Neha Madhiwalla
Beyond Listenership: AI-Predicted Interventions Drive Improvements in Maternal Health Behaviours
Jul 28, 2025Abstract:Automated voice calls with health information are a proven method for disseminating maternal and child health information among beneficiaries and are deployed in several programs around the world. However, these programs often suffer from beneficiary dropoffs and poor engagement. In previous work, through real-world trials, we showed that an AI model, specifically a restless bandit model, could identify beneficiaries who would benefit most from live service call interventions, preventing dropoffs and boosting engagement. However, one key question has remained open so far: does such improved listenership via AI-targeted interventions translate into beneficiaries' improved knowledge and health behaviors? We present a first study that shows not only listenership improvements due to AI interventions, but also simultaneously links these improvements to health behavior changes. Specifically, we demonstrate that AI-scheduled interventions, which enhance listenership, lead to statistically significant improvements in beneficiaries' health behaviors such as taking iron or calcium supplements in the postnatal period, as well as understanding of critical health topics during pregnancy and infancy. This underscores the potential of AI to drive meaningful improvements in maternal and child health.
Decision-Focused Learning in Restless Multi-Armed Bandits with Application to Maternal and Child Care Domain
Feb 02, 2022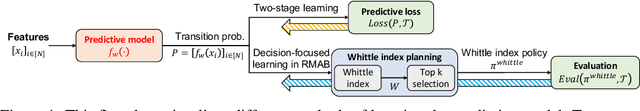
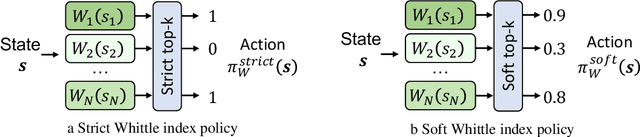

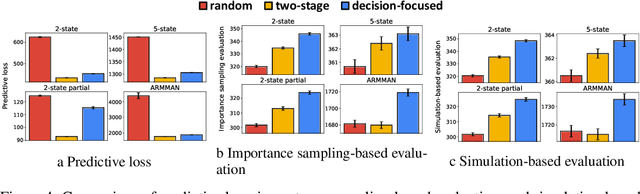
Abstract:This paper studies restless multi-armed bandit (RMAB) problems with unknown arm transition dynamics but with known correlated arm features. The goal is to learn a model to predict transition dynamics given features, where the Whittle index policy solves the RMAB problems using predicted transitions. However, prior works often learn the model by maximizing the predictive accuracy instead of final RMAB solution quality, causing a mismatch between training and evaluation objectives. To address this shortcoming we propose a novel approach for decision-focused learning in RMAB that directly trains the predictive model to maximize the Whittle index solution quality. We present three key contributions: (i) we establish the differentiability of the Whittle index policy to support decision-focused learning; (ii) we significantly improve the scalability of previous decision-focused learning approaches in sequential problems; (iii) we apply our algorithm to the service call scheduling problem on a real-world maternal and child health domain. Our algorithm is the first for decision-focused learning in RMAB that scales to large-scale real-world problems. \end{abstract}
Field Study in Deploying Restless Multi-Armed Bandits: Assisting Non-Profits in Improving Maternal and Child Health
Sep 16, 2021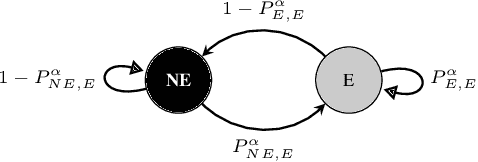
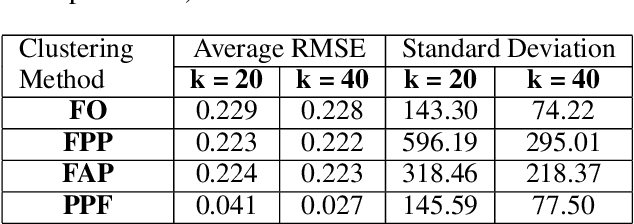
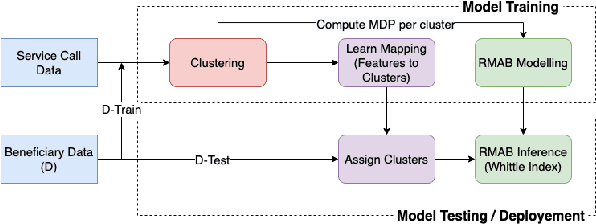
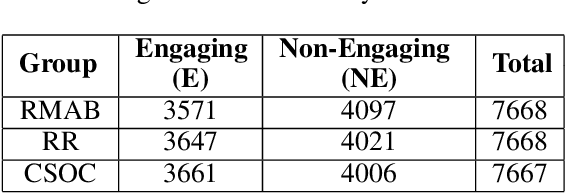
Abstract:The widespread availability of cell phones has enabled non-profits to deliver critical health information to their beneficiaries in a timely manner. This paper describes our work to assist non-profits that employ automated messaging programs to deliver timely preventive care information to beneficiaries (new and expecting mothers) during pregnancy and after delivery. Unfortunately, a key challenge in such information delivery programs is that a significant fraction of beneficiaries drop out of the program. Yet, non-profits often have limited health-worker resources (time) to place crucial service calls for live interaction with beneficiaries to prevent such engagement drops. To assist non-profits in optimizing this limited resource, we developed a Restless Multi-Armed Bandits (RMABs) system. One key technical contribution in this system is a novel clustering method of offline historical data to infer unknown RMAB parameters. Our second major contribution is evaluation of our RMAB system in collaboration with an NGO, via a real-world service quality improvement study. The study compared strategies for optimizing service calls to 23003 participants over a period of 7 weeks to reduce engagement drops. We show that the RMAB group provides statistically significant improvement over other comparison groups, reducing ~ 30% engagement drops. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study demonstrating the utility of RMABs in real world public health settings. We are transitioning our RMAB system to the NGO for real-world use.
Selective Intervention Planning using Restless Multi-Armed Bandits to Improve Maternal and Child Health Outcomes
Apr 05, 2021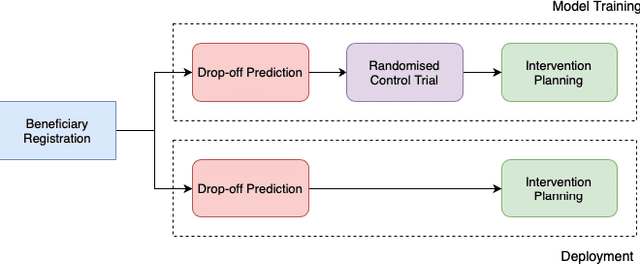
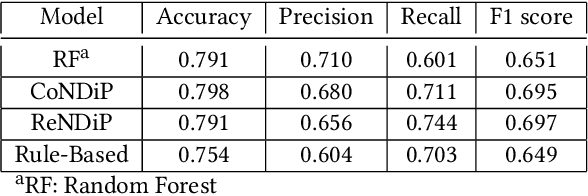
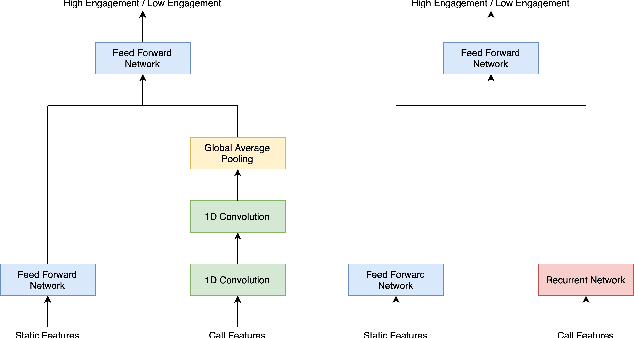
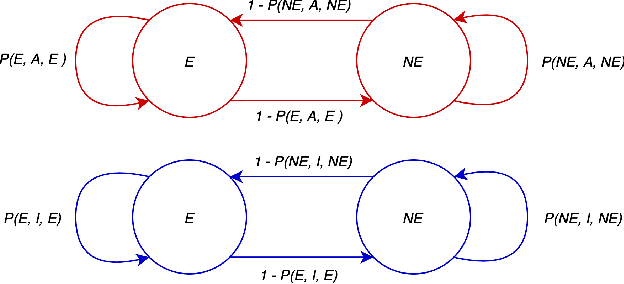
Abstract:India has a maternal mortality ratio of 113 and child mortality ratio of 2830 per 100,000 live births. Lack of access to preventive care information is a major contributing factor for these deaths, especially in low resource households. We partner with ARMMAN, a non-profit based in India employing a call-based information program to disseminate health-related information to pregnant women and women with recent child deliveries. We analyze call records of over 300,000 women registered in the program created by ARMMAN and try to identify women who might not engage with these call programs that are proven to result in positive health outcomes. We built machine learning based models to predict the long term engagement pattern from call logs and beneficiaries' demographic information, and discuss the applicability of this method in the real world through a pilot validation. Through a randomized controlled trial, we show that using our model's predictions to make interventions boosts engagement metrics by 61.37%. We then formulate the intervention planning problem as restless multi-armed bandits (RMABs), and present preliminary results using this approach.
Missed calls, Automated Calls and Health Support: Using AI to improve maternal health outcomes by increasing program engagement
Jul 06, 2020



Abstract:India accounts for 11% of maternal deaths globally where a woman dies in childbirth every fifteen minutes. Lack of access to preventive care information is a significant problem contributing to high maternal morbidity and mortality numbers, especially in low-income households. We work with ARMMAN, a non-profit based in India, to further the use of call-based information programs by early-on identifying women who might not engage on these programs that are proven to affect health parameters positively.We analyzed anonymized call-records of over 300,000 women registered in an awareness program created by ARMMAN that uses cellphone calls to regularly disseminate health related information. We built robust deep learning based models to predict short term and long term dropout risk from call logs and beneficiaries' demographic information. Our model performs 13% better than competitive baselines for short-term forecasting and 7% better for long term forecasting. We also discuss the applicability of this method in the real world through a pilot validation that uses our method to perform targeted interventions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge