Franck Dary
ASR-Generated Text for Language Model Pre-training Applied to Speech Tasks
Jul 05, 2022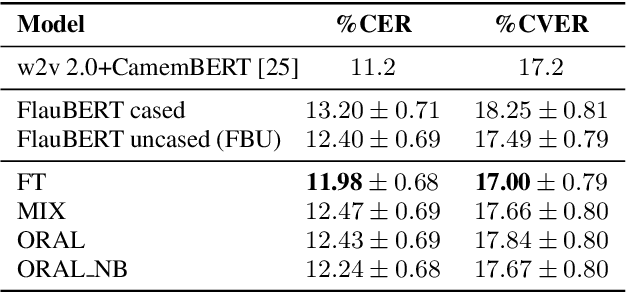
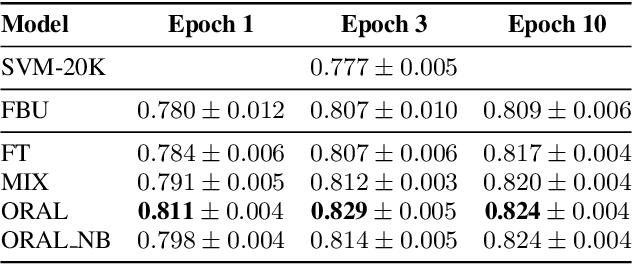
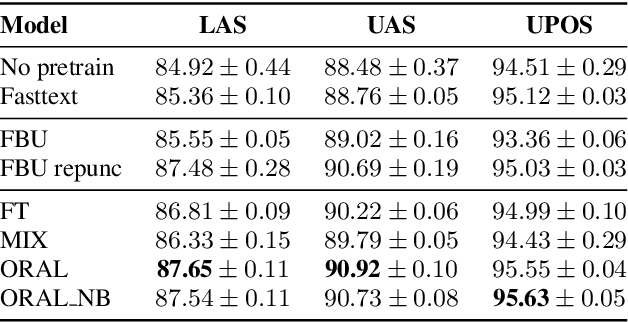
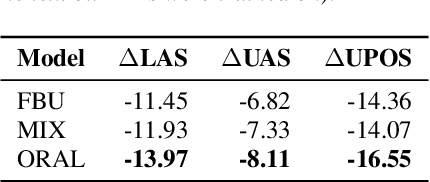
Abstract:We aim at improving spoken language modeling (LM) using very large amount of automatically transcribed speech. We leverage the INA (French National Audiovisual Institute) collection and obtain 19GB of text after applying ASR on 350,000 hours of diverse TV shows. From this, spoken language models are trained either by fine-tuning an existing LM (FlauBERT) or through training a LM from scratch. New models (FlauBERT-Oral) are shared with the community and evaluated for 3 downstream tasks: spoken language understanding, classification of TV shows and speech syntactic parsing. Results show that FlauBERT-Oral can be beneficial compared to its initial FlauBERT version demonstrating that, despite its inherent noisy nature, ASR-generated text can be used to build spoken language models.
Dependency Parsing with Backtracking using Deep Reinforcement Learning
Jun 28, 2022
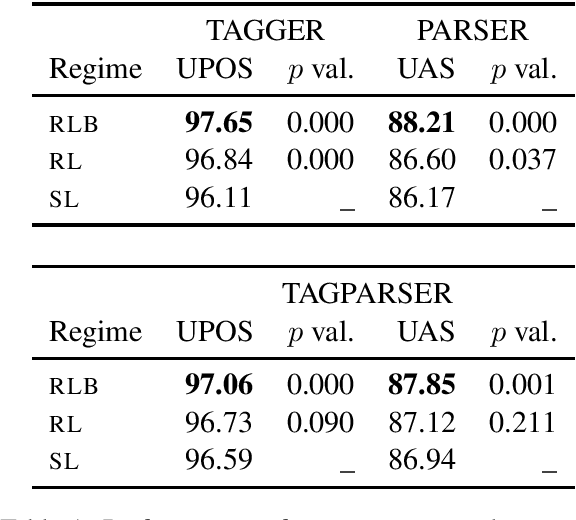
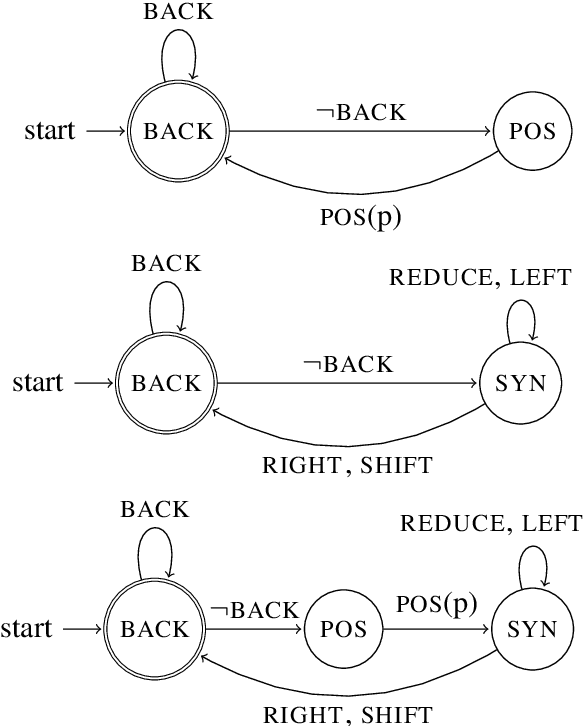
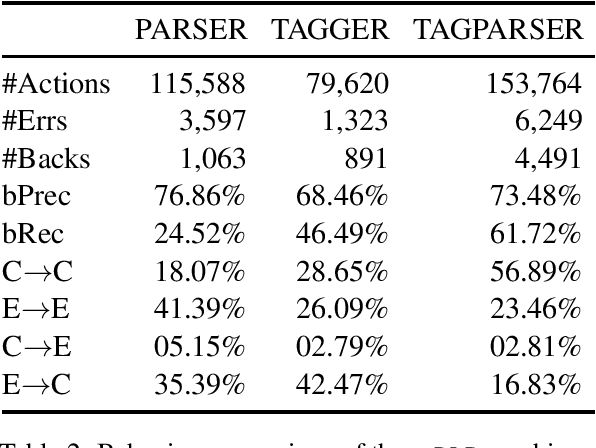
Abstract:Greedy algorithms for NLP such as transition based parsing are prone to error propagation. One way to overcome this problem is to allow the algorithm to backtrack and explore an alternative solution in cases where new evidence contradicts the solution explored so far. In order to implement such a behavior, we use reinforcement learning and let the algorithm backtrack in cases where such an action gets a better reward than continuing to explore the current solution. We test this idea on both POS tagging and dependency parsing and show that backtracking is an effective means to fight against error propagation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge