Na Du
Improving Explainable Object-induced Model through Uncertainty for Automated Vehicles
Feb 23, 2024



Abstract:The rapid evolution of automated vehicles (AVs) has the potential to provide safer, more efficient, and comfortable travel options. However, these systems face challenges regarding reliability in complex driving scenarios. Recent explainable AV architectures neglect crucial information related to inherent uncertainties while providing explanations for actions. To overcome such challenges, our study builds upon the "object-induced" model approach that prioritizes the role of objects in scenes for decision-making and integrates uncertainty assessment into the decision-making process using an evidential deep learning paradigm with a Beta prior. Additionally, we explore several advanced training strategies guided by uncertainty, including uncertainty-guided data reweighting and augmentation. Leveraging the BDD-OIA dataset, our findings underscore that the model, through these enhancements, not only offers a clearer comprehension of AV decisions and their underlying reasoning but also surpasses existing baselines across a broad range of scenarios.
Predicting Driver Takeover Time in Conditionally Automated Driving
Jul 20, 2021



Abstract:It is extremely important to ensure a safe takeover transition in conditionally automated driving. One of the critical factors that quantifies the safe takeover transition is takeover time. Previous studies identified the effects of many factors on takeover time, such as takeover lead time, non-driving tasks, modalities of the takeover requests (TORs), and scenario urgency. However, there is a lack of research to predict takeover time by considering these factors all at the same time. Toward this end, we used eXtreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost) to predict the takeover time using a dataset from a meta-analysis study [1]. In addition, we used SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanation) to analyze and explain the effects of the predictors on takeover time. We identified seven most critical predictors that resulted in the best prediction performance. Their main effects and interaction effects on takeover time were examined. The results showed that the proposed approach provided both good performance and explainability. Our findings have implications on the design of in-vehicle monitoring and alert systems to facilitate the interaction between the drivers and the automated vehicle.
Examining the Effects of Emotional Valence and Arousal on Takeover Performance in Conditionally Automated Driving
Jan 13, 2020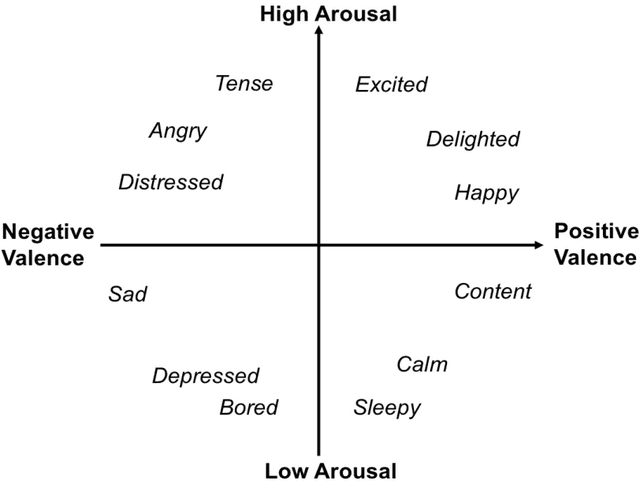
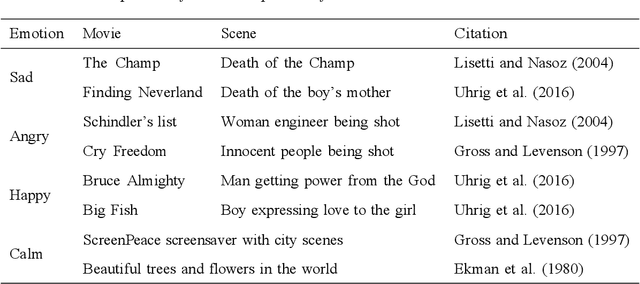
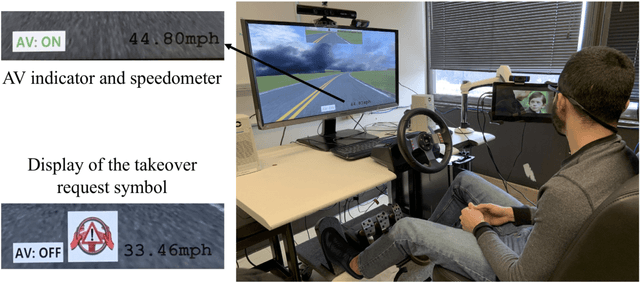
Abstract:In conditionally automated driving, drivers have difficulty in takeover transitions as they become increasingly decoupled from the operational level of driving. Factors influencing takeover performance, such as takeover lead time and the engagement of non-driving related tasks, have been studied in the past. However, despite the important role emotions play in human-machine interaction and in manual driving, little is known about how emotions influence drivers takeover performance. This study, therefore, examined the effects of emotional valence and arousal on drivers takeover timeliness and quality in conditionally automated driving. We conducted a driving simulation experiment with 32 participants. Movie clips were played for emotion induction. Participants with different levels of emotional valence and arousal were required to take over control from automated driving, and their takeover time and quality were analyzed. Results indicate that positive valence led to better takeover quality in the form of a smaller maximum resulting acceleration and a smaller maximum resulting jerk. However, high arousal did not yield an advantage in takeover time. This study contributes to the literature by demonstrating how emotional valence and arousal affect takeover performance. The benefits of positive emotions carry over from manual driving to conditionally automated driving while the benefits of arousal do not.
Look Who's Talking Now: Implications of AV's Explanations on Driver's Trust, AV Preference, Anxiety and Mental Workload
May 21, 2019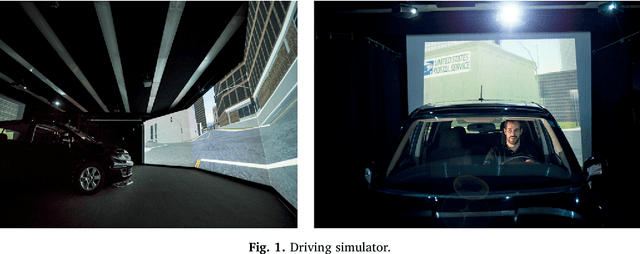

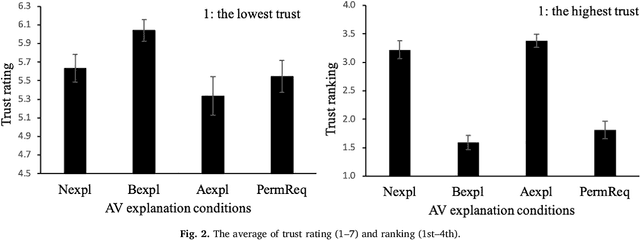
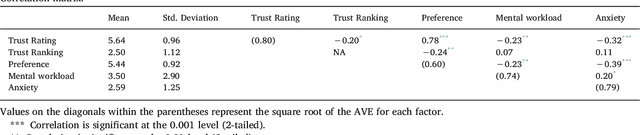
Abstract:Explanations given by automation are often used to promote automation adoption. However, it remains unclear whether explanations promote acceptance of automated vehicles (AVs). In this study, we conducted a within-subject experiment in a driving simulator with 32 participants, using four different conditions. The four conditions included: (1) no explanation, (2) explanation given before or (3) after the AV acted and (4) the option for the driver to approve or disapprove the AV's action after hearing the explanation. We examined four AV outcomes: trust, preference for AV, anxiety and mental workload. Results suggest that explanations provided before an AV acted were associated with higher trust in and preference for the AV, but there was no difference in anxiety and workload. These results have important implications for the adoption of AVs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge