Casimir J. H. Ludwig
Lost in Latent Space: Disentangled Models and the Challenge of Combinatorial Generalisation
Apr 05, 2022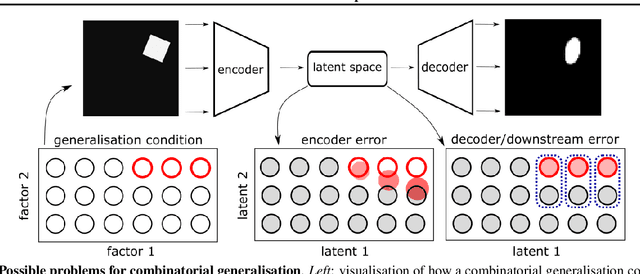
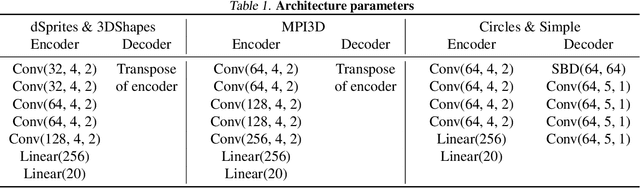
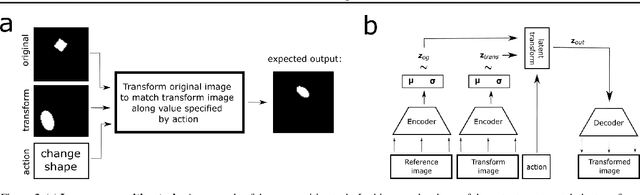
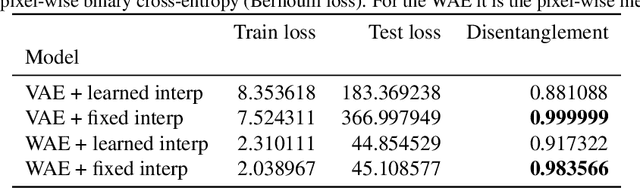
Abstract:Recent research has shown that generative models with highly disentangled representations fail to generalise to unseen combination of generative factor values. These findings contradict earlier research which showed improved performance in out-of-training distribution settings when compared to entangled representations. Additionally, it is not clear if the reported failures are due to (a) encoders failing to map novel combinations to the proper regions of the latent space or (b) novel combinations being mapped correctly but the decoder/downstream process is unable to render the correct output for the unseen combinations. We investigate these alternatives by testing several models on a range of datasets and training settings. We find that (i) when models fail, their encoders also fail to map unseen combinations to correct regions of the latent space and (ii) when models succeed, it is either because the test conditions do not exclude enough examples, or because excluded generative factors determine independent parts of the output image. Based on these results, we argue that to generalise properly, models not only need to capture factors of variation, but also understand how to invert the generative process that was used to generate the data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge