Nicholas Solovyev
Domain-Specific Retrieval-Augmented Generation Using Vector Stores, Knowledge Graphs, and Tensor Factorization
Oct 03, 2024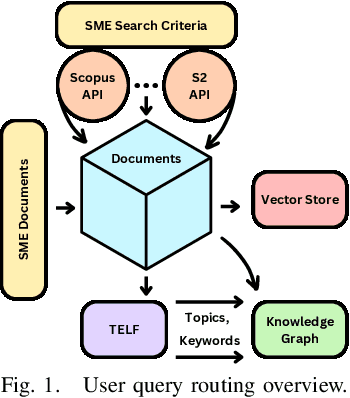
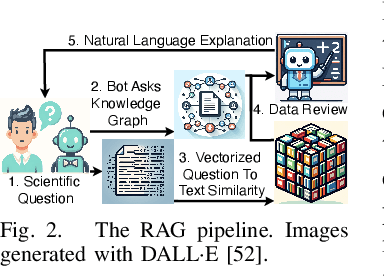
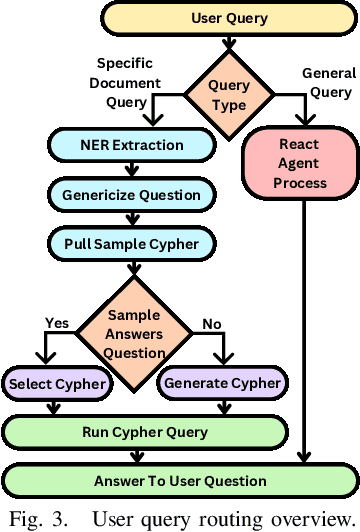
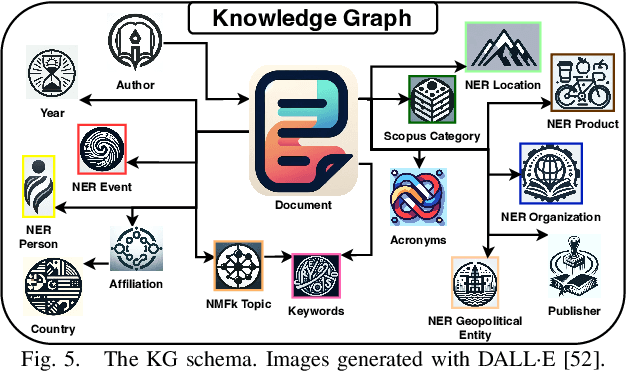
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are pre-trained on large-scale corpora and excel in numerous general natural language processing (NLP) tasks, such as question answering (QA). Despite their advanced language capabilities, when it comes to domain-specific and knowledge-intensive tasks, LLMs suffer from hallucinations, knowledge cut-offs, and lack of knowledge attributions. Additionally, fine tuning LLMs' intrinsic knowledge to highly specific domains is an expensive and time consuming process. The retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) process has recently emerged as a method capable of optimization of LLM responses, by referencing them to a predetermined ontology. It was shown that using a Knowledge Graph (KG) ontology for RAG improves the QA accuracy, by taking into account relevant sub-graphs that preserve the information in a structured manner. In this paper, we introduce SMART-SLIC, a highly domain-specific LLM framework, that integrates RAG with KG and a vector store (VS) that store factual domain specific information. Importantly, to avoid hallucinations in the KG, we build these highly domain-specific KGs and VSs without the use of LLMs, but via NLP, data mining, and nonnegative tensor factorization with automatic model selection. Pairing our RAG with a domain-specific: (i) KG (containing structured information), and (ii) VS (containing unstructured information) enables the development of domain-specific chat-bots that attribute the source of information, mitigate hallucinations, lessen the need for fine-tuning, and excel in highly domain-specific question answering tasks. We pair SMART-SLIC with chain-of-thought prompting agents. The framework is designed to be generalizable to adapt to any specific or specialized domain. In this paper, we demonstrate the question answering capabilities of our framework on a corpus of scientific publications on malware analysis and anomaly detection.
Cyber-Security Knowledge Graph Generation by Hierarchical Nonnegative Matrix Factorization
Mar 26, 2024Abstract:Much of human knowledge in cybersecurity is encapsulated within the ever-growing volume of scientific papers. As this textual data continues to expand, the importance of document organization methods becomes increasingly crucial for extracting actionable insights hidden within large text datasets. Knowledge Graphs (KGs) serve as a means to store factual information in a structured manner, providing explicit, interpretable knowledge that includes domain-specific information from the cybersecurity scientific literature. One of the challenges in constructing a KG from scientific literature is the extraction of ontology from unstructured text. In this paper, we address this topic and introduce a method for building a multi-modal KG by extracting structured ontology from scientific papers. We demonstrate this concept in the cybersecurity domain. One modality of the KG represents observable information from the papers, such as the categories in which they were published or the authors. The second modality uncovers latent (hidden) patterns of text extracted through hierarchical and semantic non-negative matrix factorization (NMF), such as named entities, topics or clusters, and keywords. We illustrate this concept by consolidating more than two million scientific papers uploaded to arXiv into the cyber-domain, using hierarchical and semantic NMF, and by building a cyber-domain-specific KG.
Interactive Distillation of Large Single-Topic Corpora of Scientific Papers
Sep 19, 2023



Abstract:Highly specific datasets of scientific literature are important for both research and education. However, it is difficult to build such datasets at scale. A common approach is to build these datasets reductively by applying topic modeling on an established corpus and selecting specific topics. A more robust but time-consuming approach is to build the dataset constructively in which a subject matter expert (SME) handpicks documents. This method does not scale and is prone to error as the dataset grows. Here we showcase a new tool, based on machine learning, for constructively generating targeted datasets of scientific literature. Given a small initial "core" corpus of papers, we build a citation network of documents. At each step of the citation network, we generate text embeddings and visualize the embeddings through dimensionality reduction. Papers are kept in the dataset if they are "similar" to the core or are otherwise pruned through human-in-the-loop selection. Additional insight into the papers is gained through sub-topic modeling using SeNMFk. We demonstrate our new tool for literature review by applying it to two different fields in machine learning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge