Mohamed Elidrisi
Cisco, USA
A Collaborative Process Parameter Recommender System for Fleets of Networked Manufacturing Machines -- with Application to 3D Printing
Jun 13, 2025Abstract:Fleets of networked manufacturing machines of the same type, that are collocated or geographically distributed, are growing in popularity. An excellent example is the rise of 3D printing farms, which consist of multiple networked 3D printers operating in parallel, enabling faster production and efficient mass customization. However, optimizing process parameters across a fleet of manufacturing machines, even of the same type, remains a challenge due to machine-to-machine variability. Traditional trial-and-error approaches are inefficient, requiring extensive testing to determine optimal process parameters for an entire fleet. In this work, we introduce a machine learning-based collaborative recommender system that optimizes process parameters for each machine in a fleet by modeling the problem as a sequential matrix completion task. Our approach leverages spectral clustering and alternating least squares to iteratively refine parameter predictions, enabling real-time collaboration among the machines in a fleet while minimizing the number of experimental trials. We validate our method using a mini 3D printing farm consisting of ten 3D printers for which we optimize acceleration and speed settings to maximize print quality and productivity. Our approach achieves significantly faster convergence to optimal process parameters compared to non-collaborative matrix completion.
Privacy-Aware Semantic Cache for Large Language Models
Mar 05, 2024Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) like ChatGPT, Google Bard, Claude, and Llama 2 have revolutionized natural language processing and search engine dynamics. However, these models incur exceptionally high computational costs. For instance, GPT-3 consists of 175 billion parameters and inference on these models also demands billions of floating-point operations. Caching is a natural solution to reduce LLM inference costs on repeated queries. However, existing caching methods are incapable of finding semantic similarities among LLM queries, leading to unacceptable false hit-and-miss rates. This paper introduces MeanCache, a semantic cache for LLMs that identifies semantically similar queries to determine cache hit or miss. Using MeanCache, the response to a user's semantically similar query can be retrieved from a local cache rather than re-querying the LLM, thus reducing costs, service provider load, and environmental impact. MeanCache leverages Federated Learning (FL) to collaboratively train a query similarity model in a distributed manner across numerous users without violating privacy. By placing a local cache in each user's device and using FL, MeanCache reduces the latency and costs and enhances model performance, resulting in lower cache false hit rates. Our experiments, benchmarked against the GPTCache, reveal that MeanCache attains an approximately 17% higher F-score and a 20% increase in precision during semantic cache hit-and-miss decisions. Furthermore, MeanCache reduces the storage requirement by 83% and accelerates semantic cache hit-and-miss decisions by 11%, while still surpassing GPTCache.
Data mining for censored time-to-event data: A Bayesian network model for predicting cardiovascular risk from electronic health record data
Apr 08, 2014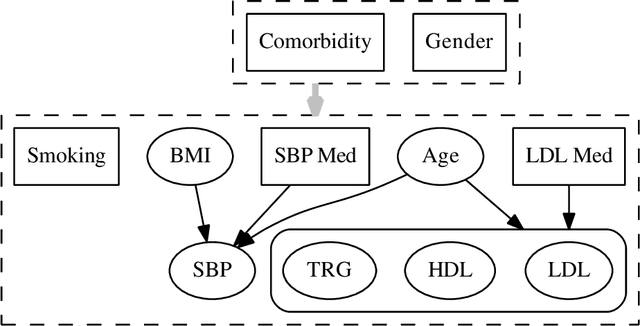


Abstract:Models for predicting the risk of cardiovascular events based on individual patient characteristics are important tools for managing patient care. Most current and commonly used risk prediction models have been built from carefully selected epidemiological cohorts. However, the homogeneity and limited size of such cohorts restricts the predictive power and generalizability of these risk models to other populations. Electronic health data (EHD) from large health care systems provide access to data on large, heterogeneous, and contemporaneous patient populations. The unique features and challenges of EHD, including missing risk factor information, non-linear relationships between risk factors and cardiovascular event outcomes, and differing effects from different patient subgroups, demand novel machine learning approaches to risk model development. In this paper, we present a machine learning approach based on Bayesian networks trained on EHD to predict the probability of having a cardiovascular event within five years. In such data, event status may be unknown for some individuals as the event time is right-censored due to disenrollment and incomplete follow-up. Since many traditional data mining methods are not well-suited for such data, we describe how to modify both modelling and assessment techniques to account for censored observation times. We show that our approach can lead to better predictive performance than the Cox proportional hazards model (i.e., a regression-based approach commonly used for censored, time-to-event data) or a Bayesian network with {\em{ad hoc}} approaches to right-censoring. Our techniques are motivated by and illustrated on data from a large U.S. Midwestern health care system.
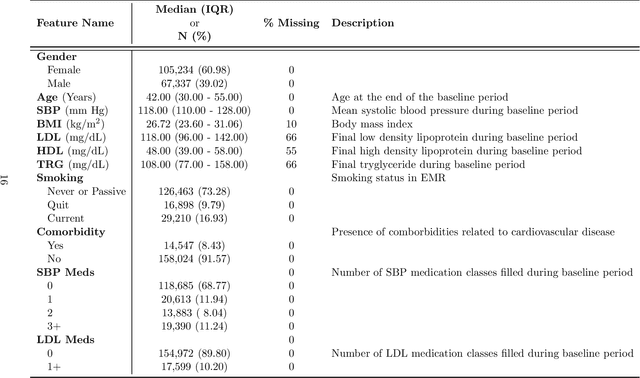
A Naive Bayes machine learning approach to risk prediction using censored, time-to-event data
Apr 08, 2014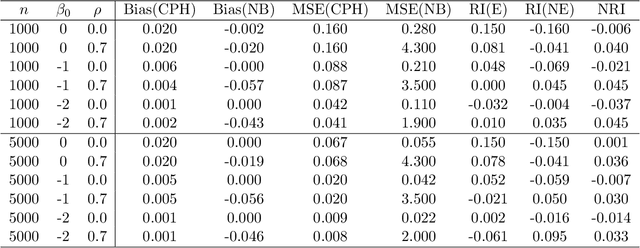
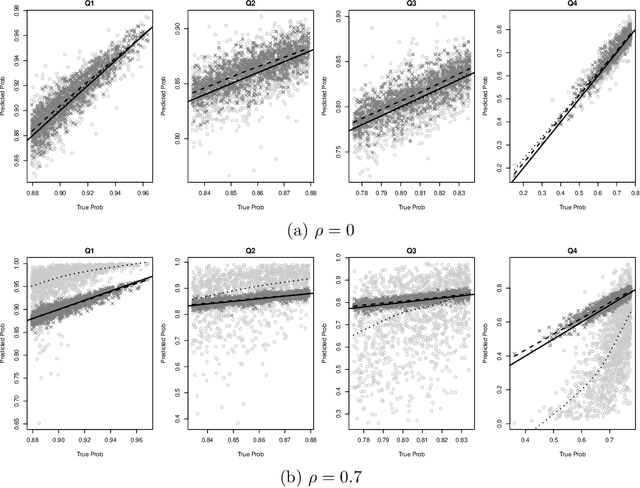
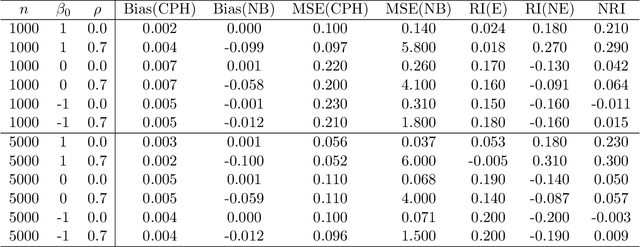
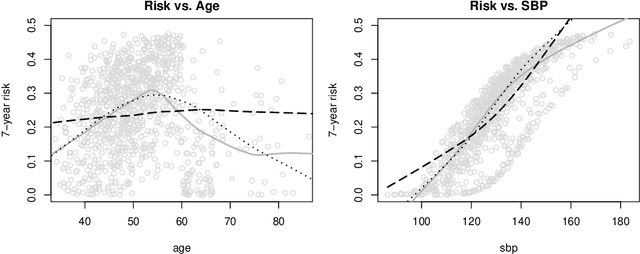
Abstract:Predicting an individual's risk of experiencing a future clinical outcome is a statistical task with important consequences for both practicing clinicians and public health experts. Modern observational databases such as electronic health records (EHRs) provide an alternative to the longitudinal cohort studies traditionally used to construct risk models, bringing with them both opportunities and challenges. Large sample sizes and detailed covariate histories enable the use of sophisticated machine learning techniques to uncover complex associations and interactions, but observational databases are often ``messy,'' with high levels of missing data and incomplete patient follow-up. In this paper, we propose an adaptation of the well-known Naive Bayes (NB) machine learning approach for classification to time-to-event outcomes subject to censoring. We compare the predictive performance of our method to the Cox proportional hazards model which is commonly used for risk prediction in healthcare populations, and illustrate its application to prediction of cardiovascular risk using an EHR dataset from a large Midwest integrated healthcare system.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge