Maximilian Zorn
Quantum Generator Kernels
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Quantum kernel methods offer significant theoretical benefits by rendering classically inseparable features separable in quantum space. Yet, the practical application of Quantum Machine Learning (QML), currently constrained by the limitations of Noisy Intermediate-Scale Quantum (NISQ) hardware, necessitates effective strategies to compress and embed large-scale real-world data like images into the constrained capacities of existing quantum devices or simulators. To this end, we propose Quantum Generator Kernels (QGKs), a generator-based approach to quantum kernels, comprising a set of Variational Generator Groups (VGGs) that merge universal generators into a parameterizable operator, ensuring scalable coverage of the available quantum space. Thereby, we address shortcomings of current leading strategies employing hybrid architectures, which might prevent exploiting quantum computing's full potential due to fixed intermediate embedding processes. To optimize the kernel alignment to the target domain, we train a weight vector to parameterize the projection of the VGGs in the current data context. Our empirical results demonstrate superior projection and classification capabilities of the QGK compared to state-of-the-art quantum and classical kernel approaches and show its potential to serve as a versatile framework for various QML applications.
Quantum King-Ring Domination in Chess: A QAOA Approach
Jan 01, 2026Abstract:The Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm (QAOA) is extensively benchmarked on synthetic random instances such as MaxCut, TSP, and SAT problems, but these lack semantic structure and human interpretability, offering limited insight into performance on real-world problems with meaningful constraints. We introduce Quantum King-Ring Domination (QKRD), a NISQ-scale benchmark derived from chess tactical positions that provides 5,000 structured instances with one-hot constraints, spatial locality, and 10--40 qubit scale. The benchmark pairs human-interpretable coverage metrics with intrinsic validation against classical heuristics, enabling algorithmic conclusions without external oracles. Using QKRD, we systematically evaluate QAOA design choices and find that constraint-preserving mixers (XY, domain-wall) converge approximately 13 steps faster than standard mixers (p<10^{-7}, d\approx0.5) while eliminating penalty tuning, warm-start strategies reduce convergence by 45 steps (p<10^{-127}, d=3.35) with energy improvements exceeding d=8, and Conditional Value-at-Risk (CVaR) optimization yields an informative negative result with worse energy (p<10^{-40}, d=1.21) and no coverage benefit. Intrinsic validation shows QAOA outperforms greedy heuristics by 12.6\% and random selection by 80.1\%. Our results demonstrate that structured benchmarks reveal advantages of problem-informed QAOA techniques obscured in random instances. We release all code, data, and experimental artifacts for reproducible NISQ algorithm research.
Topology-Guided Quantum GANs for Constrained Graph Generation
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:Quantum computing (QC) promises theoretical advantages, benefiting computational problems that would not be efficiently classically simulatable. However, much of this theoretical speedup depends on the quantum circuit design solving the problem. We argue that QC literature has yet to explore more domain specific ansatz-topologies, instead of relying on generic, one-size-fits-all architectures. In this work, we show that incorporating task-specific inductive biases -- specifically geometric priors -- into quantum circuit design can enhance the performance of hybrid Quantum Generative Adversarial Networks (QuGANs) on the task of generating geometrically constrained K4 graphs. We evaluate a portfolio of entanglement topologies and loss-function designs to assess their impact on both statistical fidelity and compliance with geometric constraints, including the Triangle and Ptolemaic inequalities. Our results show that aligning circuit topology with the underlying problem structure yields substantial benefits: the Triangle-topology QuGAN achieves the highest geometric validity among quantum models and matches the performance of classical Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN). Additionally, we showcase how specific architectural choices, such as entangling gate types, variance regularization and output-scaling govern the trade-off between geometric consistency and distributional accuracy, thus emphasizing the value of structured, task-aware quantum ansatz-topologies.
Quantum Optimization Algorithms
Nov 15, 2025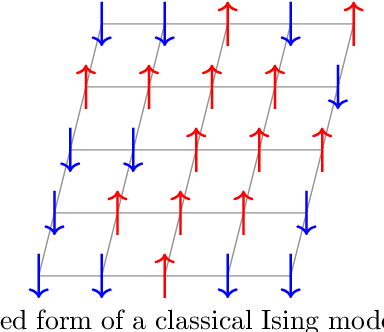
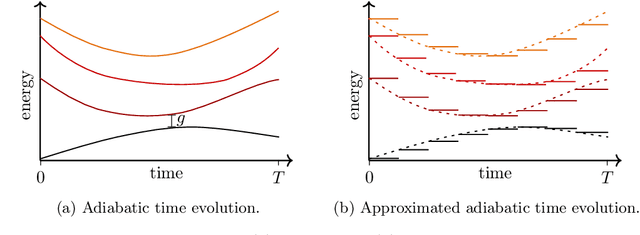
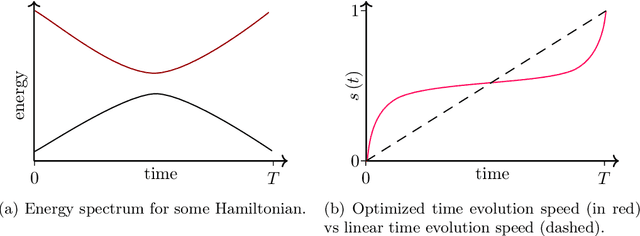
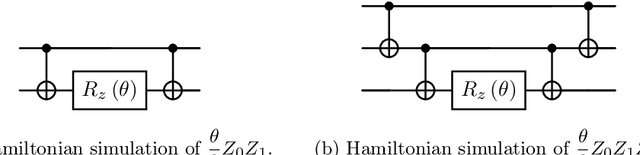
Abstract:Quantum optimization allows for up to exponential quantum speedups for specific, possibly industrially relevant problems. As the key algorithm in this field, we motivate and discuss the Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm (QAOA), which can be understood as a slightly generalized version of Quantum Annealing for gate-based quantum computers. We delve into the quantum circuit implementation of the QAOA, including Hamiltonian simulation techniques for higher-order Ising models, and discuss parameter training using the parameter shift rule. An example implementation with Pennylane source code demonstrates practical application for the Maximum Cut problem. Further, we show how constraints can be incorporated into the QAOA using Grover mixers, allowing to restrict the search space to strictly valid solutions for specific problems. Finally, we outline the Variational Quantum Eigensolver (VQE) as a generalization of the QAOA, highlighting its potential in the NISQ era and addressing challenges such as barren plateaus and ansatz design.
Towards Scalable Lottery Ticket Networks using Genetic Algorithms
Aug 12, 2025Abstract:Building modern deep learning systems that are not just effective but also efficient requires rethinking established paradigms for model training and neural architecture design. Instead of adapting highly overparameterized networks and subsequently applying model compression techniques to reduce resource consumption, a new class of high-performing networks skips the need for expensive parameter updates, while requiring only a fraction of parameters, making them highly scalable. The Strong Lottery Ticket Hypothesis posits that within randomly initialized, sufficiently overparameterized neural networks, there exist subnetworks that can match the accuracy of the trained original model-without any training. This work explores the usage of genetic algorithms for identifying these strong lottery ticket subnetworks. We find that for instances of binary and multi-class classification tasks, our approach achieves better accuracies and sparsity levels than the current state-of-the-art without requiring any gradient information. In addition, we provide justification for the need for appropriate evaluation metrics when scaling to more complex network architectures and learning tasks.
Surrogate Fitness Metrics for Interpretable Reinforcement Learning
Apr 20, 2025Abstract:We employ an evolutionary optimization framework that perturbs initial states to generate informative and diverse policy demonstrations. A joint surrogate fitness function guides the optimization by combining local diversity, behavioral certainty, and global population diversity. To assess demonstration quality, we apply a set of evaluation metrics, including the reward-based optimality gap, fidelity interquartile means (IQMs), fitness composition analysis, and trajectory visualizations. Hyperparameter sensitivity is also examined to better understand the dynamics of trajectory optimization. Our findings demonstrate that optimizing trajectory selection via surrogate fitness metrics significantly improves interpretability of RL policies in both discrete and continuous environments. In gridworld domains, evaluations reveal significantly enhanced demonstration fidelities compared to random and ablated baselines. In continuous control, the proposed framework offers valuable insights, particularly for early-stage policies, while fidelity-based optimization proves more effective for mature policies. By refining and systematically analyzing surrogate fitness functions, this study advances the interpretability of RL models. The proposed improvements provide deeper insights into RL decision-making, benefiting applications in safety-critical and explainability-focused domains.
Evaluating Mutation Techniques in Genetic Algorithm-Based Quantum Circuit Synthesis
Apr 08, 2025Abstract:Quantum computing leverages the unique properties of qubits and quantum parallelism to solve problems intractable for classical systems, offering unparalleled computational potential. However, the optimization of quantum circuits remains critical, especially for noisy intermediate-scale quantum (NISQ) devices with limited qubits and high error rates. Genetic algorithms (GAs) provide a promising approach for efficient quantum circuit synthesis by automating optimization tasks. This work examines the impact of various mutation strategies within a GA framework for quantum circuit synthesis. By analyzing how different mutations transform circuits, it identifies strategies that enhance efficiency and performance. Experiments utilized a fitness function emphasizing fidelity, while accounting for circuit depth and T operations, to optimize circuits with four to six qubits. Comprehensive hyperparameter testing revealed that combining delete and swap strategies outperformed other approaches, demonstrating their effectiveness in developing robust GA-based quantum circuit optimizers.
Investigating Parameter-Efficiency of Hybrid QuGANs Based on Geometric Properties of Generated Sea Route Graphs
Jan 15, 2025Abstract:The demand for artificially generated data for the development, training and testing of new algorithms is omnipresent. Quantum computing (QC), does offer the hope that its inherent probabilistic functionality can be utilised in this field of generative artificial intelligence. In this study, we use quantum-classical hybrid generative adversarial networks (QuGANs) to artificially generate graphs of shipping routes. We create a training dataset based on real shipping data and investigate to what extent QuGANs are able to learn and reproduce inherent distributions and geometric features of this data. We compare hybrid QuGANs with classical Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), with a special focus on their parameter efficiency. Our results indicate that QuGANs are indeed able to quickly learn and represent underlying geometric properties and distributions, although they seem to have difficulties in introducing variance into the sampled data. Compared to classical GANs of greater size, measured in the number of parameters used, some QuGANs show similar result quality. Our reference to concrete use cases, such as the generation of shipping data, provides an illustrative example and demonstrate the potential and diversity in which QC can be used.
Swarm Behavior Cloning
Dec 10, 2024Abstract:In sequential decision-making environments, the primary approaches for training agents are Reinforcement Learning (RL) and Imitation Learning (IL). Unlike RL, which relies on modeling a reward function, IL leverages expert demonstrations, where an expert policy $\pi_e$ (e.g., a human) provides the desired behavior. Formally, a dataset $D$ of state-action pairs is provided: $D = {(s, a = \pi_e(s))}$. A common technique within IL is Behavior Cloning (BC), where a policy $\pi(s) = a$ is learned through supervised learning on $D$. Further improvements can be achieved by using an ensemble of $N$ individually trained BC policies, denoted as $E = {\pi_i(s)}{1 \leq i \leq N}$. The ensemble's action $a$ for a given state $s$ is the aggregated output of the $N$ actions: $a = \frac{1}{N} \sum{i} \pi_i(s)$. This paper addresses the issue of increasing action differences -- the observation that discrepancies between the $N$ predicted actions grow in states that are underrepresented in the training data. Large action differences can result in suboptimal aggregated actions. To address this, we propose a method that fosters greater alignment among the policies while preserving the diversity of their computations. This approach reduces action differences and ensures that the ensemble retains its inherent strengths, such as robustness and varied decision-making. We evaluate our approach across eight diverse environments, demonstrating a notable decrease in action differences and significant improvements in overall performance, as measured by mean episode returns.
Optimizing Sensor Redundancy in Sequential Decision-Making Problems
Dec 10, 2024



Abstract:Reinforcement Learning (RL) policies are designed to predict actions based on current observations to maximize cumulative future rewards. In real-world applications (i.e., non-simulated environments), sensors are essential for measuring the current state and providing the observations on which RL policies rely to make decisions. A significant challenge in deploying RL policies in real-world scenarios is handling sensor dropouts, which can result from hardware malfunctions, physical damage, or environmental factors like dust on a camera lens. A common strategy to mitigate this issue is the use of backup sensors, though this comes with added costs. This paper explores the optimization of backup sensor configurations to maximize expected returns while keeping costs below a specified threshold, C. Our approach uses a second-order approximation of expected returns and includes penalties for exceeding cost constraints. We then optimize this quadratic program using Tabu Search, a meta-heuristic algorithm. The approach is evaluated across eight OpenAI Gym environments and a custom Unity-based robotic environment (RobotArmGrasping). Empirical results demonstrate that our quadratic program effectively approximates real expected returns, facilitating the identification of optimal sensor configurations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge