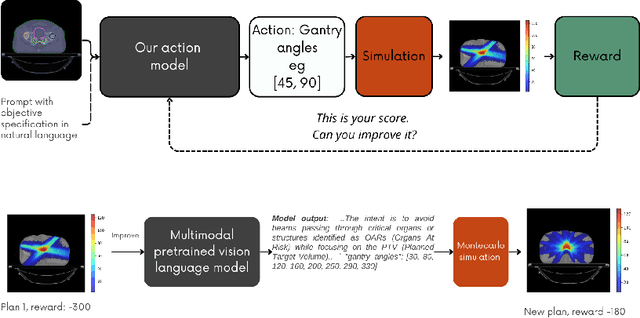
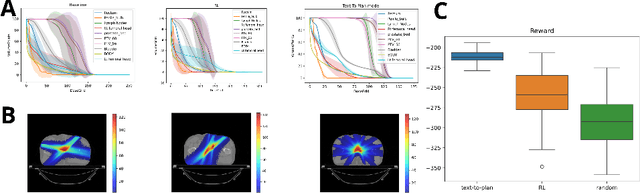
Abstract:Radiotherapy is a crucial cancer treatment that demands precise planning to balance tumor eradication and preservation of healthy tissue. Traditional treatment planning (TP) is iterative, time-consuming, and reliant on human expertise, which can potentially introduce variability and inefficiency. We propose a novel framework to transform a large multimodal foundation model (MLM) into an action model for TP using a few-shot reinforcement learning (RL) approach. Our method leverages the MLM's extensive pre-existing knowledge of physics, radiation, and anatomy, enhancing it through a few-shot learning process. This allows the model to iteratively improve treatment plans using a Monte Carlo simulator. Our results demonstrate that this method outperforms conventional RL-based approaches in both quality and efficiency, achieving higher reward scores and more optimal dose distributions in simulations on prostate cancer data. This proof-of-concept suggests a promising direction for integrating advanced AI models into clinical workflows, potentially enhancing the speed, quality, and standardization of radiotherapy treatment planning.
Towards Neural Foundation Models for Vision: Aligning EEG, MEG, and fMRI Representations for Decoding, Encoding, and Modality Conversion
Nov 14, 2024Abstract:This paper presents a novel approach towards creating a foundational model for aligning neural data and visual stimuli across multimodal representationsof brain activity by leveraging contrastive learning. We used electroencephalography (EEG), magnetoencephalography (MEG), and functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) data. Our framework's capabilities are demonstrated through three key experiments: decoding visual information from neural data, encoding images into neural representations, and converting between neural modalities. The results highlight the model's ability to accurately capture semantic information across different brain imaging techniques, illustrating its potential in decoding, encoding, and modality conversion tasks.
Genetic Motifs as a Blueprint for Mismatch-Tolerant Neuromorphic Computing
Oct 25, 2024Abstract:Mixed-signal implementations of SNNs offer a promising solution to edge computing applications that require low-power and compact embedded processing systems. However, device mismatch in the analog circuits of these neuromorphic processors poses a significant challenge to the deployment of robust processing in these systems. Here we introduce a novel architectural solution inspired by biological development to address this issue. Specifically we propose to implement architectures that incorporate network motifs found in developed brains through a differentiable re-parameterization of weight matrices based on gene expression patterns and genetic rules. Thanks to the gradient descent optimization compatibility of the method proposed, we can apply the robustness of biological neural development to neuromorphic computing. To validate this approach we benchmark it using the Yin-Yang classification dataset, and compare its performance with that of standard multilayer perceptrons trained with state-of-the-art hardware-aware training method. Our results demonstrate that the proposed method mitigates mismatch-induced noise without requiring precise device mismatch measurements, effectively outperforming alternative hardware-aware techniques proposed in the literature, and providing a more general solution for improving the robustness of SNNs in neuromorphic hardware.
R&B -- Rhythm and Brain: Cross-subject Decoding of Music from Human Brain Activity
Jun 21, 2024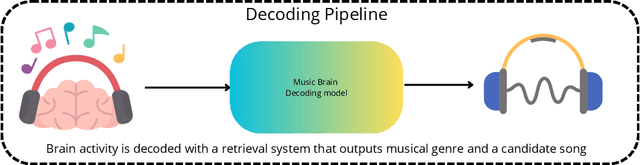

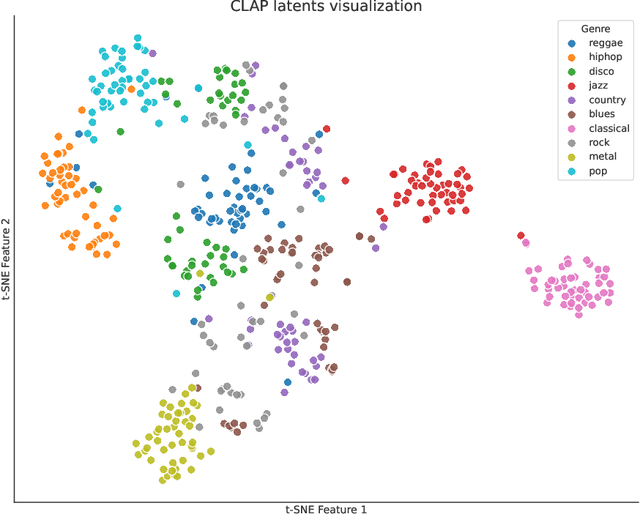
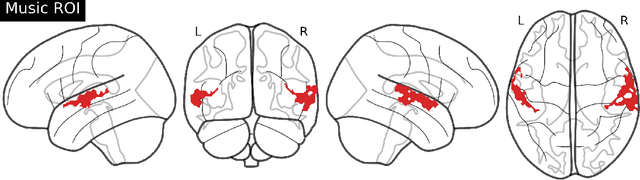
Abstract:Music is a universal phenomenon that profoundly influences human experiences across cultures. This study investigates whether music can be decoded from human brain activity measured with functional MRI (fMRI) during its perception. Leveraging recent advancements in extensive datasets and pre-trained computational models, we construct mappings between neural data and latent representations of musical stimuli. Our approach integrates functional and anatomical alignment techniques to facilitate cross-subject decoding, addressing the challenges posed by the low temporal resolution and signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) in fMRI data. Starting from the GTZan fMRI dataset, where five participants listened to 540 musical stimuli from 10 different genres while their brain activity was recorded, we used the CLAP (Contrastive Language-Audio Pretraining) model to extract latent representations of the musical stimuli and developed voxel-wise encoding models to identify brain regions responsive to these stimuli. By applying a threshold to the association between predicted and actual brain activity, we identified specific regions of interest (ROIs) which can be interpreted as key players in music processing. Our decoding pipeline, primarily retrieval-based, employs a linear map to project brain activity to the corresponding CLAP features. This enables us to predict and retrieve the musical stimuli most similar to those that originated the fMRI data. Our results demonstrate state-of-the-art identification accuracy, with our methods significantly outperforming existing approaches. Our findings suggest that neural-based music retrieval systems could enable personalized recommendations and therapeutic applications. Future work could use higher temporal resolution neuroimaging and generative models to improve decoding accuracy and explore the neural underpinnings of music perception and emotion.
Optimizing Genetically-Driven Synaptogenesis
Feb 11, 2024
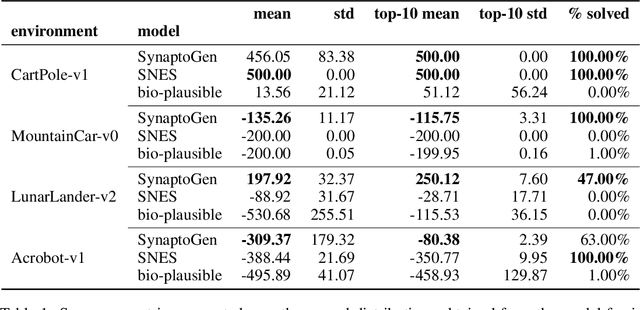

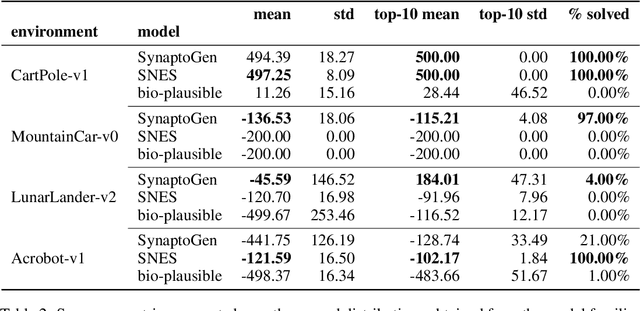
Abstract:In this paper we introduce SynaptoGen, a novel framework that aims to bridge the gap between genetic manipulations and neuronal network behavior by simulating synaptogenesis and guiding the development of neuronal networks capable of solving predetermined computational tasks. Drawing inspiration from recent advancements in the field, we propose SynaptoGen as a bio-plausible approach to modeling synaptogenesis through differentiable functions. To validate SynaptoGen, we conduct a preliminary experiment using reinforcement learning as a benchmark learning framework, demonstrating its effectiveness in generating neuronal networks capable of solving the OpenAI Gym's Cart Pole task, compared to carefully designed baselines. The results highlight the potential of SynaptoGen to inspire further advancements in neuroscience and computational modeling, while also acknowledging the need for incorporating more realistic genetic rules and synaptic conductances in future research. Overall, SynaptoGen represents a promising avenue for exploring the intersection of genetics, neuroscience, and artificial intelligence.
Decoding visual brain representations from electroencephalography through Knowledge Distillation and latent diffusion models
Sep 08, 2023Abstract:Decoding visual representations from human brain activity has emerged as a thriving research domain, particularly in the context of brain-computer interfaces. Our study presents an innovative method that employs to classify and reconstruct images from the ImageNet dataset using electroencephalography (EEG) data from subjects that had viewed the images themselves (i.e. "brain decoding"). We analyzed EEG recordings from 6 participants, each exposed to 50 images spanning 40 unique semantic categories. These EEG readings were converted into spectrograms, which were then used to train a convolutional neural network (CNN), integrated with a knowledge distillation procedure based on a pre-trained Contrastive Language-Image Pre-Training (CLIP)-based image classification teacher network. This strategy allowed our model to attain a top-5 accuracy of 80%, significantly outperforming a standard CNN and various RNN-based benchmarks. Additionally, we incorporated an image reconstruction mechanism based on pre-trained latent diffusion models, which allowed us to generate an estimate of the images which had elicited EEG activity. Therefore, our architecture not only decodes images from neural activity but also offers a credible image reconstruction from EEG only, paving the way for e.g. swift, individualized feedback experiments. Our research represents a significant step forward in connecting neural signals with visual cognition.
Brain Captioning: Decoding human brain activity into images and text
May 19, 2023
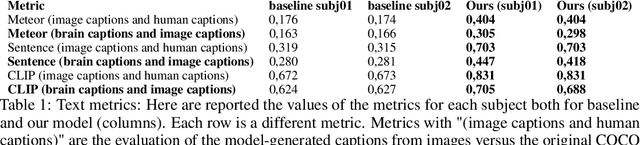

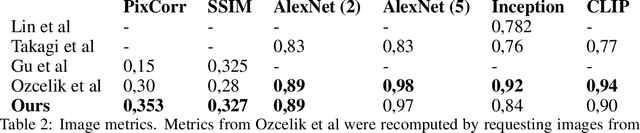
Abstract:Every day, the human brain processes an immense volume of visual information, relying on intricate neural mechanisms to perceive and interpret these stimuli. Recent breakthroughs in functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) have enabled scientists to extract visual information from human brain activity patterns. In this study, we present an innovative method for decoding brain activity into meaningful images and captions, with a specific focus on brain captioning due to its enhanced flexibility as compared to brain decoding into images. Our approach takes advantage of cutting-edge image captioning models and incorporates a unique image reconstruction pipeline that utilizes latent diffusion models and depth estimation. We utilized the Natural Scenes Dataset, a comprehensive fMRI dataset from eight subjects who viewed images from the COCO dataset. We employed the Generative Image-to-text Transformer (GIT) as our backbone for captioning and propose a new image reconstruction pipeline based on latent diffusion models. The method involves training regularized linear regression models between brain activity and extracted features. Additionally, we incorporated depth maps from the ControlNet model to further guide the reconstruction process. We evaluate our methods using quantitative metrics for both generated captions and images. Our brain captioning approach outperforms existing methods, while our image reconstruction pipeline generates plausible images with improved spatial relationships. In conclusion, we demonstrate significant progress in brain decoding, showcasing the enormous potential of integrating vision and language to better understand human cognition. Our approach provides a flexible platform for future research, with potential applications in various fields, including neural art, style transfer, and portable devices.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge