Julian Schönberger
Towards Scalable Lottery Ticket Networks using Genetic Algorithms
Aug 12, 2025Abstract:Building modern deep learning systems that are not just effective but also efficient requires rethinking established paradigms for model training and neural architecture design. Instead of adapting highly overparameterized networks and subsequently applying model compression techniques to reduce resource consumption, a new class of high-performing networks skips the need for expensive parameter updates, while requiring only a fraction of parameters, making them highly scalable. The Strong Lottery Ticket Hypothesis posits that within randomly initialized, sufficiently overparameterized neural networks, there exist subnetworks that can match the accuracy of the trained original model-without any training. This work explores the usage of genetic algorithms for identifying these strong lottery ticket subnetworks. We find that for instances of binary and multi-class classification tasks, our approach achieves better accuracies and sparsity levels than the current state-of-the-art without requiring any gradient information. In addition, we provide justification for the need for appropriate evaluation metrics when scaling to more complex network architectures and learning tasks.
PIMAEX: Multi-Agent Exploration through Peer Incentivization
Jan 02, 2025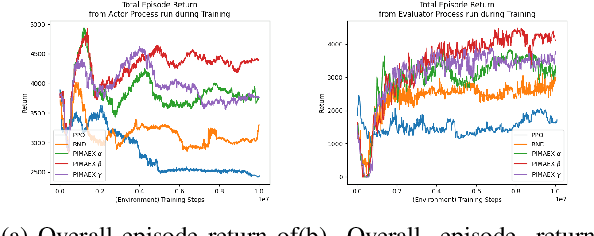
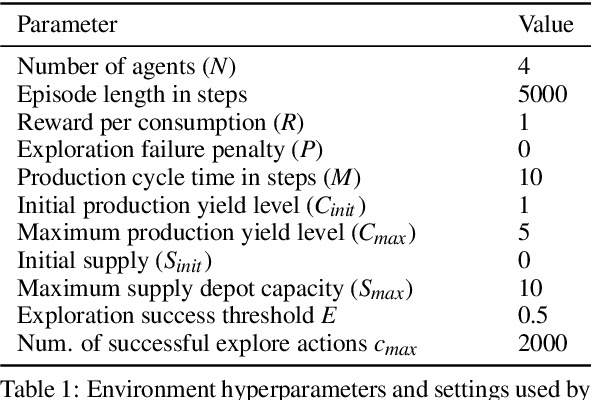
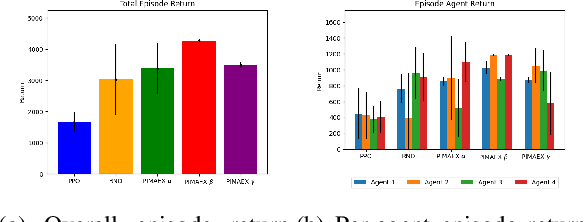
Abstract:While exploration in single-agent reinforcement learning has been studied extensively in recent years, considerably less work has focused on its counterpart in multi-agent reinforcement learning. To address this issue, this work proposes a peer-incentivized reward function inspired by previous research on intrinsic curiosity and influence-based rewards. The \textit{PIMAEX} reward, short for Peer-Incentivized Multi-Agent Exploration, aims to improve exploration in the multi-agent setting by encouraging agents to exert influence over each other to increase the likelihood of encountering novel states. We evaluate the \textit{PIMAEX} reward in conjunction with \textit{PIMAEX-Communication}, a multi-agent training algorithm that employs a communication channel for agents to influence one another. The evaluation is conducted in the \textit{Consume/Explore} environment, a partially observable environment with deceptive rewards, specifically designed to challenge the exploration vs.\ exploitation dilemma and the credit-assignment problem. The results empirically demonstrate that agents using the \textit{PIMAEX} reward with \textit{PIMAEX-Communication} outperform those that do not.
Optimizing Sensor Redundancy in Sequential Decision-Making Problems
Dec 10, 2024



Abstract:Reinforcement Learning (RL) policies are designed to predict actions based on current observations to maximize cumulative future rewards. In real-world applications (i.e., non-simulated environments), sensors are essential for measuring the current state and providing the observations on which RL policies rely to make decisions. A significant challenge in deploying RL policies in real-world scenarios is handling sensor dropouts, which can result from hardware malfunctions, physical damage, or environmental factors like dust on a camera lens. A common strategy to mitigate this issue is the use of backup sensors, though this comes with added costs. This paper explores the optimization of backup sensor configurations to maximize expected returns while keeping costs below a specified threshold, C. Our approach uses a second-order approximation of expected returns and includes penalties for exceeding cost constraints. We then optimize this quadratic program using Tabu Search, a meta-heuristic algorithm. The approach is evaluated across eight OpenAI Gym environments and a custom Unity-based robotic environment (RobotArmGrasping). Empirical results demonstrate that our quadratic program effectively approximates real expected returns, facilitating the identification of optimal sensor configurations.
Finding Strong Lottery Ticket Networks with Genetic Algorithms
Nov 07, 2024Abstract:According to the Strong Lottery Ticket Hypothesis, every sufficiently large neural network with randomly initialized weights contains a sub-network which - still with its random weights - already performs as well for a given task as the trained super-network. We present the first approach based on a genetic algorithm to find such strong lottery ticket sub-networks without training or otherwise computing any gradient. We show that, for smaller instances of binary classification tasks, our evolutionary approach even produces smaller and better-performing lottery ticket networks than the state-of-the-art approach using gradient information.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge