Mayee Chen
Olmo 3
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:We introduce Olmo 3, a family of state-of-the-art, fully-open language models at the 7B and 32B parameter scales. Olmo 3 model construction targets long-context reasoning, function calling, coding, instruction following, general chat, and knowledge recall. This release includes the entire model flow, i.e., the full lifecycle of the family of models, including every stage, checkpoint, data point, and dependency used to build it. Our flagship model, Olmo 3 Think 32B, is the strongest fully-open thinking model released to-date.
DataComp-LM: In search of the next generation of training sets for language models
Jun 18, 2024



Abstract:We introduce DataComp for Language Models (DCLM), a testbed for controlled dataset experiments with the goal of improving language models. As part of DCLM, we provide a standardized corpus of 240T tokens extracted from Common Crawl, effective pretraining recipes based on the OpenLM framework, and a broad suite of 53 downstream evaluations. Participants in the DCLM benchmark can experiment with data curation strategies such as deduplication, filtering, and data mixing at model scales ranging from 412M to 7B parameters. As a baseline for DCLM, we conduct extensive experiments and find that model-based filtering is key to assembling a high-quality training set. The resulting dataset, DCLM-Baseline enables training a 7B parameter language model from scratch to 64% 5-shot accuracy on MMLU with 2.6T training tokens. Compared to MAP-Neo, the previous state-of-the-art in open-data language models, DCLM-Baseline represents a 6.6 percentage point improvement on MMLU while being trained with 40% less compute. Our baseline model is also comparable to Mistral-7B-v0.3 and Llama 3 8B on MMLU (63% & 66%), and performs similarly on an average of 53 natural language understanding tasks while being trained with 6.6x less compute than Llama 3 8B. Our results highlight the importance of dataset design for training language models and offer a starting point for further research on data curation.
Mandoline: Model Evaluation under Distribution Shift
Jul 01, 2021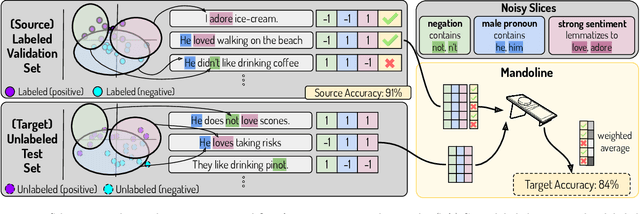
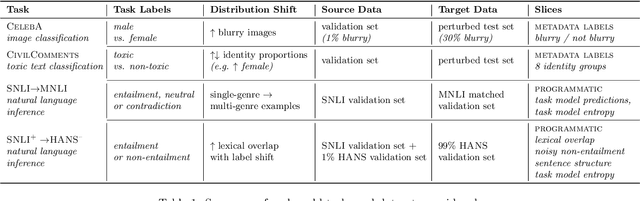
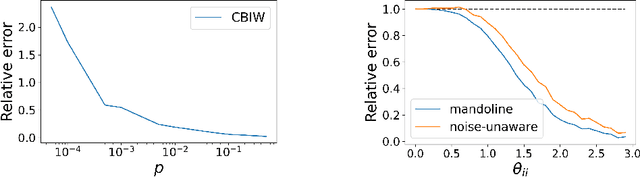
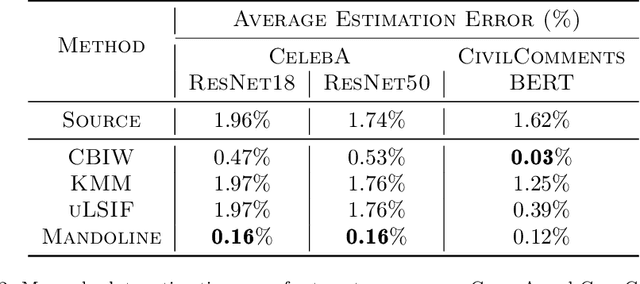
Abstract:Machine learning models are often deployed in different settings than they were trained and validated on, posing a challenge to practitioners who wish to predict how well the deployed model will perform on a target distribution. If an unlabeled sample from the target distribution is available, along with a labeled sample from a possibly different source distribution, standard approaches such as importance weighting can be applied to estimate performance on the target. However, importance weighting struggles when the source and target distributions have non-overlapping support or are high-dimensional. Taking inspiration from fields such as epidemiology and polling, we develop Mandoline, a new evaluation framework that mitigates these issues. Our key insight is that practitioners may have prior knowledge about the ways in which the distribution shifts, which we can use to better guide the importance weighting procedure. Specifically, users write simple "slicing functions" - noisy, potentially correlated binary functions intended to capture possible axes of distribution shift - to compute reweighted performance estimates. We further describe a density ratio estimation framework for the slices and show how its estimation error scales with slice quality and dataset size. Empirical validation on NLP and vision tasks shows that \name can estimate performance on the target distribution up to $3\times$ more accurately compared to standard baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge