Nathalie Camelin
LIUM
ASR-Generated Text for Language Model Pre-training Applied to Speech Tasks
Jul 05, 2022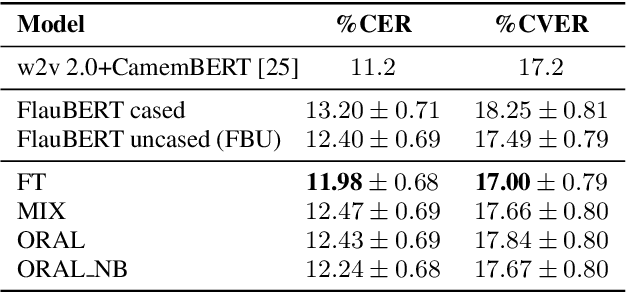
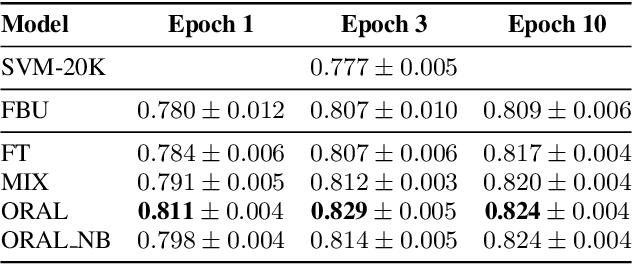
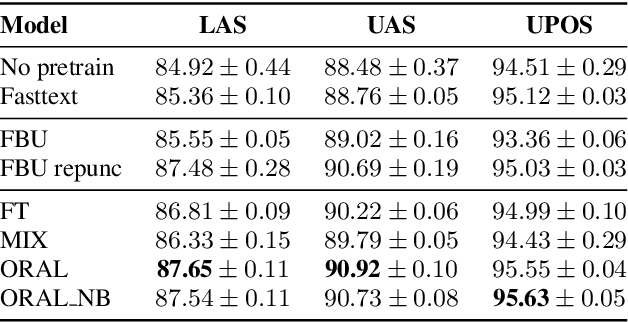
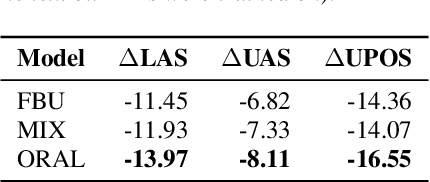
Abstract:We aim at improving spoken language modeling (LM) using very large amount of automatically transcribed speech. We leverage the INA (French National Audiovisual Institute) collection and obtain 19GB of text after applying ASR on 350,000 hours of diverse TV shows. From this, spoken language models are trained either by fine-tuning an existing LM (FlauBERT) or through training a LM from scratch. New models (FlauBERT-Oral) are shared with the community and evaluated for 3 downstream tasks: spoken language understanding, classification of TV shows and speech syntactic parsing. Results show that FlauBERT-Oral can be beneficial compared to its initial FlauBERT version demonstrating that, despite its inherent noisy nature, ASR-generated text can be used to build spoken language models.
End2End Acoustic to Semantic Transduction
Feb 01, 2021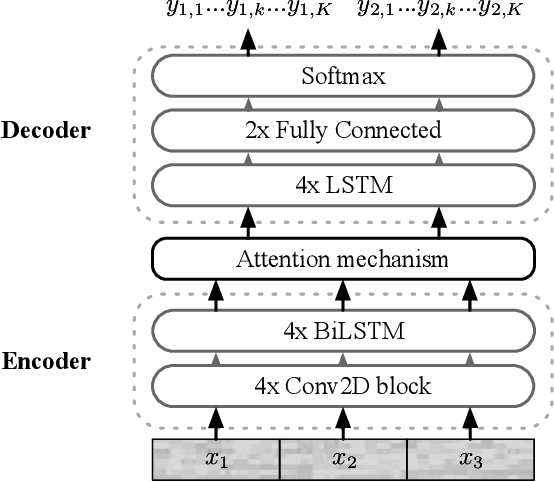

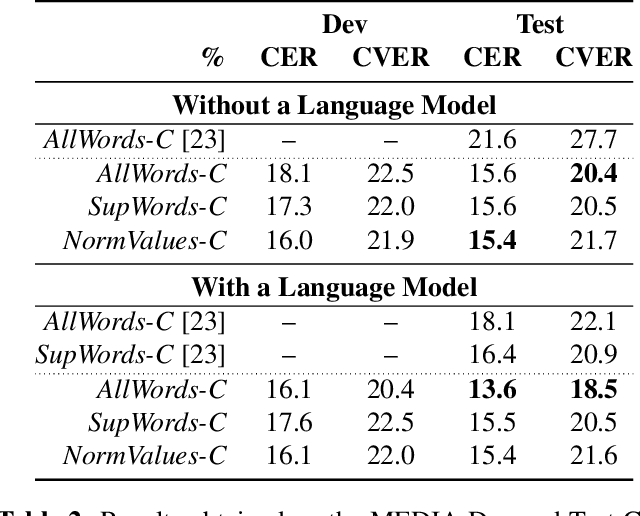
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel end-to-end sequence-to-sequence spoken language understanding model using an attention mechanism. It reliably selects contextual acoustic features in order to hypothesize semantic contents. An initial architecture capable of extracting all pronounced words and concepts from acoustic spans is designed and tested. With a shallow fusion language model, this system reaches a 13.6 concept error rate (CER) and an 18.5 concept value error rate (CVER) on the French MEDIA corpus, achieving an absolute 2.8 points reduction compared to the state-of-the-art. Then, an original model is proposed for hypothesizing concepts and their values. This transduction reaches a 15.4 CER and a 21.6 CVER without any new type of context.
Curriculum-based transfer learning for an effective end-to-end spoken language understanding and domain portability
Jun 18, 2019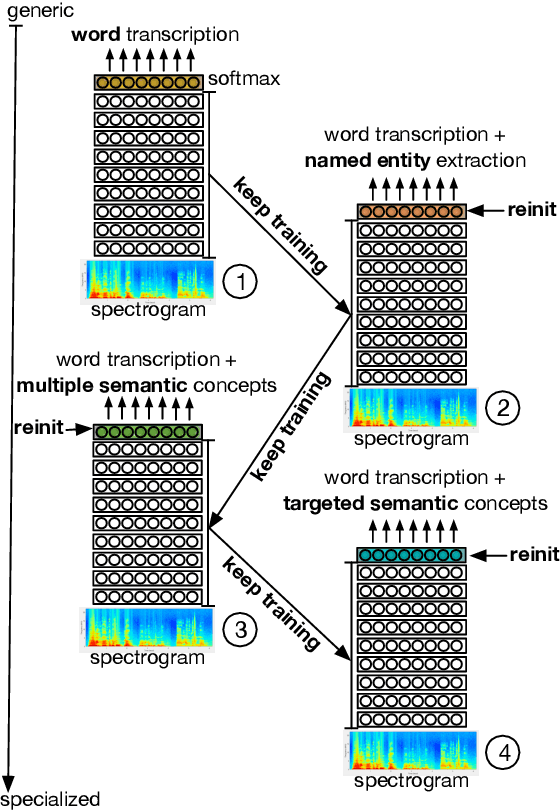
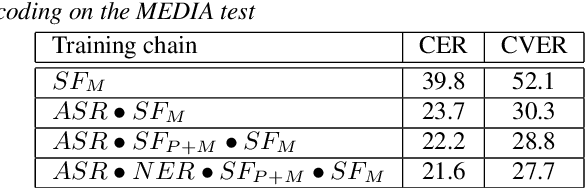

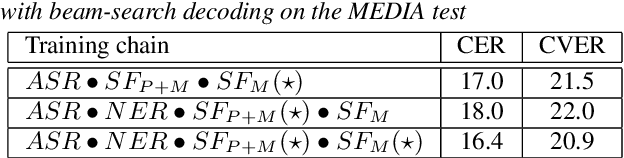
Abstract:We present an end-to-end approach to extract semantic concepts directly from the speech audio signal. To overcome the lack of data available for this spoken language understanding approach, we investigate the use of a transfer learning strategy based on the principles of curriculum learning. This approach allows us to exploit out-of-domain data that can help to prepare a fully neural architecture. Experiments are carried out on the French MEDIA and PORTMEDIA corpora and show that this end-to-end SLU approach reaches the best results ever published on this task. We compare our approach to a classical pipeline approach that uses ASR, POS tagging, lemmatizer, chunker... and other NLP tools that aim to enrich ASR outputs that feed an SLU text to concepts system. Last, we explore the promising capacity of our end-to-end SLU approach to address the problem of domain portability.
ASR error management for improving spoken language understanding
May 26, 2017


Abstract:This paper addresses the problem of automatic speech recognition (ASR) error detection and their use for improving spoken language understanding (SLU) systems. In this study, the SLU task consists in automatically extracting, from ASR transcriptions , semantic concepts and concept/values pairs in a e.g touristic information system. An approach is proposed for enriching the set of semantic labels with error specific labels and by using a recently proposed neural approach based on word embeddings to compute well calibrated ASR confidence measures. Experimental results are reported showing that it is possible to decrease significantly the Concept/Value Error Rate with a state of the art system, outperforming previously published results performance on the same experimental data. It also shown that combining an SLU approach based on conditional random fields with a neural encoder/decoder attention based architecture , it is possible to effectively identifying confidence islands and uncertain semantic output segments useful for deciding appropriate error handling actions by the dialogue manager strategy .
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge