Mateusz Lango
SRS-Stories: Vocabulary-constrained multilingual story generation for language learning
Dec 20, 2025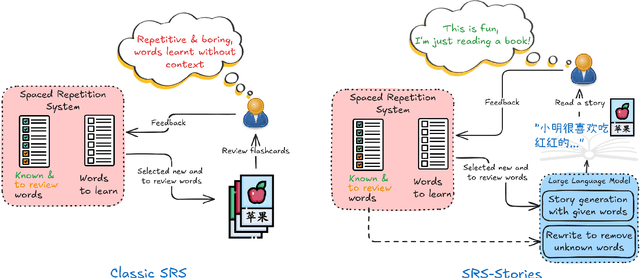
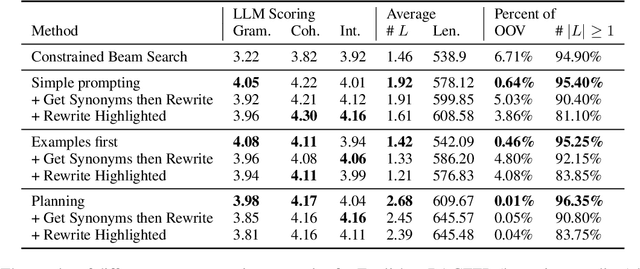
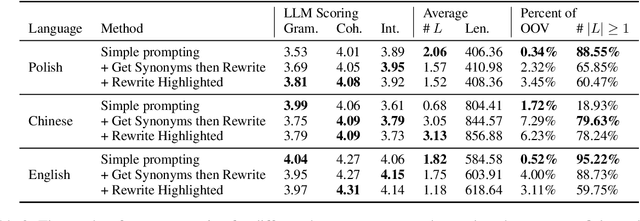
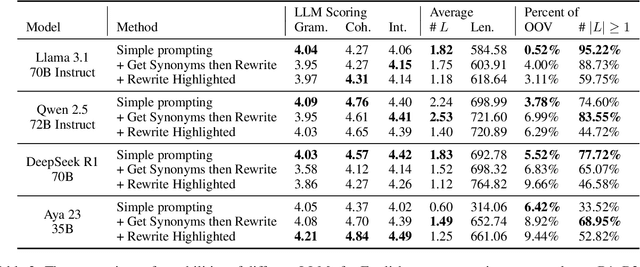
Abstract:In this paper, we use large language models to generate personalized stories for language learners, using only the vocabulary they know. The generated texts are specifically written to teach the user new vocabulary by simply reading stories where it appears in context, while at the same time seamlessly reviewing recently learned vocabulary. The generated stories are enjoyable to read and the vocabulary reviewing/learning is optimized by a Spaced Repetition System. The experiments are conducted in three languages: English, Chinese and Polish, evaluating three story generation methods and three strategies for enforcing lexical constraints. The results show that the generated stories are more grammatical, coherent, and provide better examples of word usage than texts generated by the standard constrained beam search approach
LLM Agents Implement an NLG System from Scratch: Building Interpretable Rule-Based RDF-to-Text Generators
Dec 20, 2025Abstract:We present a novel neurosymbolic framework for RDF-to-text generation, in which the model is "trained" through collaborative interactions among multiple LLM agents rather than traditional backpropagation. The LLM agents produce rule-based Python code for a generator for the given domain, based on RDF triples only, with no in-domain human reference texts. The resulting system is fully interpretable, requires no supervised training data, and generates text nearly instantaneously using only a single CPU. Our experiments on the WebNLG and OpenDialKG data show that outputs produced by our approach reduce hallucination, with only slight fluency penalties compared to finetuned or prompted language models
OpeNLGauge: An Explainable Metric for NLG Evaluation with Open-Weights LLMs
Mar 14, 2025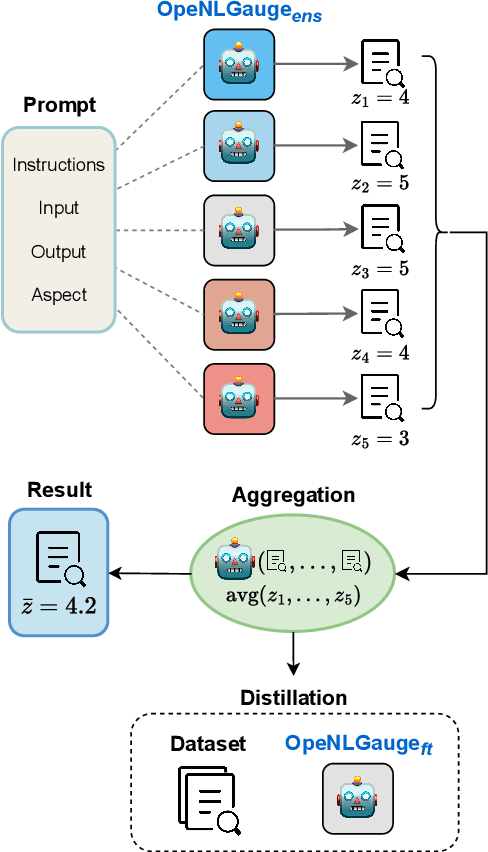
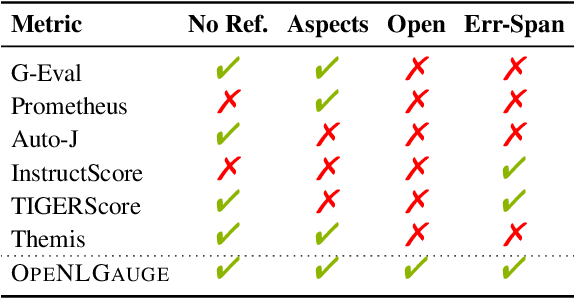

Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated great potential as evaluators of NLG systems, allowing for high-quality, reference-free, and multi-aspect assessments. However, existing LLM-based metrics suffer from two major drawbacks: reliance on proprietary models to generate training data or perform evaluations, and a lack of fine-grained, explanatory feedback. In this paper, we introduce OpeNLGauge, a fully open-source, reference-free NLG evaluation metric that provides accurate explanations based on error spans. OpeNLGauge is available as a two-stage ensemble of larger open-weight LLMs, or as a small fine-tuned evaluation model, with confirmed generalizability to unseen tasks, domains and aspects. Our extensive meta-evaluation shows that OpeNLGauge achieves competitive correlation with human judgments, outperforming state-of-the-art models on certain tasks while maintaining full reproducibility and providing explanations more than twice as accurate.
Leveraging Large Language Models for Building Interpretable Rule-Based Data-to-Text Systems
Feb 28, 2025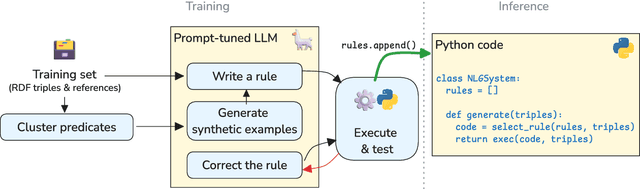
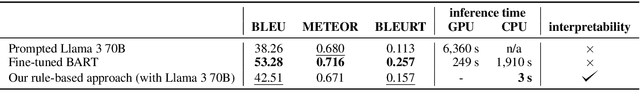
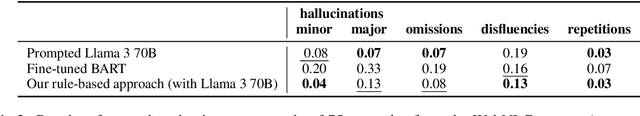
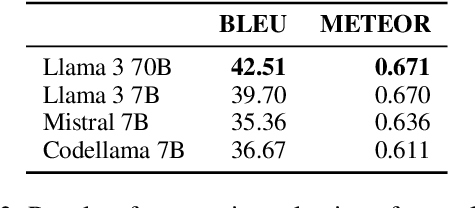
Abstract:We introduce a simple approach that uses a large language model (LLM) to automatically implement a fully interpretable rule-based data-to-text system in pure Python. Experimental evaluation on the WebNLG dataset showed that such a constructed system produces text of better quality (according to the BLEU and BLEURT metrics) than the same LLM prompted to directly produce outputs, and produces fewer hallucinations than a BART language model fine-tuned on the same data. Furthermore, at runtime, the approach generates text in a fraction of the processing time required by neural approaches, using only a single CPU
Polish-ASTE: Aspect-Sentiment Triplet Extraction Datasets for Polish
Feb 27, 2025Abstract:Aspect-Sentiment Triplet Extraction (ASTE) is one of the most challenging and complex tasks in sentiment analysis. It concerns the construction of triplets that contain an aspect, its associated sentiment polarity, and an opinion phrase that serves as a rationale for the assigned polarity. Despite the growing popularity of the task and the many machine learning methods being proposed to address it, the number of datasets for ASTE is very limited. In particular, no dataset is available for any of the Slavic languages. In this paper, we present two new datasets for ASTE containing customer opinions about hotels and purchased products expressed in Polish. We also perform experiments with two ASTE techniques combined with two large language models for Polish to investigate their performance and the difficulty of the assembled datasets. The new datasets are available under a permissive licence and have the same file format as the English datasets, facilitating their use in future research.
Counterfactual Explanations with Probabilistic Guarantees on their Robustness to Model Change
Aug 09, 2024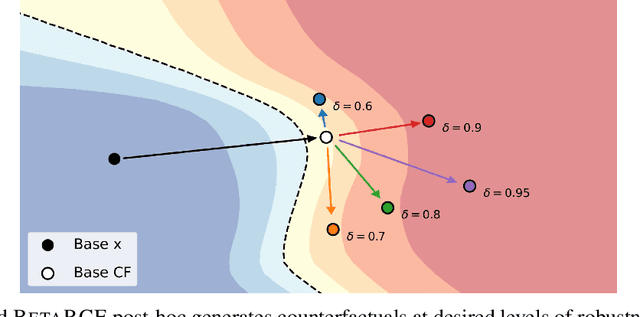
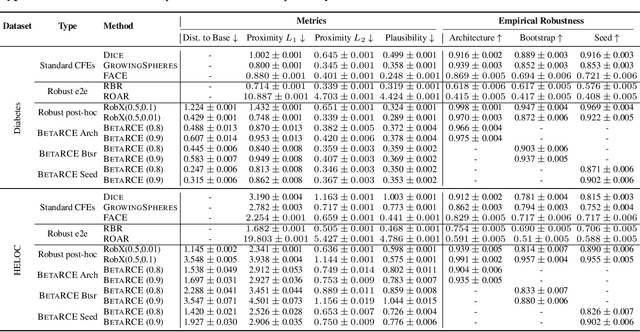
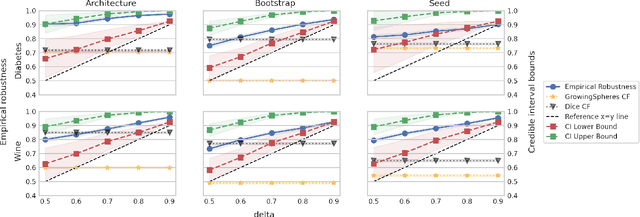
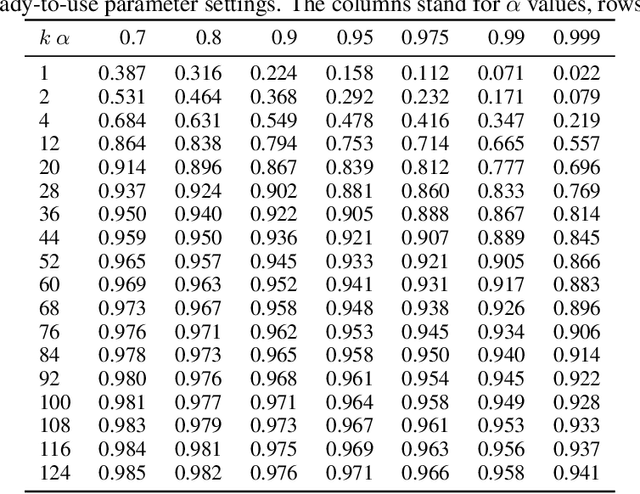
Abstract:Counterfactual explanations (CFEs) guide users on how to adjust inputs to machine learning models to achieve desired outputs. While existing research primarily addresses static scenarios, real-world applications often involve data or model changes, potentially invalidating previously generated CFEs and rendering user-induced input changes ineffective. Current methods addressing this issue often support only specific models or change types, require extensive hyperparameter tuning, or fail to provide probabilistic guarantees on CFE robustness to model changes. This paper proposes a novel approach for generating CFEs that provides probabilistic guarantees for any model and change type, while offering interpretable and easy-to-select hyperparameters. We establish a theoretical framework for probabilistically defining robustness to model change and demonstrate how our BetaRCE method directly stems from it. BetaRCE is a post-hoc method applied alongside a chosen base CFE generation method to enhance the quality of the explanation beyond robustness. It facilitates a transition from the base explanation to a more robust one with user-adjusted probability bounds. Through experimental comparisons with baselines, we show that BetaRCE yields robust, most plausible, and closest to baseline counterfactual explanations.
Faithful and Plausible Natural Language Explanations for Image Classification: A Pipeline Approach
Jul 30, 2024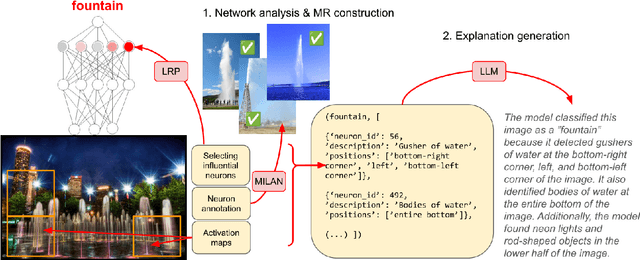
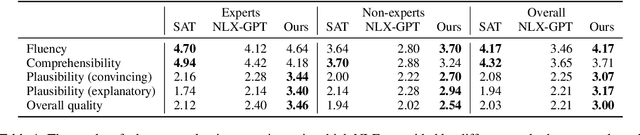
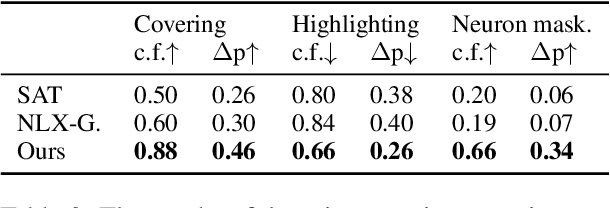
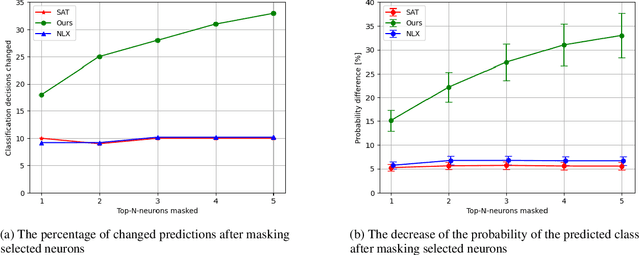
Abstract:Existing explanation methods for image classification struggle to provide faithful and plausible explanations. This paper addresses this issue by proposing a post-hoc natural language explanation method that can be applied to any CNN-based classifier without altering its training process or affecting predictive performance. By analysing influential neurons and the corresponding activation maps, the method generates a faithful description of the classifier's decision process in the form of a structured meaning representation, which is then converted into text by a language model. Through this pipeline approach, the generated explanations are grounded in the neural network architecture, providing accurate insight into the classification process while remaining accessible to non-experts. Experimental results show that the NLEs constructed by our method are significantly more plausible and faithful. In particular, user interventions in the neural network structure (masking of neurons) are three times more effective than the baselines.
A Survey of Text Style Transfer: Applications and Ethical Implications
Jul 23, 2024Abstract:Text style transfer (TST) is an important task in controllable text generation, which aims to control selected attributes of language use, such as politeness, formality, or sentiment, without altering the style-independent content of the text. The field has received considerable research attention in recent years and has already been covered in several reviews, but the focus has mostly been on the development of new algorithms and learning from different types of data (supervised, unsupervised, out-of-domain, etc.) and not so much on the application side. However, TST-related technologies are gradually reaching a production- and deployment-ready level, and therefore, the inclusion of the application perspective in TST research becomes crucial. Similarly, the often overlooked ethical considerations of TST technology have become a pressing issue. This paper presents a comprehensive review of TST applications that have been researched over the years, using both traditional linguistic approaches and more recent deep learning methods. We discuss current challenges, future research directions, and ethical implications of TST applications in text generation. By providing a holistic overview of the landscape of TST applications, we hope to stimulate further research and contribute to a better understanding of the potential as well as ethical considerations associated with TST.
Generating clickbait spoilers with an ensemble of large language models
May 25, 2024
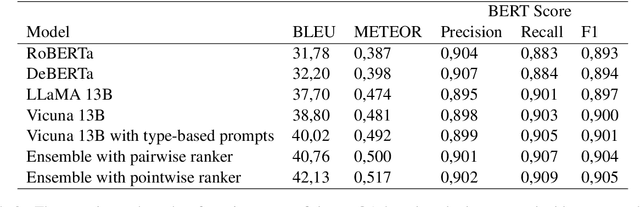
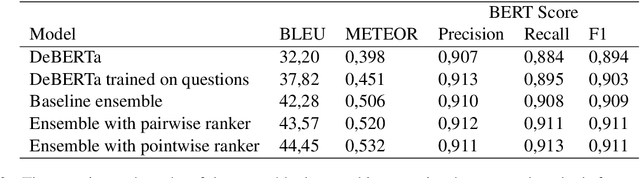
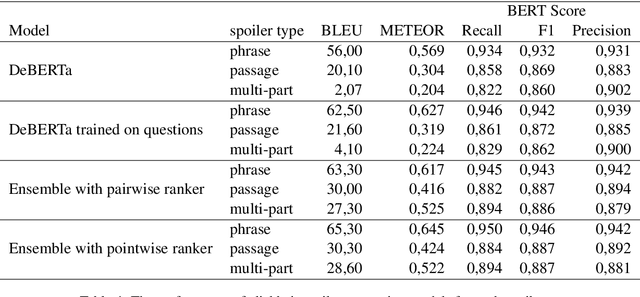
Abstract:Clickbait posts are a widespread problem in the webspace. The generation of spoilers, i.e. short texts that neutralize clickbait by providing information that satisfies the curiosity induced by it, is one of the proposed solutions to the problem. Current state-of-the-art methods are based on passage retrieval or question answering approaches and are limited to generating spoilers only in the form of a phrase or a passage. In this work, we propose an ensemble of fine-tuned large language models for clickbait spoiler generation. Our approach is not limited to phrase or passage spoilers, but is also able to generate multipart spoilers that refer to several non-consecutive parts of text. Experimental evaluation demonstrates that the proposed ensemble model outperforms the baselines in terms of BLEU, METEOR and BERTScore metrics.
Multi-criteria approach for selecting an explanation from the set of counterfactuals produced by an ensemble of explainers
Mar 20, 2024Abstract:Counterfactuals are widely used to explain ML model predictions by providing alternative scenarios for obtaining the more desired predictions. They can be generated by a variety of methods that optimize different, sometimes conflicting, quality measures and produce quite different solutions. However, choosing the most appropriate explanation method and one of the generated counterfactuals is not an easy task. Instead of forcing the user to test many different explanation methods and analysing conflicting solutions, in this paper, we propose to use a multi-stage ensemble approach that will select single counterfactual based on the multiple-criteria analysis. It offers a compromise solution that scores well on several popular quality measures. This approach exploits the dominance relation and the ideal point decision aid method, which selects one counterfactual from the Pareto front. The conducted experiments demonstrated that the proposed approach generates fully actionable counterfactuals with attractive compromise values of the considered quality measures.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge