Milton L. Montero
When Does Neuroevolution Outcompete Reinforcement Learning in Transfer Learning Tasks?
May 28, 2025Abstract:The ability to continuously and efficiently transfer skills across tasks is a hallmark of biological intelligence and a long-standing goal in artificial systems. Reinforcement learning (RL), a dominant paradigm for learning in high-dimensional control tasks, is known to suffer from brittleness to task variations and catastrophic forgetting. Neuroevolution (NE) has recently gained attention for its robustness, scalability, and capacity to escape local optima. In this paper, we investigate an understudied dimension of NE: its transfer learning capabilities. To this end, we introduce two benchmarks: a) in stepping gates, neural networks are tasked with emulating logic circuits, with designs that emphasize modular repetition and variation b) ecorobot extends the Brax physics engine with objects such as walls and obstacles and the ability to easily switch between different robotic morphologies. Crucial in both benchmarks is the presence of a curriculum that enables evaluating skill transfer across tasks of increasing complexity. Our empirical analysis shows that NE methods vary in their transfer abilities and frequently outperform RL baselines. Our findings support the potential of NE as a foundation for building more adaptable agents and highlight future challenges for scaling NE to complex, real-world problems.
Successes and Limitations of Object-centric Models at Compositional Generalisation
Dec 25, 2024Abstract:In recent years, it has been shown empirically that standard disentangled latent variable models do not support robust compositional learning in the visual domain. Indeed, in spite of being designed with the goal of factorising datasets into their constituent factors of variations, disentangled models show extremely limited compositional generalisation capabilities. On the other hand, object-centric architectures have shown promising compositional skills, albeit these have 1) not been extensively tested and 2) experiments have been limited to scene composition -- where models must generalise to novel combinations of objects in a visual scene instead of novel combinations of object properties. In this work, we show that these compositional generalisation skills extend to this later setting. Furthermore, we present evidence pointing to the source of these skills and how they can be improved through careful training. Finally, we point to one important limitation that still exists which suggests new directions of research.
Evolving Self-Assembling Neural Networks: From Spontaneous Activity to Experience-Dependent Learning
Jun 14, 2024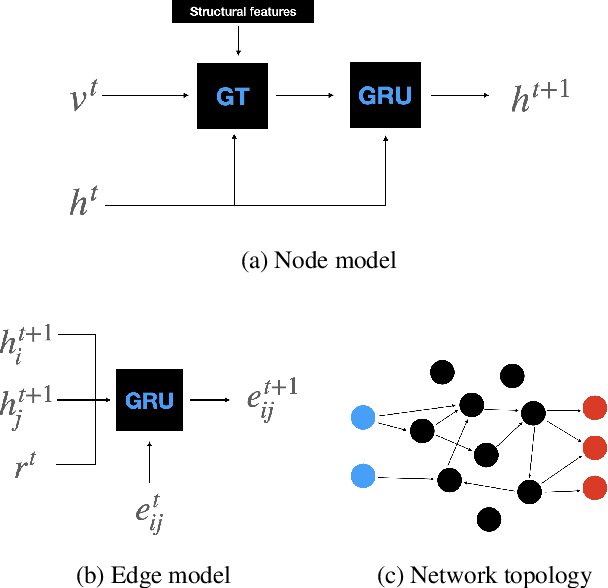
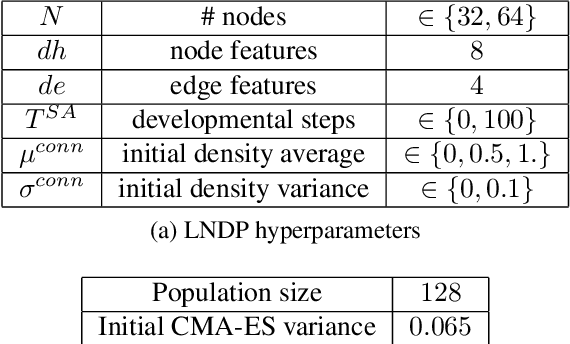
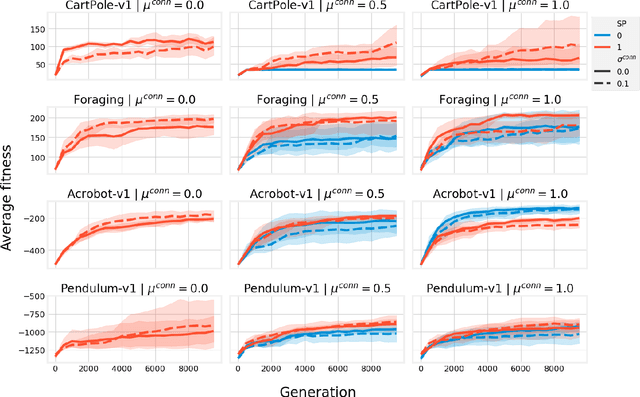
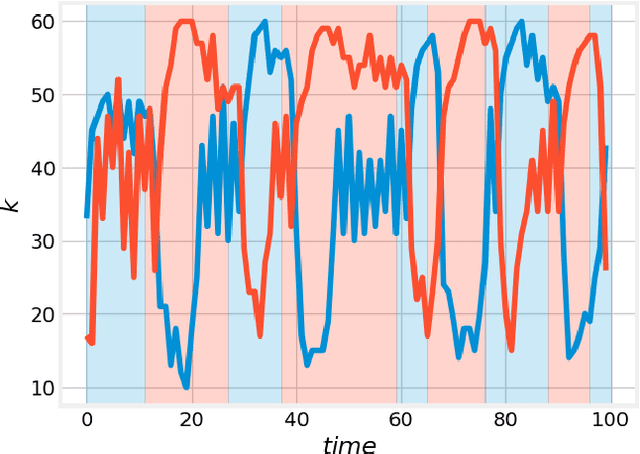
Abstract:Biological neural networks are characterized by their high degree of plasticity, a core property that enables the remarkable adaptability of natural organisms. Importantly, this ability affects both the synaptic strength and the topology of the nervous systems. Artificial neural networks, on the other hand, have been mainly designed as static, fully connected structures that can be notoriously brittle in the face of changing environments and novel inputs. Building on previous works on Neural Developmental Programs (NDPs), we propose a class of self-organizing neural networks capable of synaptic and structural plasticity in an activity and reward-dependent manner which we call Lifelong Neural Developmental Program (LNDP). We present an instance of such a network built on the graph transformer architecture and propose a mechanism for pre-experience plasticity based on the spontaneous activity of sensory neurons. Our results demonstrate the ability of the model to learn from experiences in different control tasks starting from randomly connected or empty networks. We further show that structural plasticity is advantageous in environments necessitating fast adaptation or with non-stationary rewards.
Meta-Learning an Evolvable Developmental Encoding
Jun 13, 2024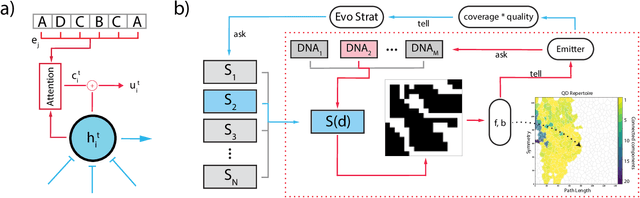
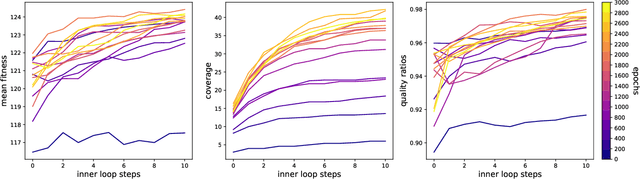
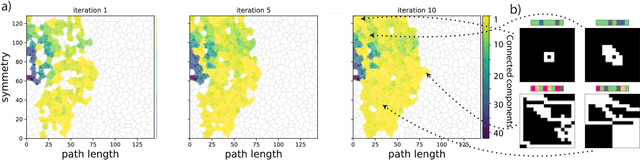
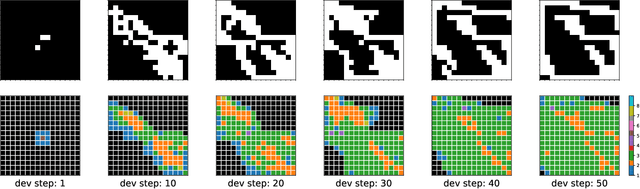
Abstract:Representations for black-box optimisation methods (such as evolutionary algorithms) are traditionally constructed using a delicate manual process. This is in contrast to the representation that maps DNAs to phenotypes in biological organisms, which is at the hear of biological complexity and evolvability. Additionally, the core of this process is fundamentally the same across nearly all forms of life, reflecting their shared evolutionary origin. Generative models have shown promise in being learnable representations for black-box optimisation but they are not per se designed to be easily searchable. Here we present a system that can meta-learn such representation by directly optimising for a representation's ability to generate quality-diversity. In more detail, we show our meta-learning approach can find one Neural Cellular Automata, in which cells can attend to different parts of a "DNA" string genome during development, enabling it to grow different solvable 2D maze structures. We show that the evolved genotype-to-phenotype mappings become more and more evolvable, not only resulting in a faster search but also increasing the quality and diversity of grown artefacts.
MindSet: Vision. A toolbox for testing DNNs on key psychological experiments
Apr 08, 2024



Abstract:Multiple benchmarks have been developed to assess the alignment between deep neural networks (DNNs) and human vision. In almost all cases these benchmarks are observational in the sense they are composed of behavioural and brain responses to naturalistic images that have not been manipulated to test hypotheses regarding how DNNs or humans perceive and identify objects. Here we introduce the toolbox MindSet: Vision, consisting of a collection of image datasets and related scripts designed to test DNNs on 30 psychological findings. In all experimental conditions, the stimuli are systematically manipulated to test specific hypotheses regarding human visual perception and object recognition. In addition to providing pre-generated datasets of images, we provide code to regenerate these datasets, offering many configurable parameters which greatly extend the dataset versatility for different research contexts, and code to facilitate the testing of DNNs on these image datasets using three different methods (similarity judgments, out-of-distribution classification, and decoder method), accessible at https://github.com/MindSetVision/mindset-vision. We test ResNet-152 on each of these methods as an example of how the toolbox can be used.
Lost in Latent Space: Disentangled Models and the Challenge of Combinatorial Generalisation
Apr 05, 2022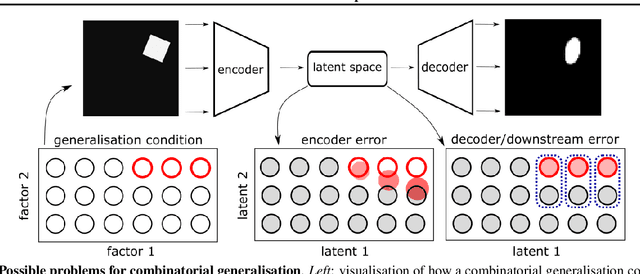
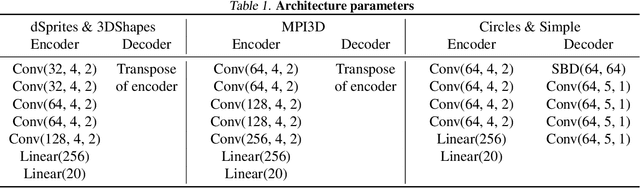
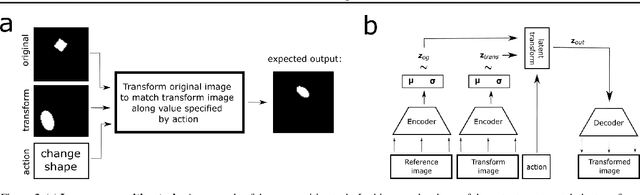
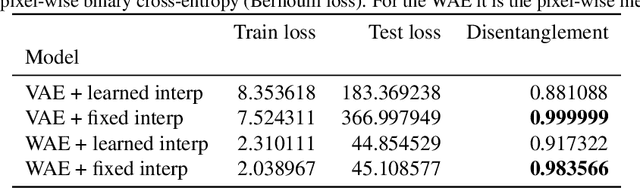
Abstract:Recent research has shown that generative models with highly disentangled representations fail to generalise to unseen combination of generative factor values. These findings contradict earlier research which showed improved performance in out-of-training distribution settings when compared to entangled representations. Additionally, it is not clear if the reported failures are due to (a) encoders failing to map novel combinations to the proper regions of the latent space or (b) novel combinations being mapped correctly but the decoder/downstream process is unable to render the correct output for the unseen combinations. We investigate these alternatives by testing several models on a range of datasets and training settings. We find that (i) when models fail, their encoders also fail to map unseen combinations to correct regions of the latent space and (ii) when models succeed, it is either because the test conditions do not exclude enough examples, or because excluded generative factors determine independent parts of the output image. Based on these results, we argue that to generalise properly, models not only need to capture factors of variation, but also understand how to invert the generative process that was used to generate the data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge