Mohammad R. Salmanpour
AllMetrics: A Unified Python Library for Standardized Metric Evaluation and Robust Data Validation in Machine Learning
May 21, 2025Abstract:Machine learning (ML) models rely heavily on consistent and accurate performance metrics to evaluate and compare their effectiveness. However, existing libraries often suffer from fragmentation, inconsistent implementations, and insufficient data validation protocols, leading to unreliable results. Existing libraries have often been developed independently and without adherence to a unified standard, particularly concerning the specific tasks they aim to support. As a result, each library tends to adopt its conventions for metric computation, input/output formatting, error handling, and data validation protocols. This lack of standardization leads to both implementation differences (ID) and reporting differences (RD), making it difficult to compare results across frameworks or ensure reliable evaluations. To address these issues, we introduce AllMetrics, an open-source unified Python library designed to standardize metric evaluation across diverse ML tasks, including regression, classification, clustering, segmentation, and image-to-image translation. The library implements class-specific reporting for multi-class tasks through configurable parameters to cover all use cases, while incorporating task-specific parameters to resolve metric computation discrepancies across implementations. Various datasets from domains like healthcare, finance, and real estate were applied to our library and compared with Python, Matlab, and R components to identify which yield similar results. AllMetrics combines a modular Application Programming Interface (API) with robust input validation mechanisms to ensure reproducibility and reliability in model evaluation. This paper presents the design principles, architectural components, and empirical analyses demonstrating the ability to mitigate evaluation errors and to enhance the trustworthiness of ML workflows.
Pathobiological Dictionary Defining Pathomics and Texture Features: Addressing Understandable AI Issues in Personalized Liver Cancer; Dictionary Version LCP1.0
May 20, 2025Abstract:Artificial intelligence (AI) holds strong potential for medical diagnostics, yet its clinical adoption is limited by a lack of interpretability and generalizability. This study introduces the Pathobiological Dictionary for Liver Cancer (LCP1.0), a practical framework designed to translate complex Pathomics and Radiomics Features (PF and RF) into clinically meaningful insights aligned with existing diagnostic workflows. QuPath and PyRadiomics, standardized according to IBSI guidelines, were used to extract 333 imaging features from hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tissue samples, including 240 PF-based-cell detection/intensity, 74 RF-based texture, and 19 RF-based first-order features. Expert-defined ROIs from the public dataset excluded artifact-prone areas, and features were aggregated at the case level. Their relevance to the WHO grading system was assessed using multiple classifiers linked with feature selectors. The resulting dictionary was validated by 8 experts in oncology and pathology. In collaboration with 10 domain experts, we developed a Pathobiological dictionary of imaging features such as PFs and RF. In our study, the Variable Threshold feature selection algorithm combined with the SVM model achieved the highest accuracy (0.80, P-value less than 0.05), selecting 20 key features, primarily clinical and pathomics traits such as Centroid, Cell Nucleus, and Cytoplasmic characteristics. These features, particularly nuclear and cytoplasmic, were strongly associated with tumor grading and prognosis, reflecting atypia indicators like pleomorphism, hyperchromasia, and cellular orientation.The LCP1.0 provides a clinically validated bridge between AI outputs and expert interpretation, enhancing model transparency and usability. Aligning AI-derived features with clinical semantics supports the development of interpretable, trustworthy diagnostic tools for liver cancer pathology.
Influence of High-Performance Image-to-Image Translation Networks on Clinical Visual Assessment and Outcome Prediction: Utilizing Ultrasound to MRI Translation in Prostate Cancer
Jan 30, 2025



Abstract:Purpose: This study examines the core traits of image-to-image translation (I2I) networks, focusing on their effectiveness and adaptability in everyday clinical settings. Methods: We have analyzed data from 794 patients diagnosed with prostate cancer (PCa), using ten prominent 2D/3D I2I networks to convert ultrasound (US) images into MRI scans. We also introduced a new analysis of Radiomic features (RF) via the Spearman correlation coefficient to explore whether networks with high performance (SSIM>85%) could detect subtle RFs. Our study further examined synthetic images by 7 invited physicians. As a final evaluation study, we have investigated the improvement that are achieved using the synthetic MRI data on two traditional machine learning and one deep learning method. Results: In quantitative assessment, 2D-Pix2Pix network substantially outperformed the other 7 networks, with an average SSIM~0.855. The RF analysis revealed that 76 out of 186 RFs were identified using the 2D-Pix2Pix algorithm alone, although half of the RFs were lost during the translation process. A detailed qualitative review by 7 medical doctors noted a deficiency in low-level feature recognition in I2I tasks. Furthermore, the study found that synthesized image-based classification outperformed US image-based classification with an average accuracy and AUC~0.93. Conclusion: This study showed that while 2D-Pix2Pix outperformed cutting-edge networks in low-level feature discovery and overall error and similarity metrics, it still requires improvement in low-level feature performance, as highlighted by Group 3. Further, the study found using synthetic image-based classification outperformed original US image-based methods.
Biological and Radiological Dictionary of Radiomics Features: Addressing Understandable AI Issues in Personalized Prostate Cancer; Dictionary version PM1.0
Dec 14, 2024



Abstract:This study investigates the connection between visual semantic features in PI-RADS and associated risk factors, moving beyond abnormal imaging findings by creating a standardized dictionary of biological/radiological radiomics features (RFs). Using multiparametric prostate MRI sequences (T2-weighted imaging [T2WI], diffusion-weighted imaging [DWI], and apparent diffusion coefficient [ADC]), six interpretable and seven complex classifiers, combined with nine feature selection algorithms (FSAs), were applied to segmented lesions to predict UCLA scores. Combining T2WI, DWI, and ADC with FSAs such as ANOVA F-test, Correlation Coefficient, and Fisher Score, and utilizing logistic regression, identified key features: the 90th percentile from T2WI (hypo-intensity linked to cancer risk), variance from T2WI (lesion heterogeneity), shape metrics like Least Axis Length and Surface Area to Volume ratio from ADC (lesion compactness), and Run Entropy from ADC (texture consistency). This approach achieved an average accuracy of 0.78, outperforming single-sequence methods (p < 0.05). The developed dictionary provides a common language, fostering collaboration between clinical professionals and AI developers to enable trustworthy, interpretable AI for reliable clinical decisions.
Enhanced Lung Cancer Survival Prediction using Semi-Supervised Pseudo-Labeling and Learning from Diverse PET/CT Datasets
Nov 25, 2024



Abstract:Objective: This study explores a semi-supervised learning (SSL), pseudo-labeled strategy using diverse datasets to enhance lung cancer (LCa) survival predictions, analyzing Handcrafted and Deep Radiomic Features (HRF/DRF) from PET/CT scans with Hybrid Machine Learning Systems (HMLS). Methods: We collected 199 LCa patients with both PET & CT images, obtained from The Cancer Imaging Archive (TCIA) and our local database, alongside 408 head&neck cancer (HNCa) PET/CT images from TCIA. We extracted 215 HRFs and 1024 DRFs by PySERA and a 3D-Autoencoder, respectively, within the ViSERA software, from segmented primary tumors. The supervised strategy (SL) employed a HMLSs: PCA connected with 4 classifiers on both HRF and DRFs. SSL strategy expanded the datasets by adding 408 pseudo-labeled HNCa cases (labeled by Random Forest algorithm) to 199 LCa cases, using the same HMLSs techniques. Furthermore, Principal Component Analysis (PCA) linked with 4 survival prediction algorithms were utilized in survival hazard ratio analysis. Results: SSL strategy outperformed SL method (p-value<0.05), achieving an average accuracy of 0.85 with DRFs from PET and PCA+ Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP), compared to 0.65 for SL strategy using DRFs from CT and PCA+ K-Nearest Neighbor (KNN). Additionally, PCA linked with Component-wise Gradient Boosting Survival Analysis on both HRFs and DRFs, as extracted from CT, had an average c-index of 0.80 with a Log Rank p-value<<0.001, confirmed by external testing. Conclusions: Shifting from HRFs and SL to DRFs and SSL strategies, particularly in contexts with limited data points, enabling CT or PET alone to significantly achieve high predictive performance.
Machine Learning Evaluation Metric Discrepancies across Programming Languages and Their Components: Need for Standardization
Nov 18, 2024



Abstract:This study evaluates metrics for tasks such as classification, regression, clustering, correlation analysis, statistical tests, segmentation, and image-to-image (I2I) translation. Metrics were compared across Python libraries, R packages, and Matlab functions to assess their consistency and highlight discrepancies. The findings underscore the need for a unified roadmap to standardize metrics, ensuring reliable and reproducible ML evaluations across platforms. This study examined a wide range of evaluation metrics across various tasks and found only some to be consistent across platforms, such as (i) Accuracy, Balanced Accuracy, Cohens Kappa, F-beta Score, MCC, Geometric Mean, AUC, and Log Loss in binary classification; (ii) Accuracy, Cohens Kappa, and F-beta Score in multi-class classification; (iii) MAE, MSE, RMSE, MAPE, Explained Variance, Median AE, MSLE, and Huber in regression; (iv) Davies-Bouldin Index and Calinski-Harabasz Index in clustering; (v) Pearson, Spearman, Kendall's Tau, Mutual Information, Distance Correlation, Percbend, Shepherd, and Partial Correlation in correlation analysis; (vi) Paired t-test, Chi-Square Test, ANOVA, Kruskal-Wallis Test, Shapiro-Wilk Test, Welchs t-test, and Bartlett's test in statistical tests; (vii) Accuracy, Precision, and Recall in 2D segmentation; (viii) Accuracy in 3D segmentation; (ix) MAE, MSE, RMSE, and R-Squared in 2D-I2I translation; and (x) MAE, MSE, and RMSE in 3D-I2I translation. Given observation of discrepancies in a number of metrics (e.g. precision, recall and F1 score in binary classification, WCSS in clustering, multiple statistical tests, and IoU in segmentation, amongst multiple metrics), this study concludes that ML evaluation metrics require standardization and recommends that future research use consistent metrics for different tasks to effectively compare ML techniques and solutions.
Do High-Performance Image-to-Image Translation Networks Enable the Discovery of Radiomic Features? Application to MRI Synthesis from Ultrasound in Prostate Cancer
Mar 27, 2024Abstract:This study investigates the foundational characteristics of image-to-image translation networks, specifically examining their suitability and transferability within the context of routine clinical environments, despite achieving high levels of performance, as indicated by a Structural Similarity Index (SSIM) exceeding 0.95. The evaluation study was conducted using data from 794 patients diagnosed with Prostate cancer. To synthesize MRI from Ultrasound images, we employed five widely recognized image to image translation networks in medical imaging: 2DPix2Pix, 2DCycleGAN, 3DCycleGAN, 3DUNET, and 3DAutoEncoder. For quantitative assessment, we report four prevalent evaluation metrics Mean Absolute Error, Mean Square Error, Structural Similarity Index (SSIM), and Peak Signal to Noise Ratio. Moreover, a complementary analysis employing Radiomic features (RF) via Spearman correlation coefficient was conducted to investigate, for the first time, whether networks achieving high performance, SSIM greater than 0.9, could identify low-level RFs. The RF analysis showed 76 features out of 186 RFs were discovered via just 2DPix2Pix algorithm while half of RFs were lost in the translation process. Finally, a detailed qualitative assessment by five medical doctors indicated a lack of low level feature discovery in image to image translation tasks.
Tensor Radiomics: Paradigm for Systematic Incorporation of Multi-Flavoured Radiomics Features
Mar 12, 2022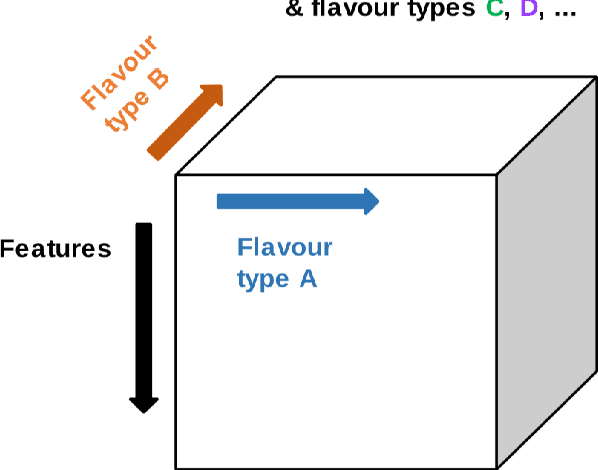
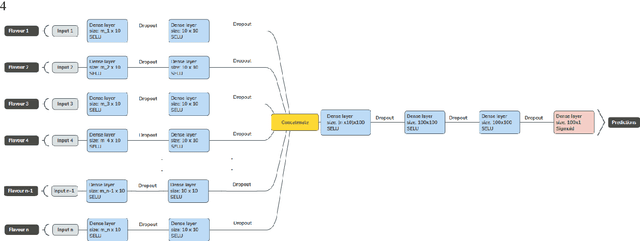
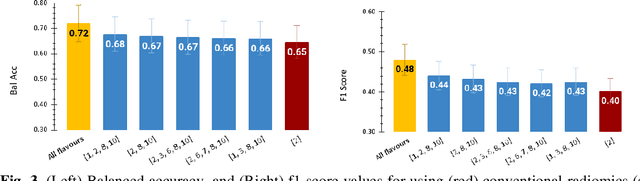
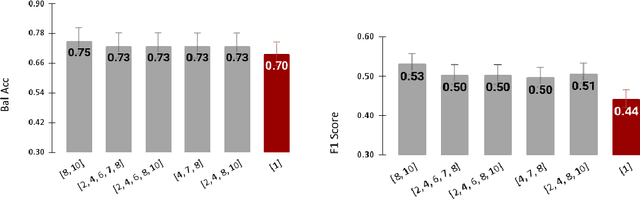
Abstract:Radiomics features extract quantitative information from medical images, towards the derivation of biomarkers for clinical tasks, such as diagnosis, prognosis, or treatment response assessment. Different image discretization parameters (e.g. bin number or size), convolutional filters, segmentation perturbation, or multi-modality fusion levels can be used to generate radiomics features and ultimately signatures. Commonly, only one set of parameters is used; resulting in only one value or flavour for a given RF. We propose tensor radiomics (TR) where tensors of features calculated with multiple combinations of parameters (i.e. flavours) are utilized to optimize the construction of radiomics signatures. We present examples of TR as applied to PET/CT, MRI, and CT imaging invoking machine learning or deep learning solutions, and reproducibility analyses: (1) TR via varying bin sizes on CT images of lung cancer and PET-CT images of head & neck cancer (HNC) for overall survival prediction. A hybrid deep neural network, referred to as TR-Net, along with two ML-based flavour fusion methods showed improved accuracy compared to regular rediomics features. (2) TR built from different segmentation perturbations and different bin sizes for classification of late-stage lung cancer response to first-line immunotherapy using CT images. TR improved predicted patient responses. (3) TR via multi-flavour generated radiomics features in MR imaging showed improved reproducibility when compared to many single-flavour features. (4) TR via multiple PET/CT fusions in HNC. Flavours were built from different fusions using methods, such as Laplacian pyramids and wavelet transforms. TR improved overall survival prediction. Our results suggest that the proposed TR paradigm has the potential to improve performance capabilities in different medical imaging tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge