Mi Wang
DeTracker: Motion-decoupled Vehicle Detection and Tracking in Unstabilized Satellite Videos
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Satellite videos provide continuous observations of surface dynamics but pose significant challenges for multi-object tracking (MOT), especially under unstabilized conditions where platform jitter and the weak appearance of tiny objects jointly degrade tracking performance. To address this problem, we propose DeTracker, a joint detection-and-tracking framework tailored for unstabilized satellite videos. DeTracker introduces a Global--Local Motion Decoupling (GLMD) module that explicitly separates satellite platform motion from true object motion through global alignment and local refinement, leading to improved trajectory stability and motion estimation accuracy. In addition, a Temporal Dependency Feature Pyramid (TDFP) module is developed to perform cross-frame temporal feature fusion, enhancing the continuity and discriminability of tiny-object representations. We further construct a new benchmark dataset, SDM-Car-SU, which simulates multi-directional and multi-speed platform motions to enable systematic evaluation of tracking robustness under varying motion perturbations. Extensive experiments on both simulated and real unstabilized satellite videos demonstrate that DeTracker significantly outperforms existing methods, achieving 61.1% MOTA on SDM-Car-SU and 47.3% MOTA on real satellite video data.
SDM-Car: A Dataset for Small and Dim Moving Vehicles Detection in Satellite Videos
Dec 24, 2024



Abstract:Vehicle detection and tracking in satellite video is essential in remote sensing (RS) applications. However, upon the statistical analysis of existing datasets, we find that the dim vehicles with low radiation intensity and limited contrast against the background are rarely annotated, which leads to the poor effect of existing approaches in detecting moving vehicles under low radiation conditions. In this paper, we address the challenge by building a \textbf{S}mall and \textbf{D}im \textbf{M}oving Cars (SDM-Car) dataset with a multitude of annotations for dim vehicles in satellite videos, which is collected by the Luojia 3-01 satellite and comprises 99 high-quality videos. Furthermore, we propose a method based on image enhancement and attention mechanisms to improve the detection accuracy of dim vehicles, serving as a benchmark for evaluating the dataset. Finally, we assess the performance of several representative methods on SDM-Car and present insightful findings. The dataset is openly available at https://github.com/TanedaM/SDM-Car.
An Improved End-to-End Multi-Target Tracking Method Based on Transformer Self-Attention
Nov 11, 2022


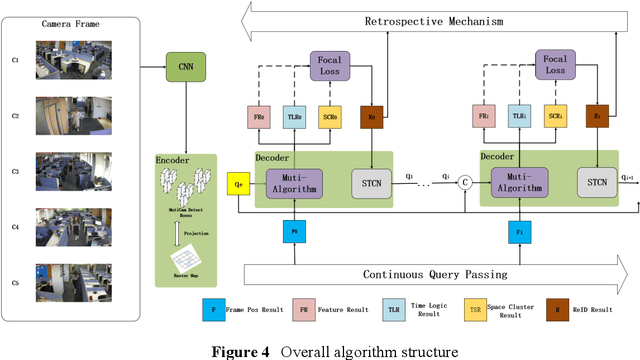
Abstract:This study proposes an improved end-to-end multi-target tracking algorithm that adapts to multi-view multi-scale scenes based on the self-attentive mechanism of the transformer's encoder-decoder structure. A multi-dimensional feature extraction backbone network is combined with a self-built semantic raster map, which is stored in the encoder for correlation and generates target position encoding and multi-dimensional feature vectors. The decoder incorporates four methods: spatial clustering and semantic filtering of multi-view targets, dynamic matching of multi-dimensional features, space-time logic-based multi-target tracking, and space-time convergence network (STCN)-based parameter passing. Through the fusion of multiple decoding methods, muti-camera targets are tracked in three dimensions: temporal logic, spatial logic, and feature matching. For the MOT17 dataset, this study's method significantly outperforms the current state-of-the-art method MiniTrackV2 [49] by 2.2% to 0.836 on Multiple Object Tracking Accuracy(MOTA) metric. Furthermore, this study proposes a retrospective mechanism for the first time, and adopts a reverse-order processing method to optimise the historical mislabeled targets for improving the Identification F1-score(IDF1). For the self-built dataset OVIT-MOT01, the IDF1 improves from 0.948 to 0.967, and the Multi-camera Tracking Accuracy(MCTA) improves from 0.878 to 0.909, which significantly improves the continuous tracking accuracy and scene adaptation. This research method introduces a new attentional tracking paradigm which is able to achieve state-of-the-art performance on multi-target tracking (MOT17 and OVIT-MOT01) tasks.
A Light-Weighted Convolutional Neural Network for Bitemporal SAR Image Change Detection
Jun 21, 2020
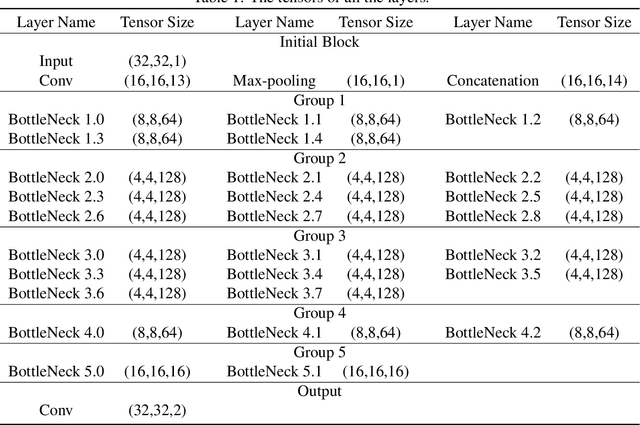


Abstract:Recently, many Convolution Neural Networks (CNN) have been successfully employed in bitemporal SAR image change detection. However, most of the existing networks are too heavy and occupy a large volume of memory for storage and calculation. Motivated by this, in this paper, we propose a lightweight neural network to reduce the computational and spatial complexity and facilitate the change detection on an edge device. In the proposed network, we replace normal convolutional layers with bottleneck layers that keep the same number of channels between input and output. Next, we employ dilated convolutional kernels with a few non-zero entries that reduce the running time in convolutional operators. Comparing with the conventional convolutional neural network, our light-weighted neural network will be more efficient with fewer parameters. We verify our light-weighted neural network on four sets of bitemporal SAR images. The experimental results show that the proposed network can obtain better performance than the conventional CNN and has better model generalization, especially on the challenging datasets with complex scenes.
SAR Image Change Detection via Spatial Metric Learning with an Improved Mahalanobis Distance
Jun 19, 2019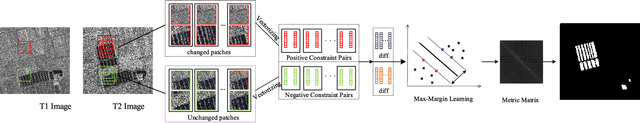


Abstract:The log-ratio (LR) operator has been widely employed to generate the difference image for synthetic aperture radar (SAR) image change detection. However, the difference image generated by this pixel-wise operator can be subject to SAR images speckle and unavoidable registration errors between bitemporal SAR images. In this letter, we proposed a spatial metric learning method to obtain a difference image more robust to the speckle by learning a metric from a set of constraint pairs. In the proposed method, spatial context is considered in constructing constraint pairs, each of which consists of patches in the same location of bitemporal SAR images. Then, a semi-definite positive metric matrix $\bf M$ can be obtained by the optimization with the max-margin criterion. Finally, we verify our proposed method on four challenging datasets of bitemporal SAR images. Experimental results demonstrate that the difference map obtained by our proposed method outperforms than other state-of-art methods.
Imbalanced Learning-based Automatic SAR Images Change Detection by Morphologically Supervised PCA-Net
Jun 19, 2019



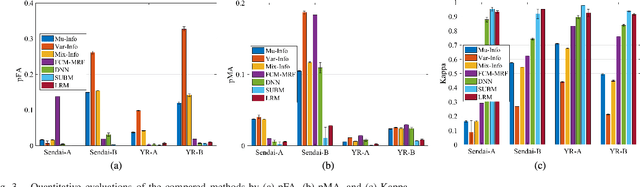
Abstract:Change detection is a quite challenging task due to the imbalance between unchanged and changed class. In addition, the traditional difference map generated by log-ratio is subject to the speckle, which will reduce the accuracy. In this letter, an imbalanced learning-based change detection is proposed based on PCA network (PCA-Net), where a supervised PCA-Net is designed to obtain the robust features directly from given multitemporal SAR images instead of a difference map. Furthermore, to tackle with the imbalance between changed and unchanged classes, we propose a morphologically supervised learning method, where the knowledge in the pixels near the boundary between two classes are exploited to guide network training. Finally, our proposed PCA-Net can be trained by the datasets with available reference maps and applied to a new dataset, which is quite practical in change detection projects. Our proposed method is verified on five sets of multiple temporal SAR images. It is demonstrated from the experiment results that with the knowledge in training samples from the boundary, the learned features benefit for change detection and make the proposed method outperforms than supervised methods trained by randomly drawing samples.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge