Michael Higgins
Automated speech tools for helping communities process restricted-access corpora for language revival efforts
Apr 24, 2022
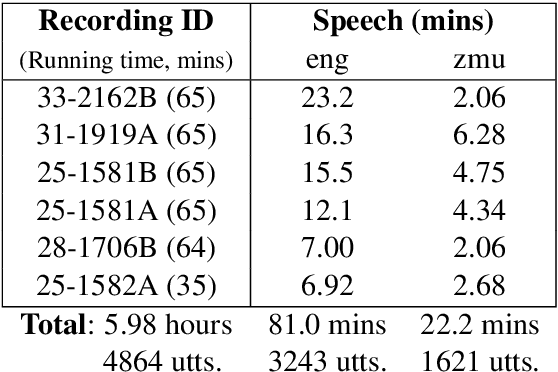
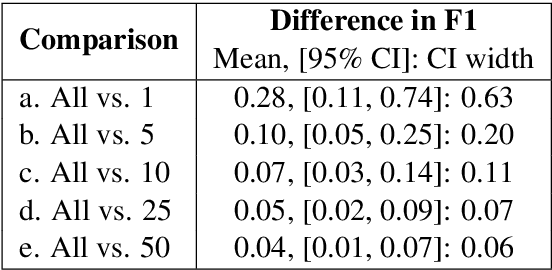
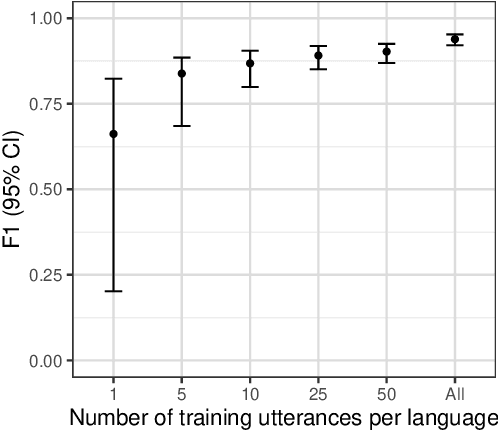
Abstract:Many archival recordings of speech from endangered languages remain unannotated and inaccessible to community members and language learning programs. One bottleneck is the time-intensive nature of annotation. An even narrower bottleneck occurs for recordings with access constraints, such as language that must be vetted or filtered by authorised community members before annotation can begin. We propose a privacy-preserving workflow to widen both bottlenecks for recordings where speech in the endangered language is intermixed with a more widely-used language such as English for meta-linguistic commentary and questions (e.g. What is the word for 'tree'?). We integrate voice activity detection (VAD), spoken language identification (SLI), and automatic speech recognition (ASR) to transcribe the metalinguistic content, which an authorised person can quickly scan to triage recordings that can be annotated by people with lower levels of access. We report work-in-progress processing 136 hours archival audio containing a mix of English and Muruwari. Our collaborative work with the Muruwari custodian of the archival materials show that this workflow reduces metalanguage transcription time by 20% even given only minimal amounts of annotated training data: 10 utterances per language for SLI and for ASR at most 39 minutes, and possibly as little as 39 seconds.
Actionable Conversational Quality Indicators for Improving Task-Oriented Dialog Systems
Sep 22, 2021
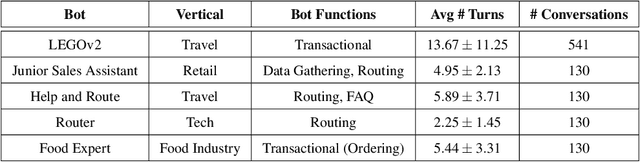
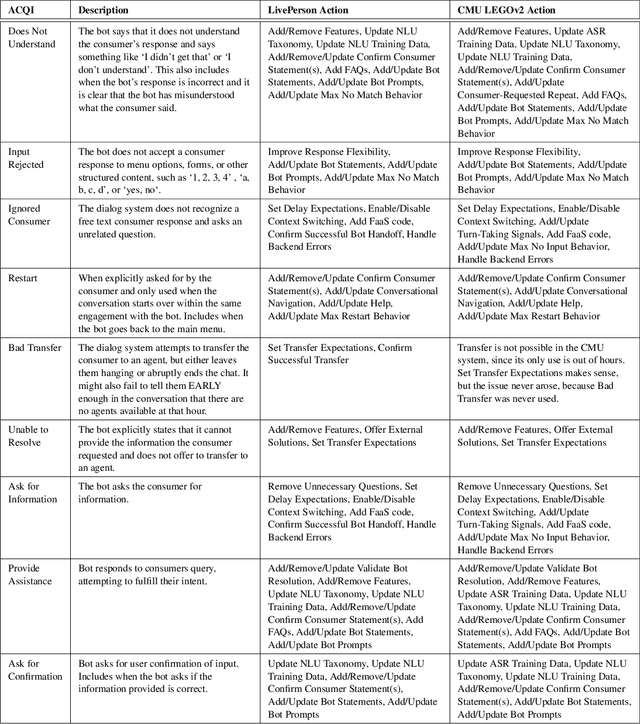

Abstract:Automatic dialog systems have become a mainstream part of online customer service. Many such systems are built, maintained, and improved by customer service specialists, rather than dialog systems engineers and computer programmers. As conversations between people and machines become commonplace, it is critical to understand what is working, what is not, and what actions can be taken to reduce the frequency of inappropriate system responses. These analyses and recommendations need to be presented in terms that directly reflect the user experience rather than the internal dialog processing. This paper introduces and explains the use of Actionable Conversational Quality Indicators (ACQIs), which are used both to recognize parts of dialogs that can be improved, and to recommend how to improve them. This combines benefits of previous approaches, some of which have focused on producing dialog quality scoring while others have sought to categorize the types of errors the dialog system is making. We demonstrate the effectiveness of using ACQIs on LivePerson internal dialog systems used in commercial customer service applications, and on the publicly available CMU LEGOv2 conversational dataset (Raux et al. 2005). We report on the annotation and analysis of conversational datasets showing which ACQIs are important to fix in various situations. The annotated datasets are then used to build a predictive model which uses a turn-based vector embedding of the message texts and achieves an 79% weighted average f1-measure at the task of finding the correct ACQI for a given conversation. We predict that if such a model worked perfectly, the range of potential improvement actions a bot-builder must consider at each turn could be reduced by an average of 81%.
Hybridized Threshold Clustering for Massive Data
Jul 05, 2019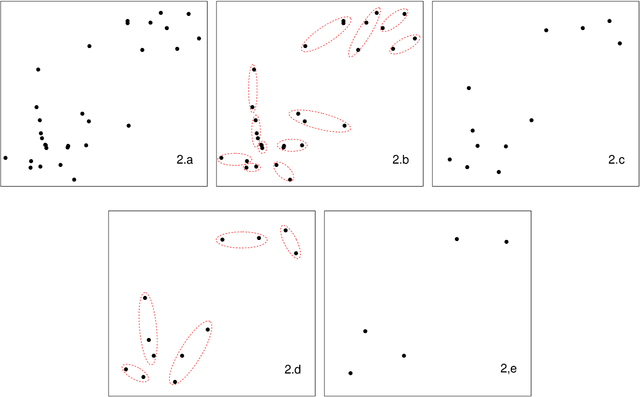
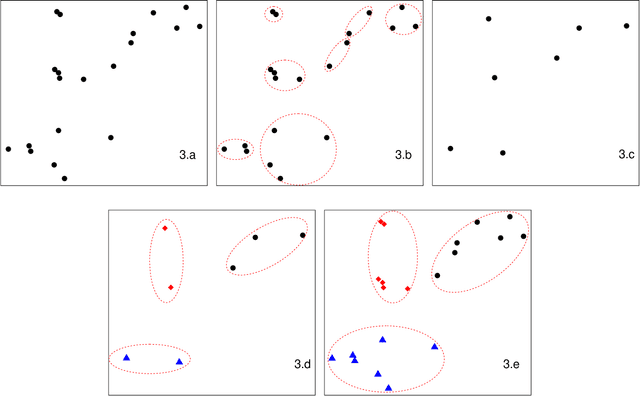
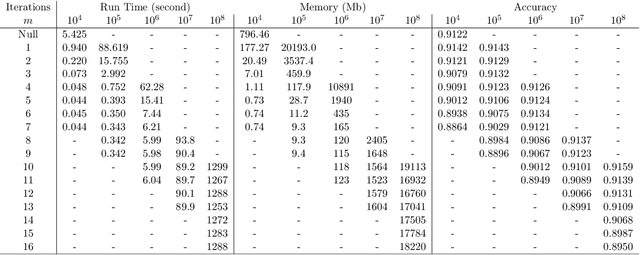
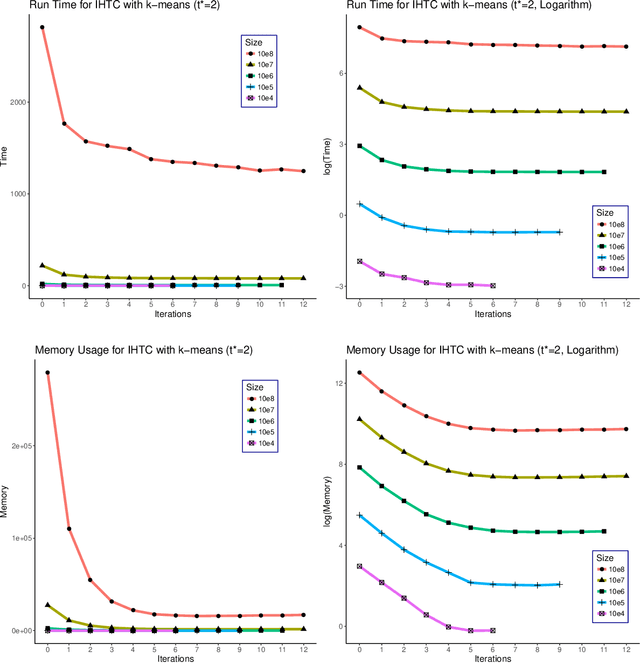
Abstract:As the size $n$ of datasets become massive, many commonly-used clustering algorithms (for example, $k$-means or hierarchical agglomerative clustering (HAC) require prohibitive computational cost and memory. In this paper, we propose a solution to these clustering problems by extending threshold clustering (TC) to problems of instance selection. TC is a recently developed clustering algorithm designed to partition data into many small clusters in linearithmic time (on average). Our proposed clustering method is as follows. First, TC is performed and clusters are reduced into single "prototype" points. Then, TC is applied repeatedly on these prototype points until sufficient data reduction has been obtained. Finally, a more sophisticated clustering algorithm is applied to the reduced prototype points, thereby obtaining a clustering on all $n$ data points. This entire procedure for clustering is called iterative hybridized threshold clustering (IHTC). Through simulation results and by applying our methodology on several real datasets, we show that IHTC combined with $k$-means or HAC substantially reduces the run time and memory usage of the original clustering algorithms while still preserving their performance. Additionally, IHTC helps prevent singular data points from being overfit by clustering algorithms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge