Miao He
HyperPotter: Spell the Charm of High-Order Interactions in Audio Deepfake Detection
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Advances in AIGC technologies have enabled the synthesis of highly realistic audio deepfakes capable of deceiving human auditory perception. Although numerous audio deepfake detection (ADD) methods have been developed, most rely on local temporal/spectral features or pairwise relations, overlooking high-order interactions (HOIs). HOIs capture discriminative patterns that emerge from multiple feature components beyond their individual contributions. We propose HyperPotter, a hypergraph-based framework that explicitly models these synergistic HOIs through clustering-based hyperedges with class-aware prototype initialization. Extensive experiments demonstrate that HyperPotter surpasses its baseline by an average relative gain of 22.15% across 11 datasets and outperforms state-of-the-art methods by 13.96% on 4 challenging cross-domain datasets, demonstrating superior generalization to diverse attacks and speakers.
Semantic Distance Measurement based on Multi-Kernel Gaussian Processes
Dec 13, 2025Abstract:Semantic distance measurement is a fundamental problem in computational linguistics, providing a quantitative characterization of similarity or relatedness between text segments, and underpinning tasks such as text retrieval and text classification. From a mathematical perspective, a semantic distance can be viewed as a metric defined on a space of texts or on a representation space derived from them. However, most classical semantic distance methods are essentially fixed, making them difficult to adapt to specific data distributions and task requirements. In this paper, a semantic distance measure based on multi-kernel Gaussian processes (MK-GP) was proposed. The latent semantic function associated with texts was modeled as a Gaussian process, with its covariance function given by a combined kernel combining Matérn and polynomial components. The kernel parameters were learned automatically from data under supervision, rather than being hand-crafted. This semantic distance was instantiated and evaluated in the context of fine-grained sentiment classification with large language models under an in-context learning (ICL) setup. The experimental results demonstrated the effectiveness of the proposed measure.
AuscultaBase: A Foundational Step Towards AI-Powered Body Sound Diagnostics
Nov 12, 2024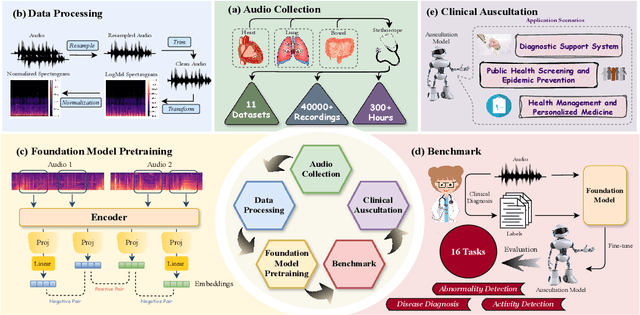
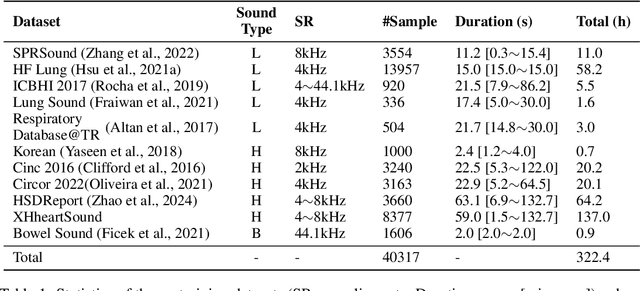
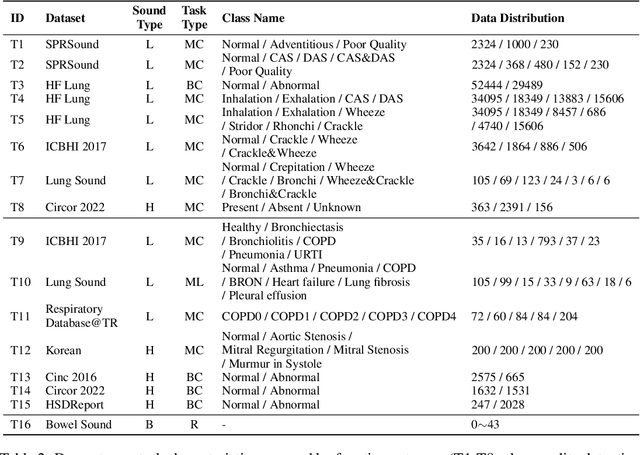
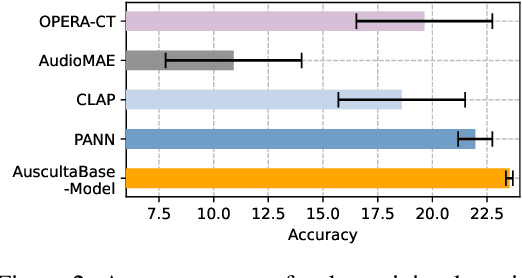
Abstract:Auscultation of internal body sounds is essential for diagnosing a range of health conditions, yet its effectiveness is often limited by clinicians' expertise and the acoustic constraints of human hearing, restricting its use across various clinical scenarios. To address these challenges, we introduce AuscultaBase, a foundational framework aimed at advancing body sound diagnostics through innovative data integration and contrastive learning techniques. Our contributions include the following: First, we compile AuscultaBase-Corpus, a large-scale, multi-source body sound database encompassing 11 datasets with 40,317 audio recordings and totaling 322.4 hours of heart, lung, and bowel sounds. Second, we develop AuscultaBase-Model, a foundational diagnostic model for body sounds, utilizing contrastive learning on the compiled corpus. Third, we establish AuscultaBase-Bench, a comprehensive benchmark containing 16 sub-tasks, assessing the performance of various open-source acoustic pre-trained models. Evaluation results indicate that our model outperforms all other open-source models in 12 out of 16 tasks, demonstrating the efficacy of our approach in advancing diagnostic capabilities for body sound analysis.
Predictive Modeling of Flexible EHD Pumps using Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks
May 13, 2024


Abstract:We present a novel approach to predicting the pressure and flow rate of flexible electrohydrodynamic pumps using the Kolmogorov-Arnold Network. Inspired by the Kolmogorov-Arnold representation theorem, KAN replaces fixed activation functions with learnable spline-based activation functions, enabling it to approximate complex nonlinear functions more effectively than traditional models like Multi-Layer Perceptron and Random Forest. We evaluated KAN on a dataset of flexible EHD pump parameters and compared its performance against RF, and MLP models. KAN achieved superior predictive accuracy, with Mean Squared Errors of 12.186 and 0.001 for pressure and flow rate predictions, respectively. The symbolic formulas extracted from KAN provided insights into the nonlinear relationships between input parameters and pump performance. These findings demonstrate that KAN offers exceptional accuracy and interpretability, making it a promising alternative for predictive modeling in electrohydrodynamic pumping.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge