Shasha Liu
Sum Rate and Worst Case SINR Optimization in Multi HAPS Ground Integrated Networks
Nov 09, 2025Abstract:Balancing throughput and fairness promises to be a key enabler for achieving large-scale digital inclusion in future vertical heterogeneous networks (VHetNets). In an attempt to address the global digital divide problem, this paper explores a multi-high-altitude platform system (HAPS)-ground integrated network, in which multiple HAPSs collaborate with ground base stations (BSs) to enhance the users' quality of service on the ground to achieve the highly sought-after digital equity. To this end, this paper considers maximizing both the network-wide weighted sum rate function and the worst-case signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio (SINR) function subject to the same system level constraints. More specifically, the paper tackles the two different optimization problems so as to balance throughput and fairness, by accounting for the individual HAPS payload connectivity constraints, HAPS and BS distinct power limitations, and per-user rate requirements. This paper solves the considered problems using techniques from optimization theory by adopting a generalized assignment problem (GAP)-based methodology to determine the user association variables, jointly with successive convex approximation (SCA)-based iterative algorithms for optimizing the corresponding beamforming vectors. One of the main advantages of the proposed algorithms is their amenability for distributed implementation across the multiple HAPSs and BSs. The simulation results particularly validate the performance of the presented algorithms, demonstrating the capability of multi-HAPS networks to boost-up the overall network digital inclusion toward democratizing future digital services.
NeuronsMAE: A Novel Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning Environment for Cooperative and Competitive Multi-Robot Tasks
Mar 22, 2023Abstract:Multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) has achieved remarkable success in various challenging problems. Meanwhile, more and more benchmarks have emerged and provided some standards to evaluate the algorithms in different fields. On the one hand, the virtual MARL environments lack knowledge of real-world tasks and actuator abilities, and on the other hand, the current task-specified multi-robot platform has poor support for the generality of multi-agent reinforcement learning algorithms and lacks support for transferring from simulation to the real environment. Bridging the gap between the virtual MARL environments and the real multi-robot platform becomes the key to promoting the practicability of MARL algorithms. This paper proposes a novel MARL environment for real multi-robot tasks named NeuronsMAE (Neurons Multi-Agent Environment). This environment supports cooperative and competitive multi-robot tasks and is configured with rich parameter interfaces to study the multi-agent policy transfer from simulation to reality. With this platform, we evaluate various popular MARL algorithms and build a new MARL benchmark for multi-robot tasks. We hope that this platform will facilitate the research and application of MARL algorithms for real robot tasks. Information about the benchmark and the open-source code will be released.
Machine Learning-Based User Scheduling in Integrated Satellite-HAPS-Ground Networks
Jun 04, 2022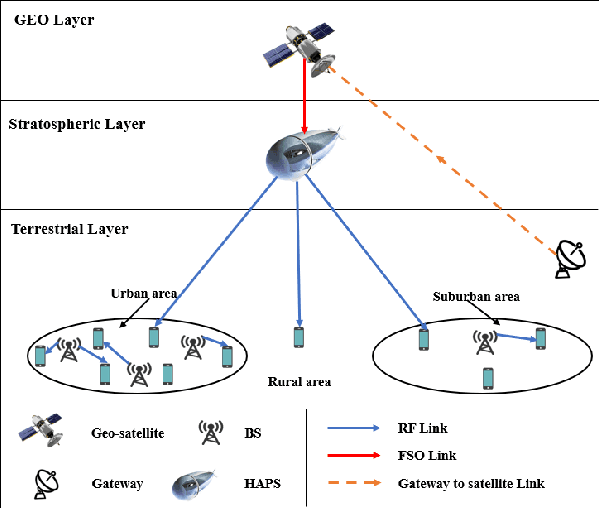
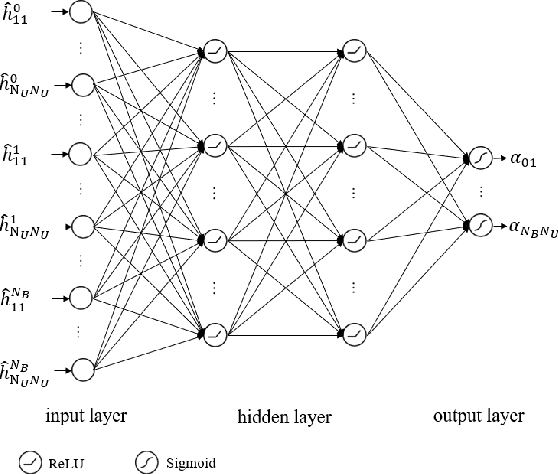
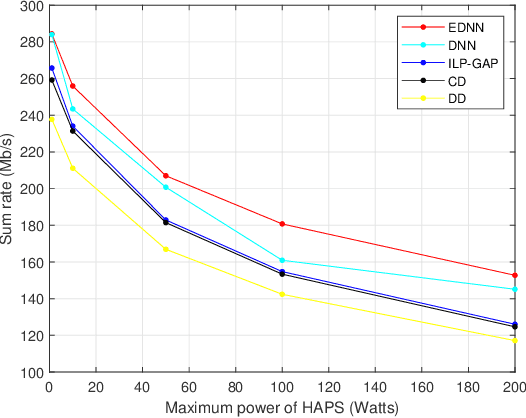
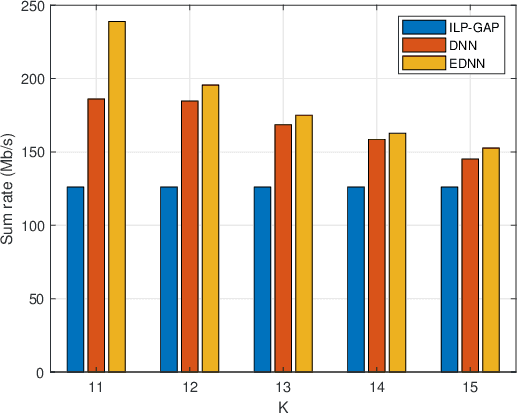
Abstract:Integrated space-air-ground networks promise to offer a valuable solution space for empowering the sixth generation of communication networks (6G), particularly in the context of connecting the unconnected and ultraconnecting the connected. Such digital inclusion thrive makes resource management problems, especially those accounting for load-balancing considerations, of particular interest. The conventional model-based optimization methods, however, often fail to meet the real-time processing and quality-of-service needs, due to the high heterogeneity of the space-air-ground networks, and the typical complexity of the classical algorithms. Given the premises of artificial intelligence at automating wireless networks design, this paper focuses on showcasing the prospects of machine learning in the context of user scheduling in integrated space-air-ground communications. The paper first overviews the most relevant state-of-the art in the context of machine learning applications to the resource allocation problems, with a dedicated attention to space-air-ground networks. The paper then proposes, and shows the benefit of, one specific application that uses ensembling deep neural networks for optimizing the user scheduling policies in integrated space-high altitude platform station (HAPS)-ground networks. Finally, the paper sheds light on the challenges and open issues that promise to spur the integration of machine learning in space-air-ground networks, namely, online HAPS power adaptation, learning-based channel sensing, data-driven multi-HAPSs resource management, and intelligent flying taxis-empowered systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge