Mingjun Ma
3DTeethSAM: Taming SAM2 for 3D Teeth Segmentation
Dec 12, 2025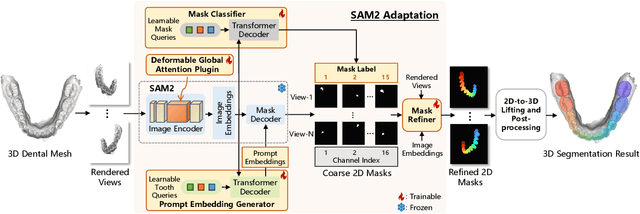
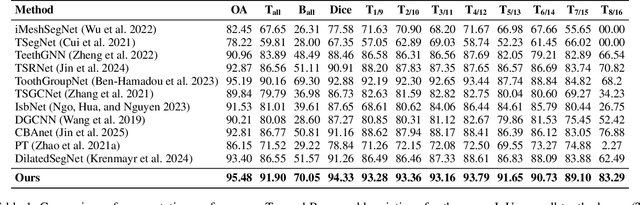
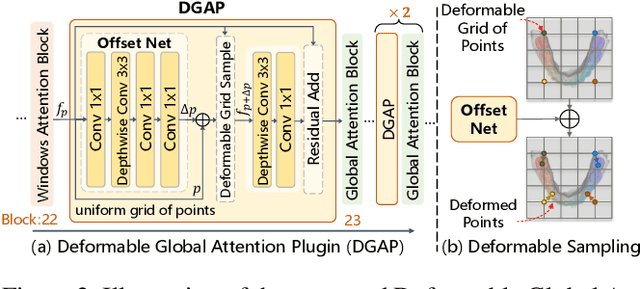
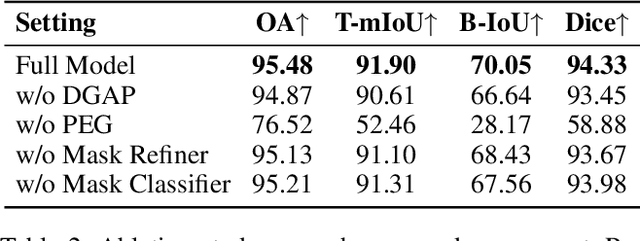
Abstract:3D teeth segmentation, involving the localization of tooth instances and their semantic categorization in 3D dental models, is a critical yet challenging task in digital dentistry due to the complexity of real-world dentition. In this paper, we propose 3DTeethSAM, an adaptation of the Segment Anything Model 2 (SAM2) for 3D teeth segmentation. SAM2 is a pretrained foundation model for image and video segmentation, demonstrating a strong backbone in various downstream scenarios. To adapt SAM2 for 3D teeth data, we render images of 3D teeth models from predefined views, apply SAM2 for 2D segmentation, and reconstruct 3D results using 2D-3D projections. Since SAM2's performance depends on input prompts and its initial outputs often have deficiencies, and given its class-agnostic nature, we introduce three light-weight learnable modules: (1) a prompt embedding generator to derive prompt embeddings from image embeddings for accurate mask decoding, (2) a mask refiner to enhance SAM2's initial segmentation results, and (3) a mask classifier to categorize the generated masks. Additionally, we incorporate Deformable Global Attention Plugins (DGAP) into SAM2's image encoder. The DGAP enhances both the segmentation accuracy and the speed of the training process. Our method has been validated on the 3DTeethSeg benchmark, achieving an IoU of 91.90% on high-resolution 3D teeth meshes, establishing a new state-of-the-art in the field.
NeuronsMAE: A Novel Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning Environment for Cooperative and Competitive Multi-Robot Tasks
Mar 22, 2023Abstract:Multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) has achieved remarkable success in various challenging problems. Meanwhile, more and more benchmarks have emerged and provided some standards to evaluate the algorithms in different fields. On the one hand, the virtual MARL environments lack knowledge of real-world tasks and actuator abilities, and on the other hand, the current task-specified multi-robot platform has poor support for the generality of multi-agent reinforcement learning algorithms and lacks support for transferring from simulation to the real environment. Bridging the gap between the virtual MARL environments and the real multi-robot platform becomes the key to promoting the practicability of MARL algorithms. This paper proposes a novel MARL environment for real multi-robot tasks named NeuronsMAE (Neurons Multi-Agent Environment). This environment supports cooperative and competitive multi-robot tasks and is configured with rich parameter interfaces to study the multi-agent policy transfer from simulation to reality. With this platform, we evaluate various popular MARL algorithms and build a new MARL benchmark for multi-robot tasks. We hope that this platform will facilitate the research and application of MARL algorithms for real robot tasks. Information about the benchmark and the open-source code will be released.
ABCP: Automatic Block-wise and Channel-wise Network Pruning via Joint Search
Oct 08, 2021



Abstract:Currently, an increasing number of model pruning methods are proposed to resolve the contradictions between the computer powers required by the deep learning models and the resource-constrained devices. However, most of the traditional rule-based network pruning methods can not reach a sufficient compression ratio with low accuracy loss and are time-consuming as well as laborious. In this paper, we propose Automatic Block-wise and Channel-wise Network Pruning (ABCP) to jointly search the block-wise and channel-wise pruning action with deep reinforcement learning. A joint sample algorithm is proposed to simultaneously generate the pruning choice of each residual block and the channel pruning ratio of each convolutional layer from the discrete and continuous search space respectively. The best pruning action taking both the accuracy and the complexity of the model into account is obtained finally. Compared with the traditional rule-based pruning method, this pipeline saves human labor and achieves a higher compression ratio with lower accuracy loss. Tested on the mobile robot detection dataset, the pruned YOLOv3 model saves 99.5% FLOPs, reduces 99.5% parameters, and achieves 37.3 times speed up with only 2.8% mAP loss. The results of the transfer task on the sim2real detection dataset also show that our pruned model has much better robustness performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge