Matteo Ciferri
Simple Models, Rich Representations: Visual Decoding from Primate Intracortical Neural Signals
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:Understanding how neural activity gives rise to perception is a central challenge in neuroscience. We address the problem of decoding visual information from high-density intracortical recordings in primates, using the THINGS Ventral Stream Spiking Dataset. We systematically evaluate the effects of model architecture, training objectives, and data scaling on decoding performance. Results show that decoding accuracy is mainly driven by modeling temporal dynamics in neural signals, rather than architectural complexity. A simple model combining temporal attention with a shallow MLP achieves up to 70% top-1 image retrieval accuracy, outperforming linear baselines as well as recurrent and convolutional approaches. Scaling analyses reveal predictable diminishing returns with increasing input dimensionality and dataset size. Building on these findings, we design a modular generative decoding pipeline that combines low-resolution latent reconstruction with semantically conditioned diffusion, generating plausible images from 200 ms of brain activity. This framework provides principles for brain-computer interfaces and semantic neural decoding.
R&B -- Rhythm and Brain: Cross-subject Decoding of Music from Human Brain Activity
Jun 21, 2024

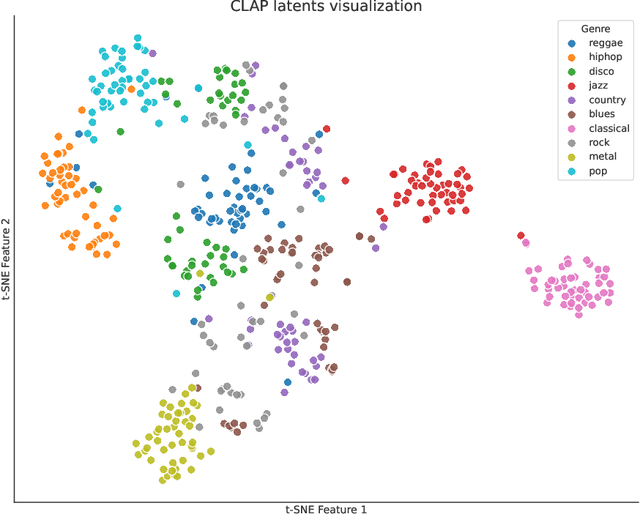
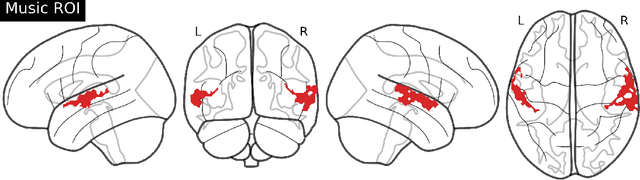
Abstract:Music is a universal phenomenon that profoundly influences human experiences across cultures. This study investigates whether music can be decoded from human brain activity measured with functional MRI (fMRI) during its perception. Leveraging recent advancements in extensive datasets and pre-trained computational models, we construct mappings between neural data and latent representations of musical stimuli. Our approach integrates functional and anatomical alignment techniques to facilitate cross-subject decoding, addressing the challenges posed by the low temporal resolution and signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) in fMRI data. Starting from the GTZan fMRI dataset, where five participants listened to 540 musical stimuli from 10 different genres while their brain activity was recorded, we used the CLAP (Contrastive Language-Audio Pretraining) model to extract latent representations of the musical stimuli and developed voxel-wise encoding models to identify brain regions responsive to these stimuli. By applying a threshold to the association between predicted and actual brain activity, we identified specific regions of interest (ROIs) which can be interpreted as key players in music processing. Our decoding pipeline, primarily retrieval-based, employs a linear map to project brain activity to the corresponding CLAP features. This enables us to predict and retrieve the musical stimuli most similar to those that originated the fMRI data. Our results demonstrate state-of-the-art identification accuracy, with our methods significantly outperforming existing approaches. Our findings suggest that neural-based music retrieval systems could enable personalized recommendations and therapeutic applications. Future work could use higher temporal resolution neuroimaging and generative models to improve decoding accuracy and explore the neural underpinnings of music perception and emotion.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge