Minseon Gwak
Layer-Adaptive State Pruning for Deep State Space Models
Nov 05, 2024



Abstract:Due to the lack of state dimension optimization methods, deep state space models (SSMs) have sacrificed model capacity, training search space, or stability to alleviate computational costs caused by high state dimensions. In this work, we provide a structured pruning method for SSMs, Layer-Adaptive STate pruning (LAST), which reduces the state dimension of each layer in minimizing model-level energy loss by extending modal truncation for a single system. LAST scores are evaluated using $\mathcal{H}_{\infty}$ norms of subsystems for each state and layer-wise energy normalization. The scores serve as global pruning criteria, enabling cross-layer comparison of states and layer-adaptive pruning. Across various sequence benchmarks, LAST optimizes previous SSMs, revealing the redundancy and compressibility of their state spaces. Notably, we demonstrate that, on average, pruning 33% of states still maintains performance with 0.52% accuracy loss in multi-input multi-output SSMs without retraining. Code is available at $\href{https://github.com/msgwak/LAST}{\text{this https URL}}$.
Improving Perceptual Quality, Intelligibility, and Acoustics on VoIP Platforms
Mar 16, 2023Abstract:In this paper, we present a method for fine-tuning models trained on the Deep Noise Suppression (DNS) 2020 Challenge to improve their performance on Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) applications. Our approach involves adapting the DNS 2020 models to the specific acoustic characteristics of VoIP communications, which includes distortion and artifacts caused by compression, transmission, and platform-specific processing. To this end, we propose a multi-task learning framework for VoIP-DNS that jointly optimizes noise suppression and VoIP-specific acoustics for speech enhancement. We evaluate our approach on a diverse VoIP scenarios and show that it outperforms both industry performance and state-of-the-art methods for speech enhancement on VoIP applications. Our results demonstrate the potential of models trained on DNS-2020 to be improved and tailored to different VoIP platforms using VoIP-DNS, whose findings have important applications in areas such as speech recognition, voice assistants, and telecommunication.
Speech Enhancement for Virtual Meetings on Cellular Networks
Feb 16, 2023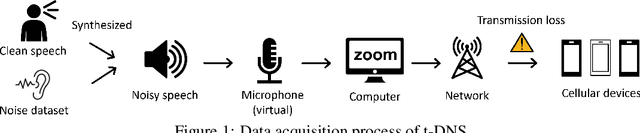
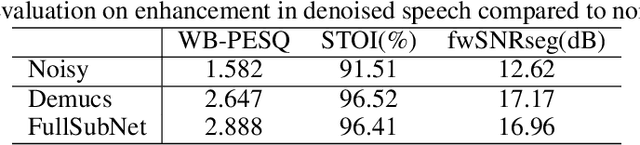

Abstract:We study speech enhancement using deep learning (DL) for virtual meetings on cellular devices, where transmitted speech has background noise and transmission loss that affects speech quality. Since the Deep Noise Suppression (DNS) Challenge dataset does not contain practical disturbance, we collect a transmitted DNS (t-DNS) dataset using Zoom Meetings over T-Mobile network. We select two baseline models: Demucs and FullSubNet. The Demucs is an end-to-end model that takes time-domain inputs and outputs time-domain denoised speech, and the FullSubNet takes time-frequency-domain inputs and outputs the energy ratio of the target speech in the inputs. The goal of this project is to enhance the speech transmitted over the cellular networks using deep learning models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge