Mattias Billast
Safety Aware Autonomous Path Planning Using Model Predictive Reinforcement Learning for Inland Waterways
Nov 16, 2023Abstract:In recent years, interest in autonomous shipping in urban waterways has increased significantly due to the trend of keeping cars and trucks out of city centers. Classical approaches such as Frenet frame based planning and potential field navigation often require tuning of many configuration parameters and sometimes even require a different configuration depending on the situation. In this paper, we propose a novel path planning approach based on reinforcement learning called Model Predictive Reinforcement Learning (MPRL). MPRL calculates a series of waypoints for the vessel to follow. The environment is represented as an occupancy grid map, allowing us to deal with any shape of waterway and any number and shape of obstacles. We demonstrate our approach on two scenarios and compare the resulting path with path planning using a Frenet frame and path planning based on a proximal policy optimization (PPO) agent. Our results show that MPRL outperforms both baselines in both test scenarios. The PPO based approach was not able to reach the goal in either scenario while the Frenet frame approach failed in the scenario consisting of a corner with obstacles. MPRL was able to safely (collision free) navigate to the goal in both of the test scenarios.
Improved inter-scanner MS lesion segmentation by adversarial training on longitudinal data
Feb 03, 2020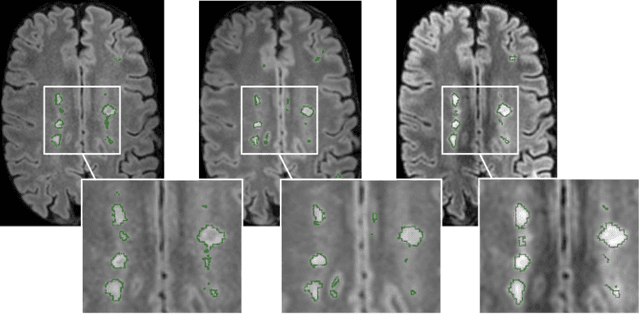
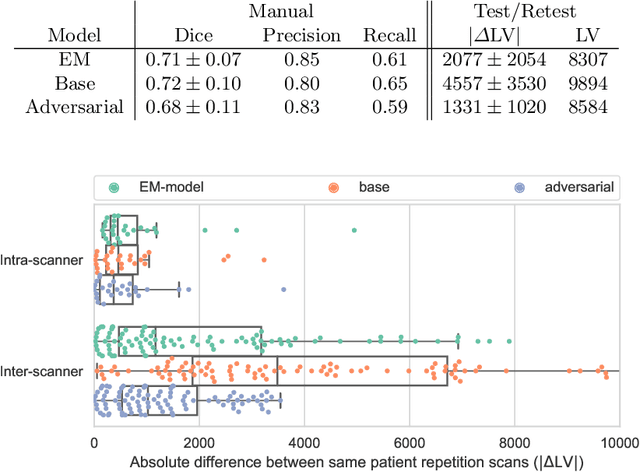
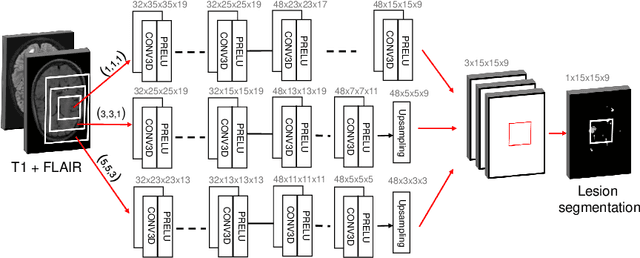
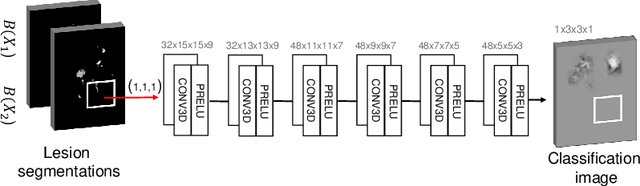
Abstract:The evaluation of white matter lesion progression is an important biomarker in the follow-up of MS patients and plays a crucial role when deciding the course of treatment. Current automated lesion segmentation algorithms are susceptible to variability in image characteristics related to MRI scanner or protocol differences. We propose a model that improves the consistency of MS lesion segmentations in inter-scanner studies. First, we train a CNN base model to approximate the performance of icobrain, an FDA-approved clinically available lesion segmentation software. A discriminator model is then trained to predict if two lesion segmentations are based on scans acquired using the same scanner type or not, achieving a 78% accuracy in this task. Finally, the base model and the discriminator are trained adversarially on multi-scanner longitudinal data to improve the inter-scanner consistency of the base model. The performance of the models is evaluated on an unseen dataset containing manual delineations. The inter-scanner variability is evaluated on test-retest data, where the adversarial network produces improved results over the base model and the FDA-approved solution.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge