Minxian Xu
BucketServe: Bucket-Based Dynamic Batching for Smart and Efficient LLM Inference Serving
Jul 23, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have become increasingly popular in various areas, traditional business gradually shifting from rule-based systems to LLM-based solutions. However, the inference of LLMs is resource-intensive or latency-sensitive, posing significant challenges for serving systems. Existing LLM serving systems often use static or continuous batching strategies, which can lead to inefficient GPU memory utilization and increased latency, especially under heterogeneous workloads. These methods may also struggle to adapt to dynamic workload fluctuations, resulting in suboptimal throughput and potential service level objective (SLO) violations. In this paper, we introduce BucketServe, a bucket-based dynamic batching framework designed to optimize LLM inference performance. By grouping requests into size-homogeneous buckets based on sequence length, BucketServe minimizes padding overhead and optimizes GPU memory usage through real-time batch size adjustments preventing out-of-memory (OOM) errors. It introduces adaptive bucket splitting/merging and priority-aware scheduling to mitigate resource fragmentation and ensure SLO compliance. Experiment shows that BucketServe significantly outperforms UELLM in throughput, achieving up to 3.58x improvement. It can also handle 1.93x more request load under the SLO attainment of 80% compared with DistServe and demonstrates 1.975x higher system load capacity compared to the UELLM.
HUNTER: AI based Holistic Resource Management for Sustainable Cloud Computing
Oct 28, 2021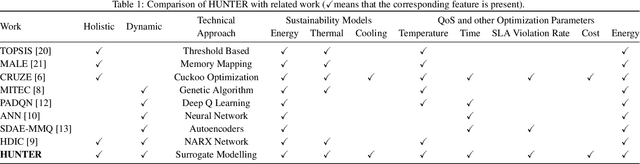
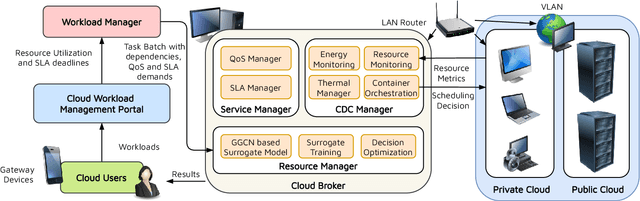
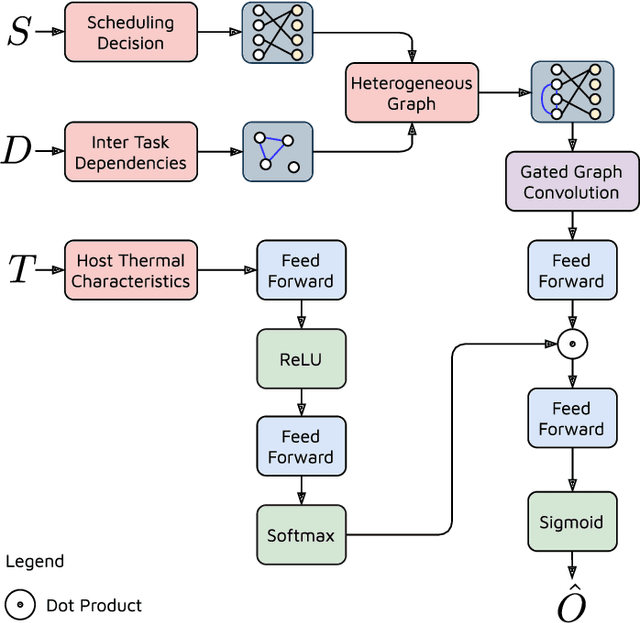
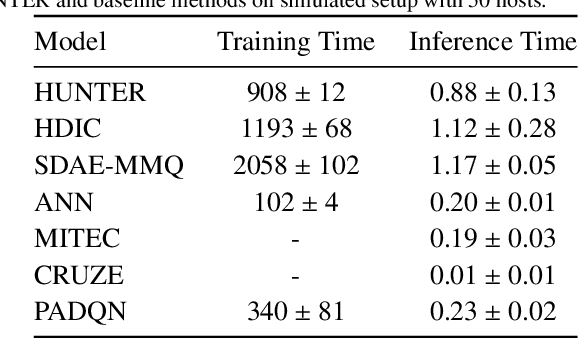
Abstract:The worldwide adoption of cloud data centers (CDCs) has given rise to the ubiquitous demand for hosting application services on the cloud. Further, contemporary data-intensive industries have seen a sharp upsurge in the resource requirements of modern applications. This has led to the provisioning of an increased number of cloud servers, giving rise to higher energy consumption and, consequently, sustainability concerns. Traditional heuristics and reinforcement learning based algorithms for energy-efficient cloud resource management address the scalability and adaptability related challenges to a limited extent. Existing work often fails to capture dependencies across thermal characteristics of hosts, resource consumption of tasks and the corresponding scheduling decisions. This leads to poor scalability and an increase in the compute resource requirements, particularly in environments with non-stationary resource demands. To address these limitations, we propose an artificial intelligence (AI) based holistic resource management technique for sustainable cloud computing called HUNTER. The proposed model formulates the goal of optimizing energy efficiency in data centers as a multi-objective scheduling problem, considering three important models: energy, thermal and cooling. HUNTER utilizes a Gated Graph Convolution Network as a surrogate model for approximating the Quality of Service (QoS) for a system state and generating optimal scheduling decisions. Experiments on simulated and physical cloud environments using the CloudSim toolkit and the COSCO framework show that HUNTER outperforms state-of-the-art baselines in terms of energy consumption, SLA violation, scheduling time, cost and temperature by up to 12, 35, 43, 54 and 3 percent respectively.
Machine Learning-based Orchestration of Containers: A Taxonomy and Future Directions
Jun 24, 2021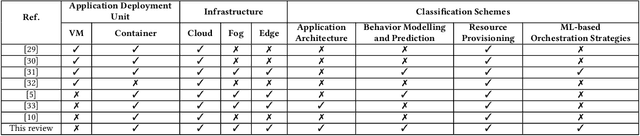
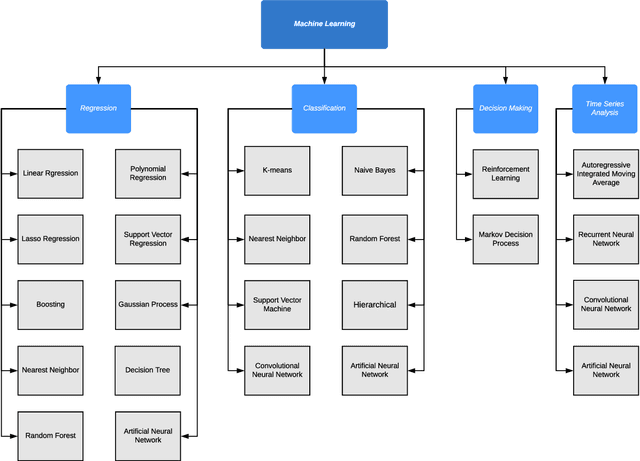
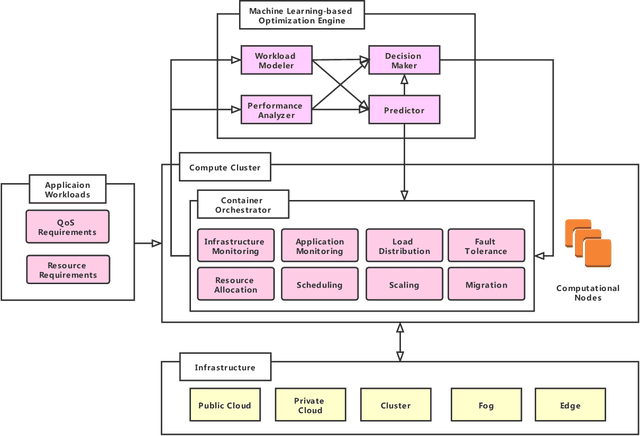
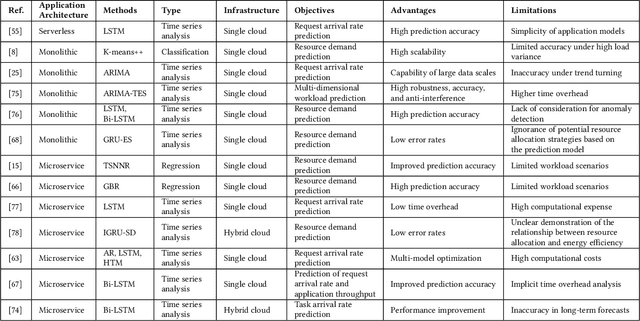
Abstract:Containerization is a lightweight application virtualization technology, providing high environmental consistency, operating system distribution portability, and resource isolation. Existing mainstream cloud service providers have prevalently adopted container technologies in their distributed system infrastructures for automated application management. To handle the automation of deployment, maintenance, autoscaling, and networking of containerized applications, container orchestration is proposed as an essential research problem. However, the highly dynamic and diverse feature of cloud workloads and environments considerably raises the complexity of orchestration mechanisms. Machine learning algorithms are accordingly employed by container orchestration systems for behavior modelling and prediction of multi-dimensional performance metrics. Such insights could further improve the quality of resource provisioning decisions in response to the changing workloads under complex environments. In this paper, we present a comprehensive literature review of existing machine learning-based container orchestration approaches. Detailed taxonomies are proposed to classify the current researches by their common features. Moreover, the evolution of machine learning-based container orchestration technologies from the year 2016 to 2021 has been designed based on objectives and metrics. A comparative analysis of the reviewed techniques is conducted according to the proposed taxonomies, with emphasis on their key characteristics. Finally, various open research challenges and potential future directions are highlighted.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge