Nawar Shara
RECOVER: Designing a Large Language Model-based Remote Patient Monitoring System for Postoperative Gastrointestinal Cancer Care
Feb 09, 2025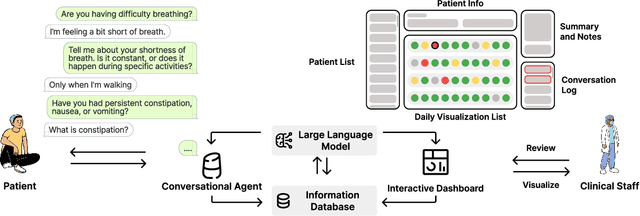

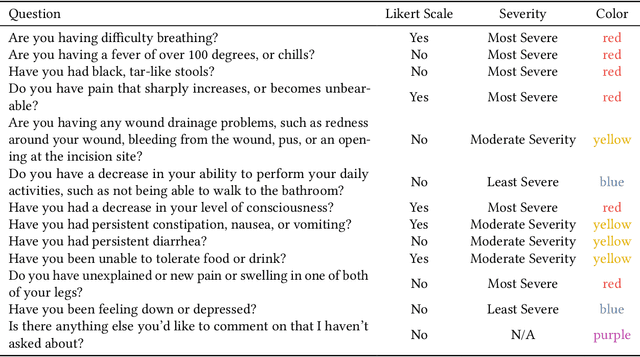
Abstract:Cancer surgery is a key treatment for gastrointestinal (GI) cancers, a group of cancers that account for more than 35% of cancer-related deaths worldwide, but postoperative complications are unpredictable and can be life-threatening. In this paper, we investigate how recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) can benefit remote patient monitoring (RPM) systems through clinical integration by designing RECOVER, an LLM-powered RPM system for postoperative GI cancer care. To closely engage stakeholders in the design process, we first conducted seven participatory design sessions with five clinical staff and interviewed five cancer patients to derive six major design strategies for integrating clinical guidelines and information needs into LLM-based RPM systems. We then designed and implemented RECOVER, which features an LLM-powered conversational agent for cancer patients and an interactive dashboard for clinical staff to enable efficient postoperative RPM. Finally, we used RECOVER as a pilot system to assess the implementation of our design strategies with four clinical staff and five patients, providing design implications by identifying crucial design elements, offering insights on responsible AI, and outlining opportunities for future LLM-powered RPM systems.
Talk2Care: Facilitating Asynchronous Patient-Provider Communication with Large-Language-Model
Sep 22, 2023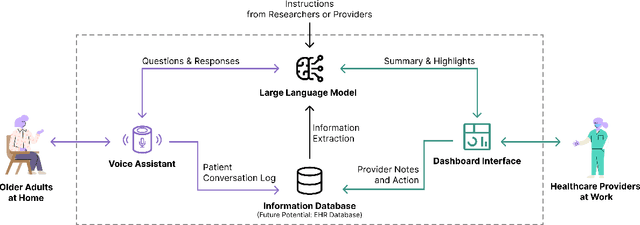
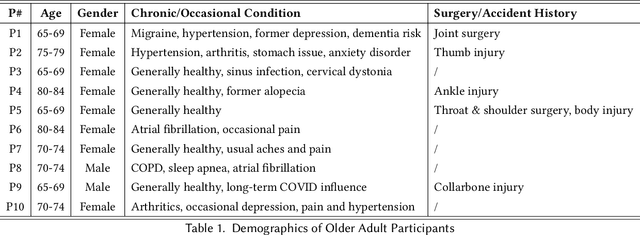
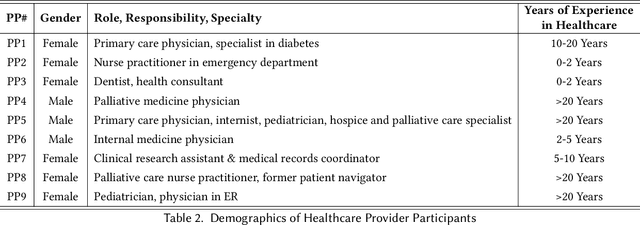
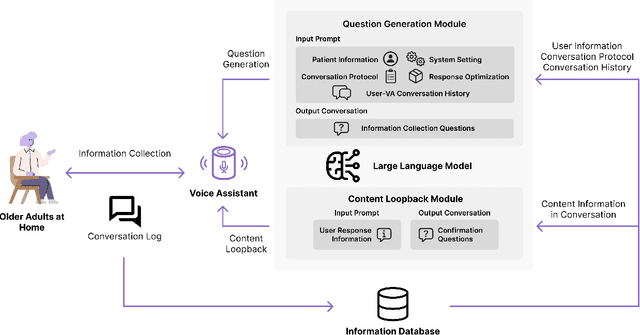
Abstract:Despite the plethora of telehealth applications to assist home-based older adults and healthcare providers, basic messaging and phone calls are still the most common communication methods, which suffer from limited availability, information loss, and process inefficiencies. One promising solution to facilitate patient-provider communication is to leverage large language models (LLMs) with their powerful natural conversation and summarization capability. However, there is a limited understanding of LLMs' role during the communication. We first conducted two interview studies with both older adults (N=10) and healthcare providers (N=9) to understand their needs and opportunities for LLMs in patient-provider asynchronous communication. Based on the insights, we built an LLM-powered communication system, Talk2Care, and designed interactive components for both groups: (1) For older adults, we leveraged the convenience and accessibility of voice assistants (VAs) and built an LLM-powered VA interface for effective information collection. (2) For health providers, we built an LLM-based dashboard to summarize and present important health information based on older adults' conversations with the VA. We further conducted two user studies with older adults and providers to evaluate the usability of the system. The results showed that Talk2Care could facilitate the communication process, enrich the health information collected from older adults, and considerably save providers' efforts and time. We envision our work as an initial exploration of LLMs' capability in the intersection of healthcare and interpersonal communication.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge