Ngoc Duong
LTCI
Inplace knowledge distillation with teacher assistant for improved training of flexible deep neural networks
May 18, 2021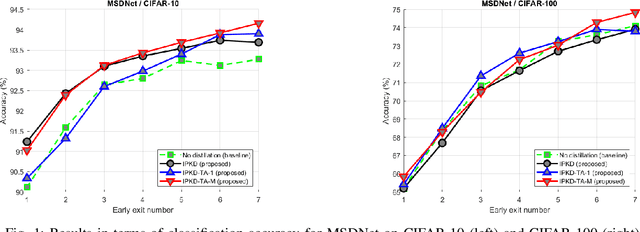
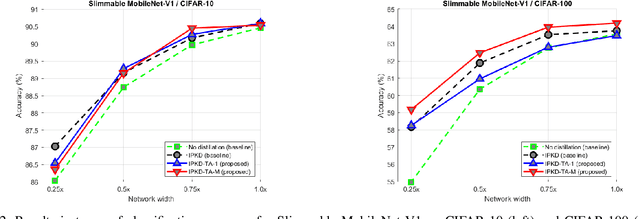
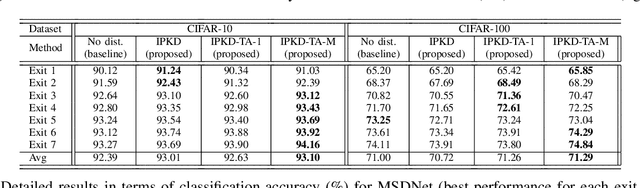
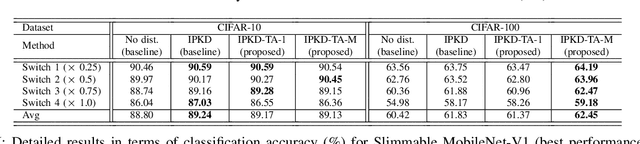
Abstract:Deep neural networks (DNNs) have achieved great success in various machine learning tasks. However, most existing powerful DNN models are computationally expensive and memory demanding, hindering their deployment in devices with low memory and computational resources or in applications with strict latency requirements. Thus, several resource-adaptable or flexible approaches were recently proposed that train at the same time a big model and several resource-specific sub-models. Inplace knowledge distillation (IPKD) became a popular method to train those models and consists in distilling the knowledge from a larger model (teacher) to all other sub-models (students). In this work a novel generic training method called IPKD with teacher assistant (IPKD-TA) is introduced, where sub-models themselves become teacher assistants teaching smaller sub-models. We evaluated the proposed IPKD-TA training method using two state-of-the-art flexible models (MSDNet and Slimmable MobileNet-V1) with two popular image classification benchmarks (CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100). Our results demonstrate that the IPKD-TA is on par with the existing state of the art while improving it in most cases.
Identify, locate and separate: Audio-visual object extraction in large video collections using weak supervision
Nov 09, 2018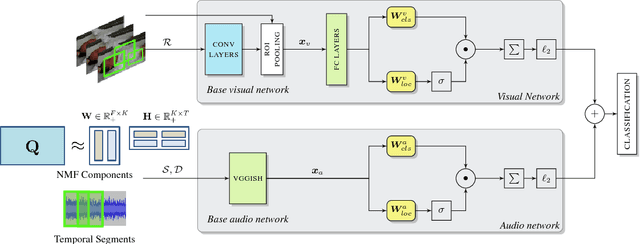
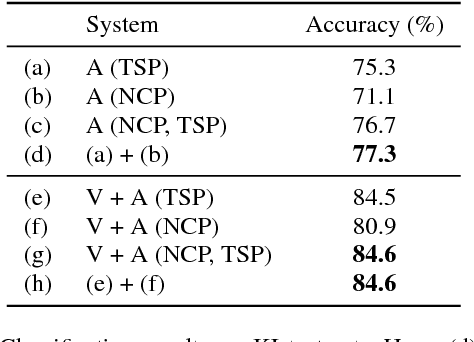

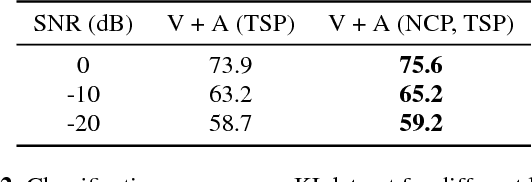
Abstract:We tackle the problem of audiovisual scene analysis for weakly-labeled data. To this end, we build upon our previous audiovisual representation learning framework to perform object classification in noisy acoustic environments and integrate audio source enhancement capability. This is made possible by a novel use of non-negative matrix factorization for the audio modality. Our approach is founded on the multiple instance learning paradigm. Its effectiveness is established through experiments over a challenging dataset of music instrument performance videos. We also show encouraging visual object localization results.
MediaEval 2018: Predicting Media Memorability Task
Jul 03, 2018Abstract:In this paper, we present the Predicting Media Memorability task, which is proposed as part of the MediaEval 2018 Benchmarking Initiative for Multimedia Evaluation. Participants are expected to design systems that automatically predict memorability scores for videos, which reflect the probability of a video being remembered. In contrast to previous work in image memorability prediction, where memorability was measured a few minutes after memorization, the proposed dataset comes with short-term and long-term memorability annotations. All task characteristics are described, namely: the task's challenges and breakthrough, the released data set and ground truth, the required participant runs and the evaluation metrics.
Under-determined reverberant audio source separation using a full-rank spatial covariance model
Dec 14, 2009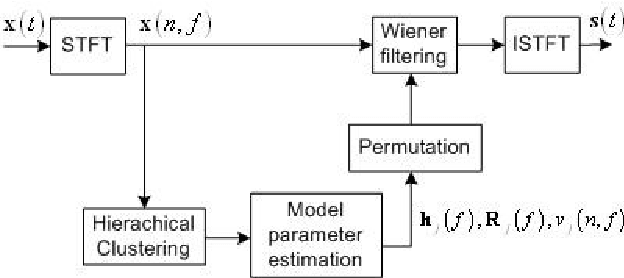
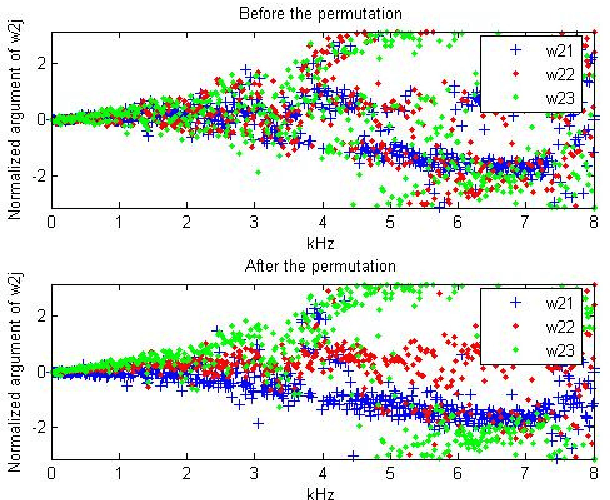
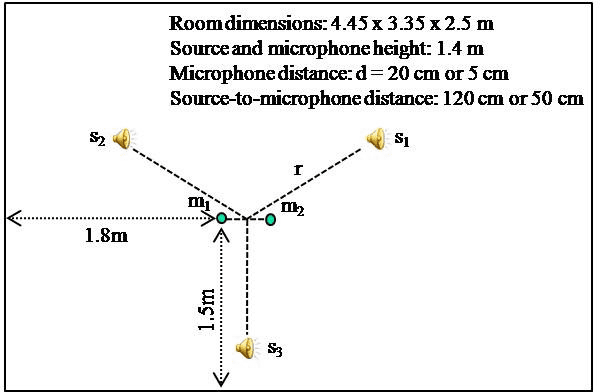
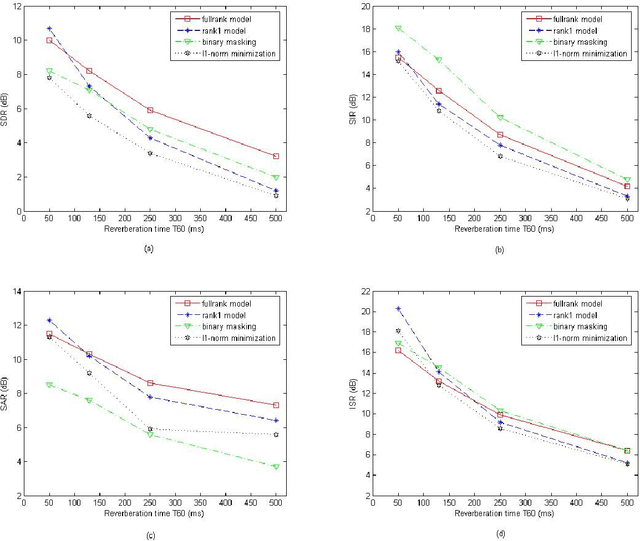
Abstract:This article addresses the modeling of reverberant recording environments in the context of under-determined convolutive blind source separation. We model the contribution of each source to all mixture channels in the time-frequency domain as a zero-mean Gaussian random variable whose covariance encodes the spatial characteristics of the source. We then consider four specific covariance models, including a full-rank unconstrained model. We derive a family of iterative expectationmaximization (EM) algorithms to estimate the parameters of each model and propose suitable procedures to initialize the parameters and to align the order of the estimated sources across all frequency bins based on their estimated directions of arrival (DOA). Experimental results over reverberant synthetic mixtures and live recordings of speech data show the effectiveness of the proposed approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge