Michal Busta
ICDAR2019 Robust Reading Challenge on Multi-lingual Scene Text Detection and Recognition -- RRC-MLT-2019
Jul 01, 2019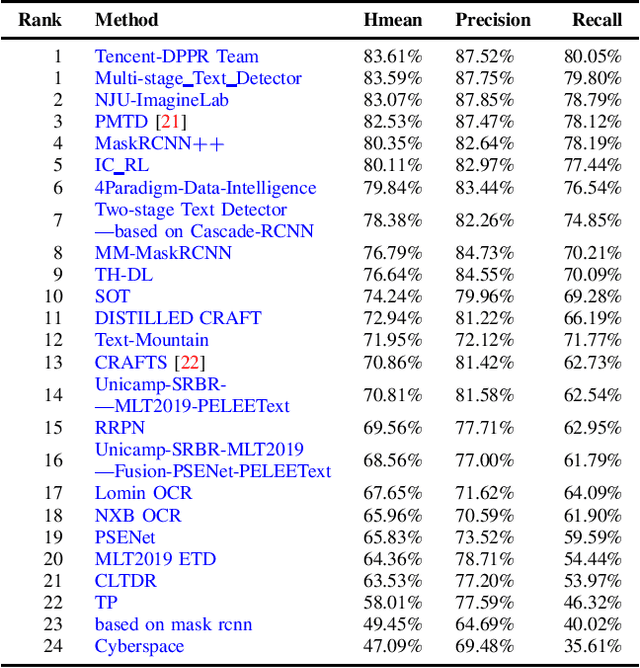
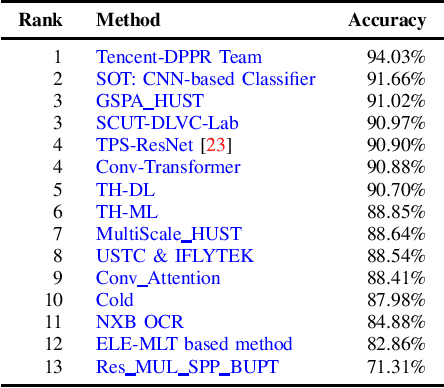
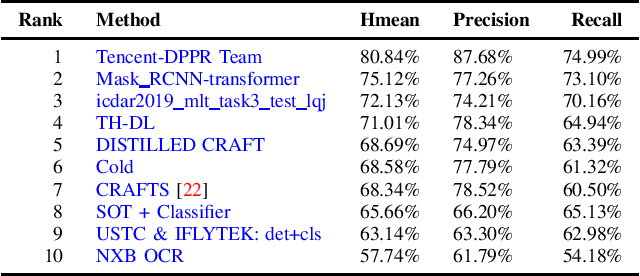
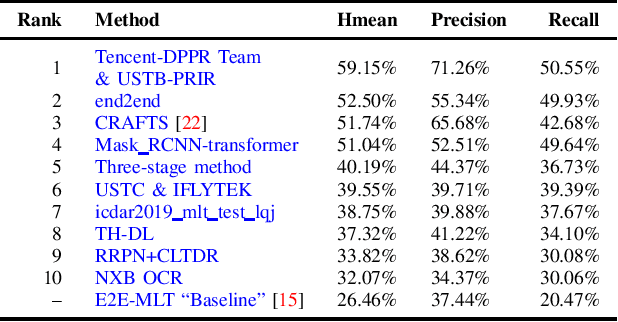
Abstract:With the growing cosmopolitan culture of modern cities, the need of robust Multi-Lingual scene Text (MLT) detection and recognition systems has never been more immense. With the goal to systematically benchmark and push the state-of-the-art forward, the proposed competition builds on top of the RRC-MLT-2017 with an additional end-to-end task, an additional language in the real images dataset, a large scale multi-lingual synthetic dataset to assist the training, and a baseline End-to-End recognition method. The real dataset consists of 20,000 images containing text from 10 languages. The challenge has 4 tasks covering various aspects of multi-lingual scene text: (a) text detection, (b) cropped word script classification, (c) joint text detection and script classification and (d) end-to-end detection and recognition. In total, the competition received 60 submissions from the research and industrial communities. This paper presents the dataset, the tasks and the findings of the presented RRC-MLT-2019 challenge.
Feed-forward Uncertainty Propagation in Belief and Neural Networks
Nov 01, 2018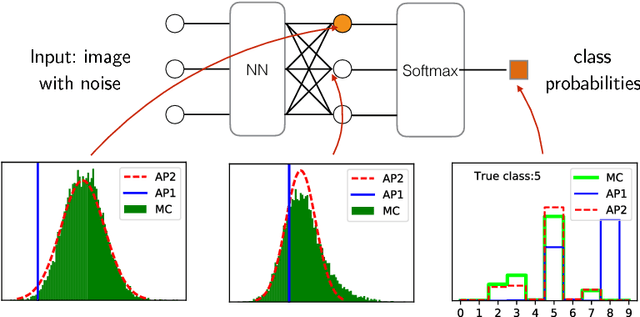
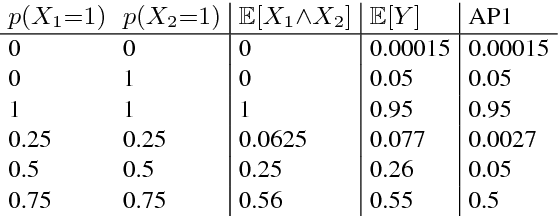
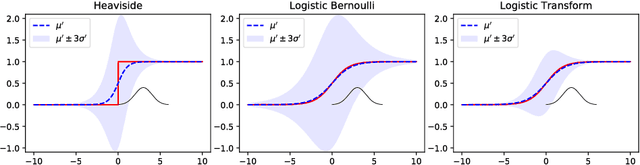
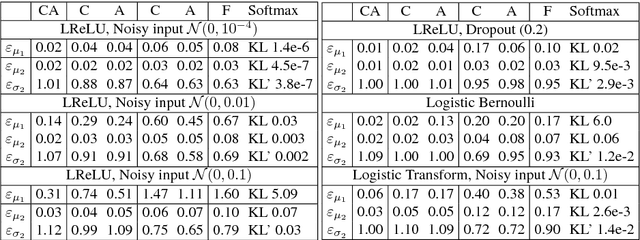
Abstract:We propose a feed-forward inference method applicable to belief and neural networks. In a belief network, the method estimates an approximate factorized posterior of all hidden units given the input. In neural networks the method propagates uncertainty of the input through all the layers. In neural networks with injected noise, the method analytically takes into account uncertainties resulting from this noise. Such feed-forward analytic propagation is differentiable in parameters and can be trained end-to-end. Compared to standard NN, which can be viewed as propagating only the means, we propagate the mean and variance. The method can be useful in all scenarios that require knowledge of the neuron statistics, e.g. when dealing with uncertain inputs, considering sigmoid activations as probabilities of Bernoulli units, training the models regularized by injected noise (dropout) or estimating activation statistics over the dataset (as needed for normalization methods). In the experiments we show the possible utility of the method in all these tasks as well as its current limitations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge