Mattia Risiglione
R-LGP: A Reachability-guided Logic-geometric Programming Framework for Optimal Task and Motion Planning on Mobile Manipulators
Oct 04, 2023



Abstract:This paper presents an optimization-based solution to task and motion planning (TAMP) on mobile manipulators. Logic-geometric programming (LGP) has shown promising capabilities for optimally dealing with hybrid TAMP problems that involve abstract and geometric constraints. However, LGP does not scale well to high-dimensional systems (e.g. mobile manipulators) and can suffer from obstacle avoidance issues. In this work, we extend LGP with a sampling-based reachability graph to enable solving optimal TAMP on high-DoF mobile manipulators. The proposed reachability graph can incorporate environmental information (obstacles) to provide the planner with sufficient geometric constraints. This reachability-aware heuristic efficiently prunes infeasible sequences of actions in the continuous domain, hence, it reduces replanning by securing feasibility at the final full trajectory optimization. Our framework proves to be time-efficient in computing optimal and collision-free solutions, while outperforming the current state of the art on metrics of success rate, planning time, path length and number of steps. We validate our framework on the physical Toyota HSR robot and report comparisons on a series of mobile manipulation tasks of increasing difficulty.
Kinematically-Decoupled Impedance Control for Fast Object Visual Servoing and Grasping on Quadruped Manipulators
Jul 10, 2023



Abstract:We propose a control pipeline for SAG (Searching, Approaching, and Grasping) of objects, based on a decoupled arm kinematic chain and impedance control, which integrates image-based visual servoing (IBVS). The kinematic decoupling allows for fast end-effector motions and recovery that leads to robust visual servoing. The whole approach and pipeline can be generalized for any mobile platform (wheeled or tracked vehicles), but is most suitable for dynamically moving quadruped manipulators thanks to their reactivity against disturbances. The compliance of the impedance controller makes the robot safer for interactions with humans and the environment. We demonstrate the performance and robustness of the proposed approach with various experiments on our 140 kg HyQReal quadruped robot equipped with a 7-DoF manipulator arm. The experiments consider dynamic locomotion, tracking under external disturbances, and fast motions of the target object.
A Whole-Body Controller Based on a Simplified Template for Rendering Impedances in Quadruped Manipulators
Aug 01, 2022



Abstract:Quadrupedal manipulators require to be compliant when dealing with external forces during autonomous manipulation, tele-operation or physical human-robot interaction. This paper presents a whole-body controller that allows for the implementation of a Cartesian impedance control to coordinate tracking performance and desired compliance for the robot base and manipulator arm. The controller is formulated through an optimization problem using Quadratic Programming (QP) to impose a desired behavior for the system while satisfying friction cone constraints, unilateral force constraints, joint and torque limits. The presented strategy decouples the arm and the base of the platform, enforcing the behavior of a linear double-mass spring damper system, and allows to independently tune their inertia, stiffness and damping properties. The control architecture is validated through an extensive simulation study using the 90kg HyQ robot equipped with a 7-DoF manipulator arm. Simulation results show the impedance rendering performance when external forces are applied at the arm's end-effector. The paper presents results for full stance condition (all legs on the ground) and, for the first time, also shows how the impedance rendering is affected by the contact conditions during a dynamic gait.
Passivity-based control for haptic teleoperation of a legged manipulator in presence of time-delays
Aug 17, 2021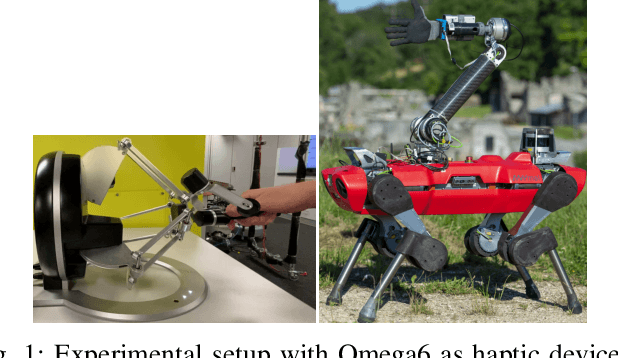
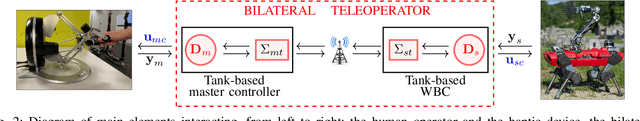
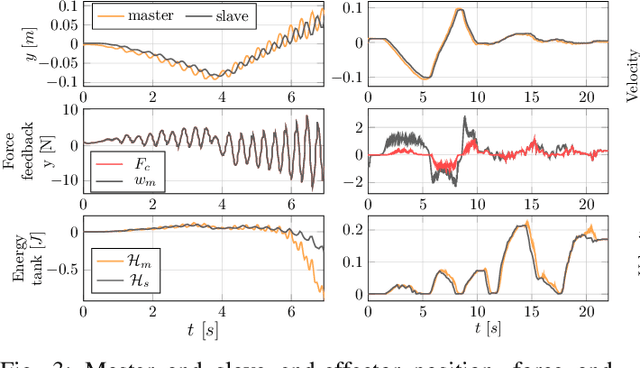
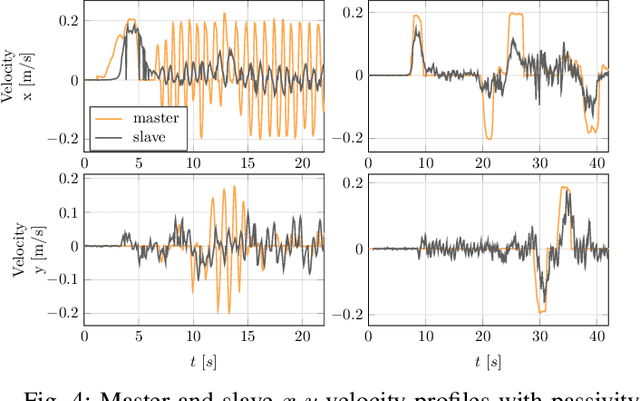
Abstract:When dealing with the haptic teleoperation of multi-limbed mobile manipulators, the problem of mitigating the destabilizing effects arising from the communication link between the haptic device and the remote robot has not been properly addressed. In this work, we propose a passive control architecture to haptically teleoperate a legged mobile manipulator, while remaining stable in the presence of time delays and frequency mismatches in the master and slave controllers. At the master side, a discrete-time energy modulation of the control input is proposed. At the slave side, passivity constraints are included in an optimization-based whole-body controller to satisfy the energy limitations. A hybrid teleoperation scheme allows the human operator to remotely operate the robot's end-effector while in stance mode, and its base velocity in locomotion mode. The resulting control architecture is demonstrated on a quadrupedal robot with an artificial delay added to the network.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge