Massimo Stella
Cognitive networks reconstruct mindsets about STEM subjects and educational contexts in almost 1000 high-schoolers, University students and LLM-based digital twins
Feb 16, 2026Abstract:Attitudes toward STEM develop from the interaction of conceptual knowledge, educational experiences, and affect. Here we use cognitive network science to reconstruct group mindsets as behavioural forma mentis networks (BFMNs). In this case, nodes are cue words and free associations, edges are empirical associative links, and each concept is annotated with perceived valence. We analyse BFMNs from N = 994 observations spanning high school students, university students, and early-career STEM experts, alongside LLM (GPT-oss) "digital twins" prompted to emulate comparable profiles. Focusing also on semantic neighbourhoods ("frames") around key target concepts (e.g., STEM subjects or educational actors/places), we quantify frames in terms of valence auras, emotional profiles, network overlap (Jaccard similarity), and concreteness relative to null baselines. Across student groups, science and research are consistently framed positively, while their core quantitative subjects (mathematics and statistics) exhibit more negative and anxiety related auras, amplified in higher math-anxiety subgroups, evidencing a STEM-science cognitive and emotional dissonance. High-anxiety frames are also less concrete than chance, suggesting more abstract and decontextualised representations of threatening quantitative domains. Human networks show greater overlapping between mathematics and anxiety than GPT-oss. The results highlight how BFMNs capture cognitive-affective signatures of mindsets towards the target domains and indicate that LLM-based digital twins approximate cultural attitudes but miss key context-sensitive, experience-based components relevant to replicate human educational anxiety.
How to predict creativity ratings from written narratives: A comparison of co-occurrence and textual forma mentis networks
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:This tutorial paper provides a step-by-step workflow for building and analysing semantic networks from short creative texts. We introduce and compare two widely used text-to-network approaches: word co-occurrence networks and textual forma mentis networks (TFMNs). We also demonstrate how they can be used in machine learning to predict human creativity ratings. Using a corpus of 1029 short stories, we guide readers through text preprocessing, network construction, feature extraction (structural measures, spreading-activation indices, and emotion scores), and application of regression models. We evaluate how network-construction choices influence both network topology and predictive performance. Across all modelling settings, TFMNs consistently outperformed co-occurrence networks through lower prediction errors (best MAE = 0.581 for TFMN, vs 0.592 for co-occurrence with window size 3). Network-structural features dominated predictive performance (MAE = 0.591 for TFMN), whereas emotion features performed worse (MAE = 0.711 for TFMN) and spreading-activation measures contributed little (MAE = 0.788 for TFMN). This paper offers practical guidance for researchers interested in applying network-based methods for cognitive fields like creativity research. we show when syntactic networks are preferable to surface co-occurrence models, and provide an open, reproducible workflow accessible to newcomers in the field, while also offering deeper methodological insight for experienced researchers.
Measuring and identifying factors of individuals' trust in Large Language Models
Feb 28, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) can engage in human-looking conversational exchanges. Although conversations can elicit trust between users and LLMs, scarce empirical research has examined trust formation in human-LLM contexts, beyond LLMs' trustworthiness or human trust in AI in general. Here, we introduce the Trust-In-LLMs Index (TILLMI) as a new framework to measure individuals' trust in LLMs, extending McAllister's cognitive and affective trust dimensions to LLM-human interactions. We developed TILLMI as a psychometric scale, prototyped with a novel protocol we called LLM-simulated validity. The LLM-based scale was then validated in a sample of 1,000 US respondents. Exploratory Factor Analysis identified a two-factor structure. Two items were then removed due to redundancy, yielding a final 6-item scale with a 2-factor structure. Confirmatory Factor Analysis on a separate subsample showed strong model fit ($CFI = .995$, $TLI = .991$, $RMSEA = .046$, $p_{X^2} > .05$). Convergent validity analysis revealed that trust in LLMs correlated positively with openness to experience, extraversion, and cognitive flexibility, but negatively with neuroticism. Based on these findings, we interpreted TILLMI's factors as "closeness with LLMs" (affective dimension) and "reliance on LLMs" (cognitive dimension). Younger males exhibited higher closeness with- and reliance on LLMs compared to older women. Individuals with no direct experience with LLMs exhibited lower levels of trust compared to LLMs' users. These findings offer a novel empirical foundation for measuring trust in AI-driven verbal communication, informing responsible design, and fostering balanced human-AI collaboration.
Cognitive networks highlight differences and similarities in the STEM mindsets of human and LLM-simulated trainees, experts and academics
Feb 26, 2025Abstract:Understanding attitudes towards STEM means quantifying the cognitive and emotional ways in which individuals, and potentially large language models too, conceptualise such subjects. This study uses behavioural forma mentis networks (BFMNs) to investigate the STEM-focused mindset, i.e. ways of associating and perceiving ideas, of 177 human participants and 177 artificial humans simulated by GPT-3.5. Participants were split in 3 groups - trainees, experts and academics - to compare the influence of expertise level on their mindset. The results revealed that human forma mentis networks exhibited significantly higher clustering coefficients compared to GPT-3.5, indicating that human mindsets displayed a tendency to form and close triads of conceptual associations while recollecting STEM ideas. Human experts, in particular, demonstrated robust clustering coefficients, reflecting better integration of STEM concepts into their cognitive networks. In contrast, GPT-3.5 produced sparser mindsets. Furthermore, both human and GPT mindsets framed mathematics in neutral or positive terms, differently from STEM high schoolers, researchers and other large language models sampled in other works. This research contributes to understanding how mindset structure can provide cognitive insights about memory structure and machine limitations.
The "LLM World of Words" English free association norms generated by large language models
Dec 02, 2024Abstract:Free associations have been extensively used in cognitive psychology and linguistics for studying how conceptual knowledge is organized. Recently, the potential of applying a similar approach for investigating the knowledge encoded in LLMs has emerged, specifically as a method for investigating LLM biases. However, the absence of large-scale LLM-generated free association norms that are comparable with human-generated norms is an obstacle to this new research direction. To address this limitation, we create a new dataset of LLM-generated free association norms modeled after the "Small World of Words" (SWOW) human-generated norms consisting of approximately 12,000 cue words. We prompt three LLMs, namely Mistral, Llama3, and Haiku, with the same cues as those in the SWOW norms to generate three novel comparable datasets, the "LLM World of Words" (LWOW). Using both SWOW and LWOW norms, we construct cognitive network models of semantic memory that represent the conceptual knowledge possessed by humans and LLMs. We demonstrate how these datasets can be used for investigating implicit biases in humans and LLMs, such as the harmful gender stereotypes that are prevalent both in society and LLM outputs.
Forma mentis networks predict creativity ratings of short texts via interpretable artificial intelligence in human and GPT-simulated raters
Nov 30, 2024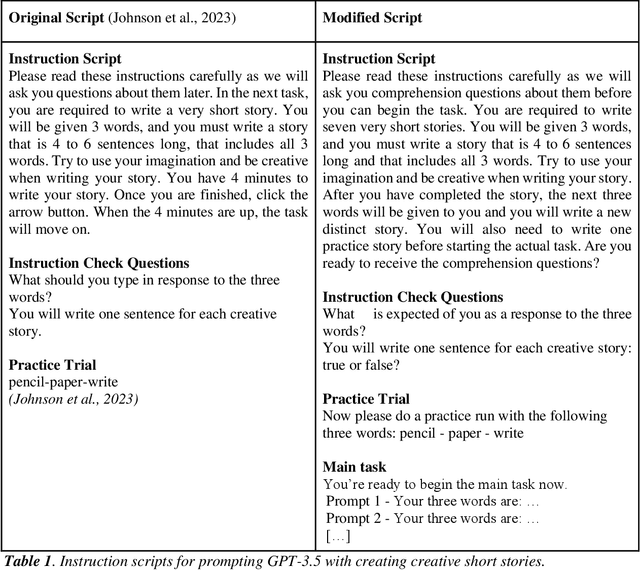
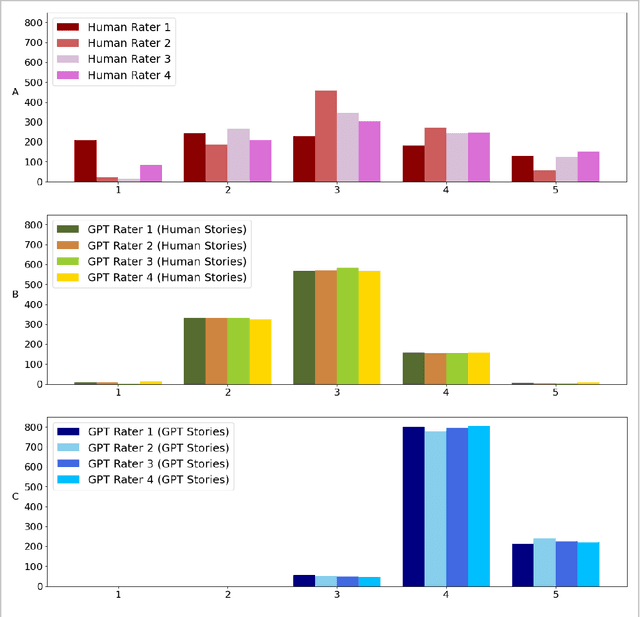
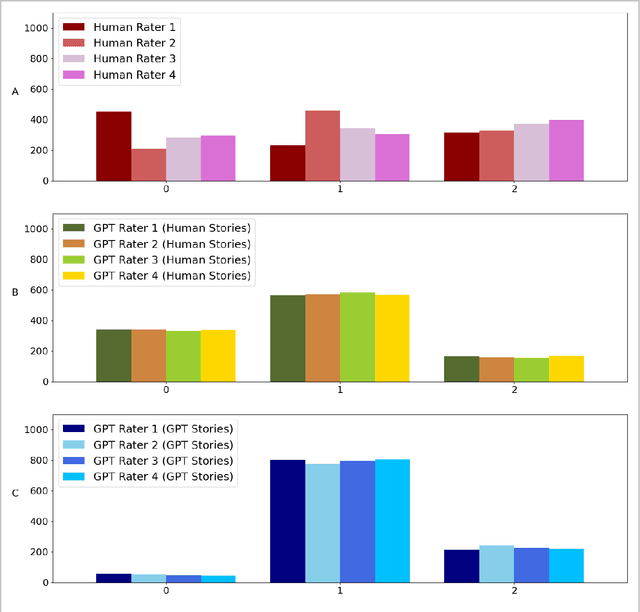
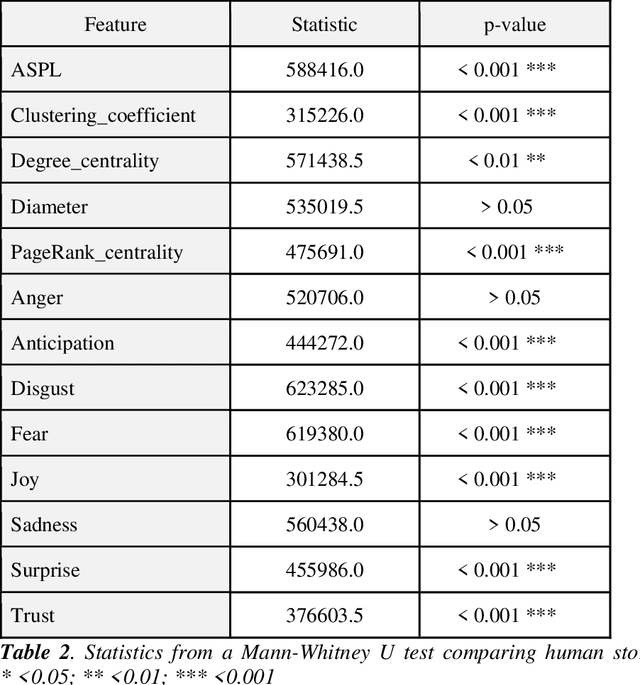
Abstract:Creativity is a fundamental skill of human cognition. We use textual forma mentis networks (TFMN) to extract network (semantic/syntactic associations) and emotional features from approximately one thousand human- and GPT3.5-generated stories. Using Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI), we test whether features relative to Mednick's associative theory of creativity can explain creativity ratings assigned by humans and GPT-3.5. Using XGBoost, we examine three scenarios: (i) human ratings of human stories, (ii) GPT-3.5 ratings of human stories, and (iii) GPT-3.5 ratings of GPT-generated stories. Our findings reveal that GPT-3.5 ratings differ significantly from human ratings not only in terms of correlations but also because of feature patterns identified with XAI methods. GPT-3.5 favours 'its own' stories and rates human stories differently from humans. Feature importance analysis with SHAP scores shows that: (i) network features are more predictive for human creativity ratings but also for GPT-3.5's ratings of human stories; (ii) emotional features played a greater role than semantic/syntactic network structure in GPT-3.5 rating its own stories. These quantitative results underscore key limitations in GPT-3.5's ability to align with human assessments of creativity. We emphasise the need for caution when using GPT-3.5 to assess and generate creative content, as it does not yet capture the nuanced complexity that characterises human creativity.
Y Social: an LLM-powered Social Media Digital Twin
Aug 01, 2024



Abstract:In this paper we introduce Y, a new-generation digital twin designed to replicate an online social media platform. Digital twins are virtual replicas of physical systems that allow for advanced analyses and experimentation. In the case of social media, a digital twin such as Y provides a powerful tool for researchers to simulate and understand complex online interactions. {\tt Y} leverages state-of-the-art Large Language Models (LLMs) to replicate sophisticated agent behaviors, enabling accurate simulations of user interactions, content dissemination, and network dynamics. By integrating these aspects, Y offers valuable insights into user engagement, information spread, and the impact of platform policies. Moreover, the integration of LLMs allows Y to generate nuanced textual content and predict user responses, facilitating the study of emergent phenomena in online environments. To better characterize the proposed digital twin, in this paper we describe the rationale behind its implementation, provide examples of the analyses that can be performed on the data it enables to be generated, and discuss its relevance for multidisciplinary research.
Towards hypergraph cognitive networks as feature-rich models of knowledge
Apr 13, 2023Abstract:Semantic networks provide a useful tool to understand how related concepts are retrieved from memory. However, most current network approaches use pairwise links to represent memory recall patterns. Pairwise connections neglect higher-order associations, i.e. relationships between more than two concepts at a time. These higher-order interactions might covariate with (and thus contain information about) how similar concepts are along psycholinguistic dimensions like arousal, valence, familiarity, gender and others. We overcome these limits by introducing feature-rich cognitive hypergraphs as quantitative models of human memory where: (i) concepts recalled together can all engage in hyperlinks involving also more than two concepts at once (cognitive hypergraph aspect), and (ii) each concept is endowed with a vector of psycholinguistic features (feature-rich aspect). We build hypergraphs from word association data and use evaluation methods from machine learning features to predict concept concreteness. Since concepts with similar concreteness tend to cluster together in human memory, we expect to be able to leverage this structure. Using word association data from the Small World of Words dataset, we compared a pairwise network and a hypergraph with N=3586 concepts/nodes. Interpretable artificial intelligence models trained on (1) psycholinguistic features only, (2) pairwise-based feature aggregations, and on (3) hypergraph-based aggregations show significant differences between pairwise and hypergraph links. Specifically, our results show that higher-order and feature-rich hypergraph models contain richer information than pairwise networks leading to improved prediction of word concreteness. The relation with previous studies about conceptual clustering and compartmentalisation in associative knowledge and human memory are discussed.
Cognitive modelling with multilayer networks: Insights, advancements and future challenges
Oct 02, 2022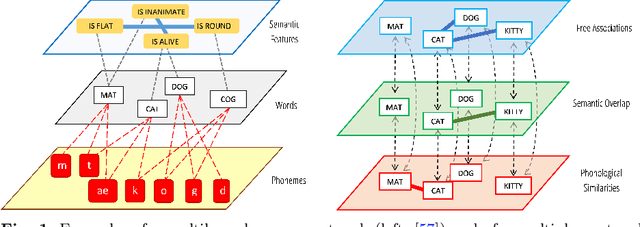
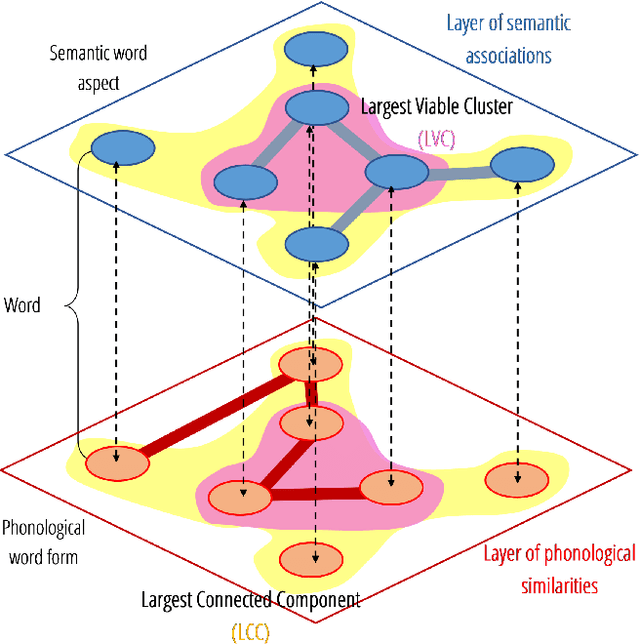
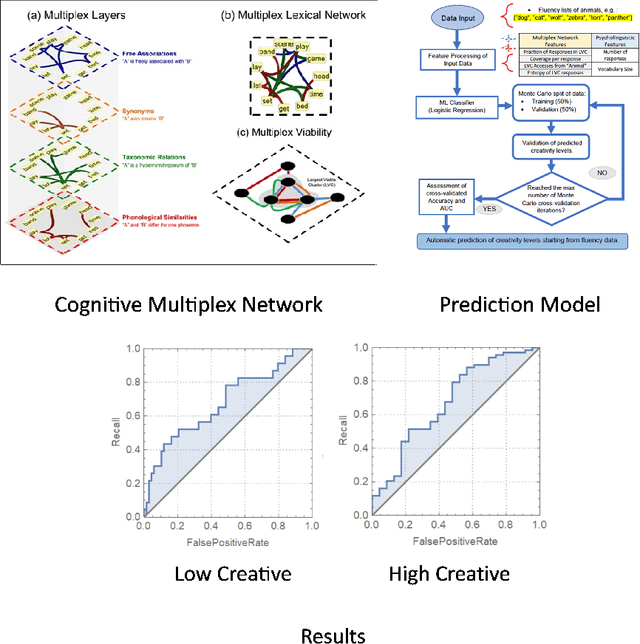
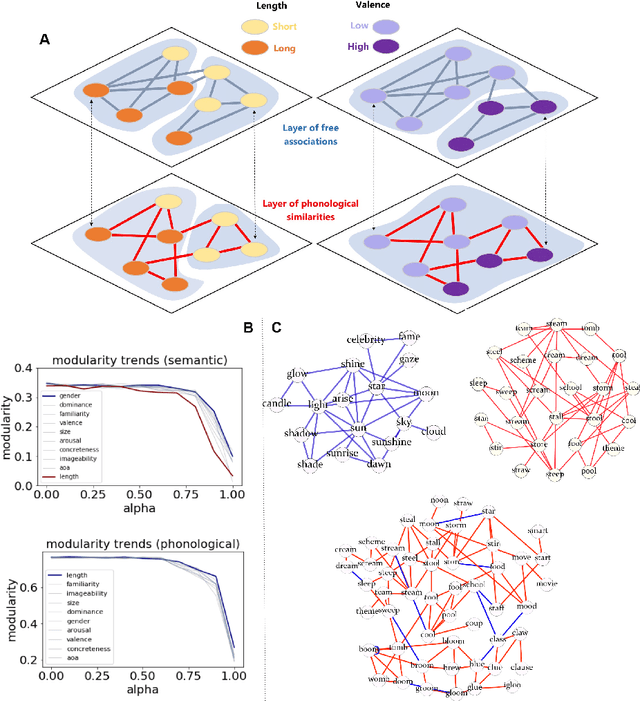
Abstract:The mental lexicon is a complex cognitive system representing information about the words/concepts that one knows. Decades of psychological experiments have shown that conceptual associations across multiple, interactive cognitive levels can greatly influence word acquisition, storage, and processing. How can semantic, phonological, syntactic, and other types of conceptual associations be mapped within a coherent mathematical framework to study how the mental lexicon works? We here review cognitive multilayer networks as a promising quantitative and interpretative framework for investigating the mental lexicon. Cognitive multilayer networks can map multiple types of information at once, thus capturing how different layers of associations might co-exist within the mental lexicon and influence cognitive processing. This review starts with a gentle introduction to the structure and formalism of multilayer networks. We then discuss quantitative mechanisms of psychological phenomena that could not be observed in single-layer networks and were only unveiled by combining multiple layers of the lexicon: (i) multiplex viability highlights language kernels and facilitative effects of knowledge processing in healthy and clinical populations; (ii) multilayer community detection enables contextual meaning reconstruction depending on psycholinguistic features; (iii) layer analysis can mediate latent interactions of mediation, suppression and facilitation for lexical access. By outlining novel quantitative perspectives where multilayer networks can shed light on cognitive knowledge representations, also in next-generation brain/mind models, we discuss key limitations and promising directions for cutting-edge future research.
Writing about COVID-19 vaccines: Emotional profiling unravels how mainstream and alternative press framed AstraZeneca, Pfizer and vaccination campaigns
Jan 19, 2022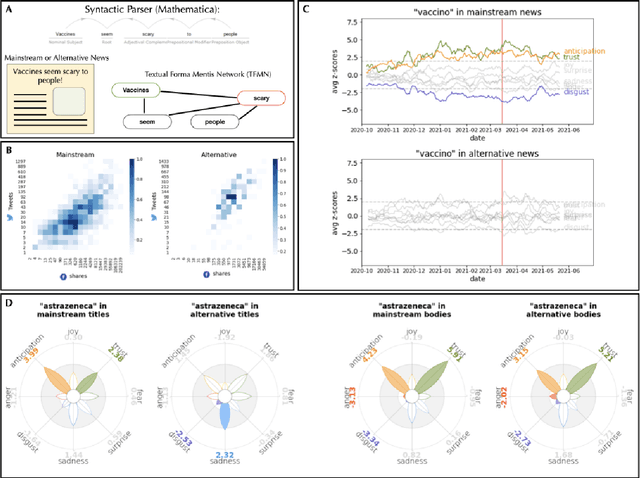
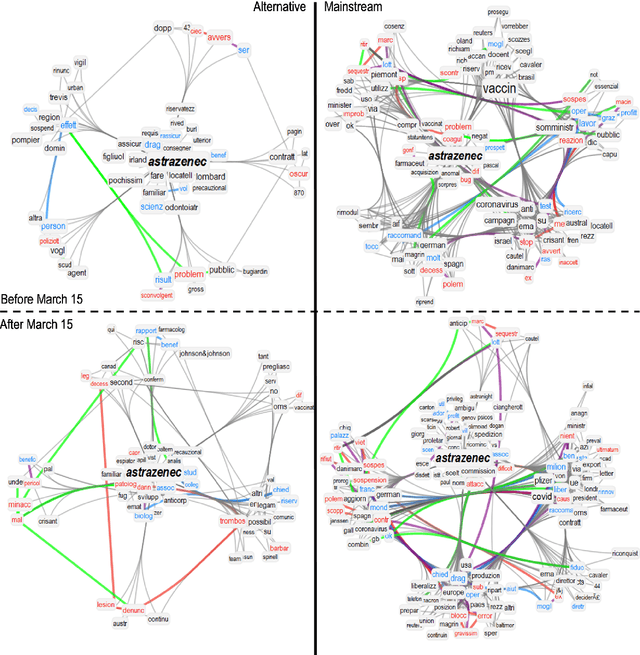
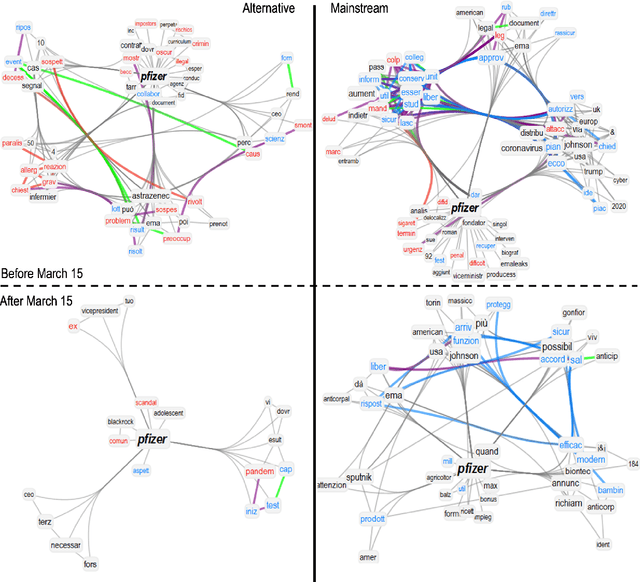
Abstract:Since their announcement in November 2020, COVID-19 vaccines were largely debated by the press and social media. With most studies focusing on COVID-19 disinformation in social media, little attention has been paid to how mainstream news outlets framed COVID-19 narratives compared to alternative sources. To fill this gap, we use cognitive network science and natural language processing to reconstruct time-evolving semantic and emotional frames of 5745 Italian news, that were massively re-shared on Facebook and Twitter, about COVID-19 vaccines. We found consistently high levels of trust/anticipation and less disgust in the way mainstream sources framed the general idea of "vaccine/vaccino". These emotions were crucially missing in the ways alternative sources framed COVID-19 vaccines. More differences were found within specific instances of vaccines. Alternative news included titles framing the AstraZeneca vaccine with strong levels of sadness, absent in mainstream titles. Mainstream news initially framed "Pfizer" along more negative associations with side effects than "AstraZeneca". With the temporary suspension of the latter, on March 15th 2021, we identified a semantic/emotional shift: Even mainstream article titles framed "AstraZeneca" as semantically richer in negative associations with side effects, while "Pfizer" underwent a positive shift in valence, mostly related to its higher efficacy. "Thrombosis" entered the frame of vaccines together with fearful conceptual associations, while "death" underwent an emotional shift, steering towards fear in alternative titles and losing its hopeful connotation in mainstream titles. Our findings expose crucial aspects of the emotional narratives around COVID-19 vaccines adopted by the press, highlighting the need to understand how alternative and mainstream media report vaccination news.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge