Yoed N. Kenett
Cognitive networks highlight differences and similarities in the STEM mindsets of human and LLM-simulated trainees, experts and academics
Feb 26, 2025Abstract:Understanding attitudes towards STEM means quantifying the cognitive and emotional ways in which individuals, and potentially large language models too, conceptualise such subjects. This study uses behavioural forma mentis networks (BFMNs) to investigate the STEM-focused mindset, i.e. ways of associating and perceiving ideas, of 177 human participants and 177 artificial humans simulated by GPT-3.5. Participants were split in 3 groups - trainees, experts and academics - to compare the influence of expertise level on their mindset. The results revealed that human forma mentis networks exhibited significantly higher clustering coefficients compared to GPT-3.5, indicating that human mindsets displayed a tendency to form and close triads of conceptual associations while recollecting STEM ideas. Human experts, in particular, demonstrated robust clustering coefficients, reflecting better integration of STEM concepts into their cognitive networks. In contrast, GPT-3.5 produced sparser mindsets. Furthermore, both human and GPT mindsets framed mathematics in neutral or positive terms, differently from STEM high schoolers, researchers and other large language models sampled in other works. This research contributes to understanding how mindset structure can provide cognitive insights about memory structure and machine limitations.
Originality in scientific titles and abstracts can predict citation count
Feb 03, 2025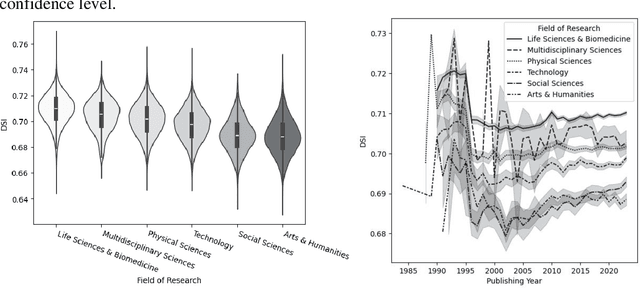
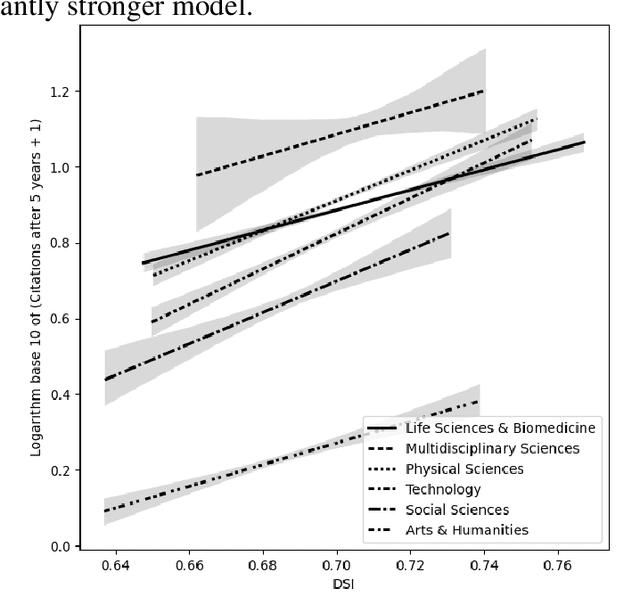
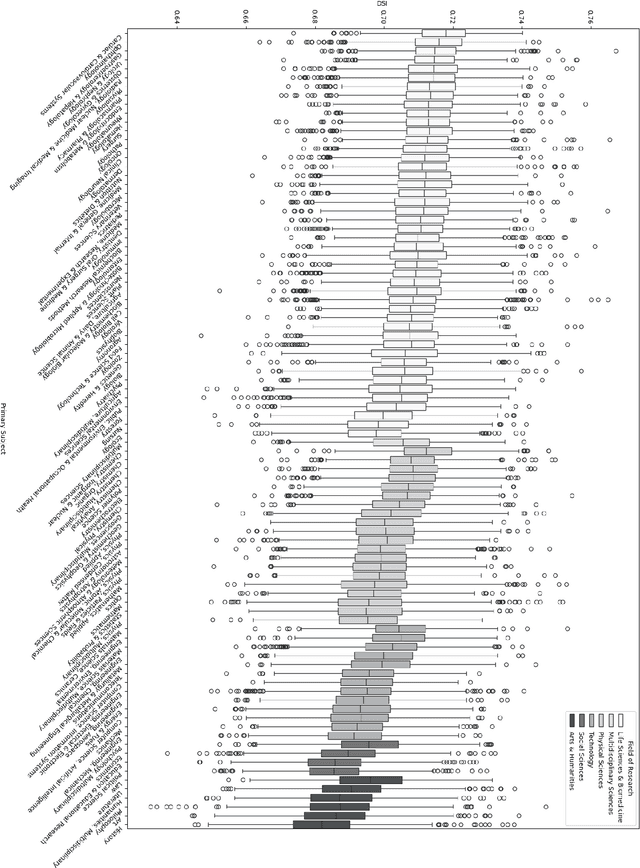
Abstract:In this research-in-progress paper, we apply a computational measure correlating with originality from creativity science: Divergent Semantic Integration (DSI), to a selection of 99,557 scientific abstracts and titles selected from the Web of Science. We observe statistically significant differences in DSI between subject and field of research, and a slight rise in DSI over time. We model the base 10 logarithm of the citation count after 5 years with DSI and find a statistically significant positive correlation in all fields of research with an adjusted $R^2$ of 0.13.
Applying Text Mining to Analyze Human Question Asking in Creativity Research
Jan 03, 2025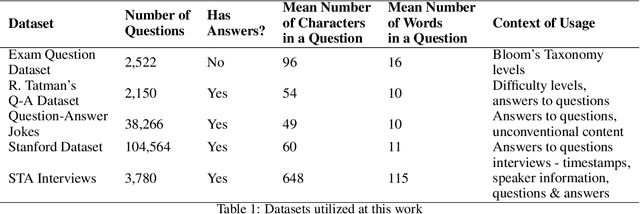



Abstract:Creativity relates to the ability to generate novel and effective ideas in the areas of interest. How are such creative ideas generated? One possible mechanism that supports creative ideation and is gaining increased empirical attention is by asking questions. Question asking is a likely cognitive mechanism that allows defining problems, facilitating creative problem solving. However, much is unknown about the exact role of questions in creativity. This work presents an attempt to apply text mining methods to measure the cognitive potential of questions, taking into account, among others, (a) question type, (b) question complexity, and (c) the content of the answer. This contribution summarizes the history of question mining as a part of creativity research, along with the natural language processing methods deemed useful or helpful in the study. In addition, a novel approach is proposed, implemented, and applied to five datasets. The experimental results obtained are comprehensively analyzed, suggesting that natural language processing has a role to play in creative research.
Cognitive modelling with multilayer networks: Insights, advancements and future challenges
Oct 02, 2022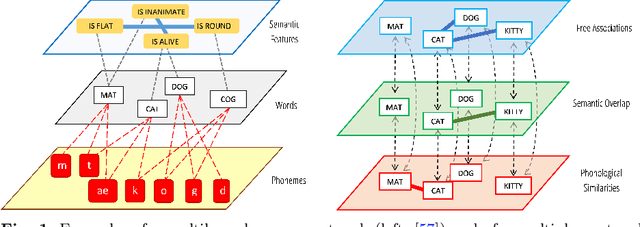
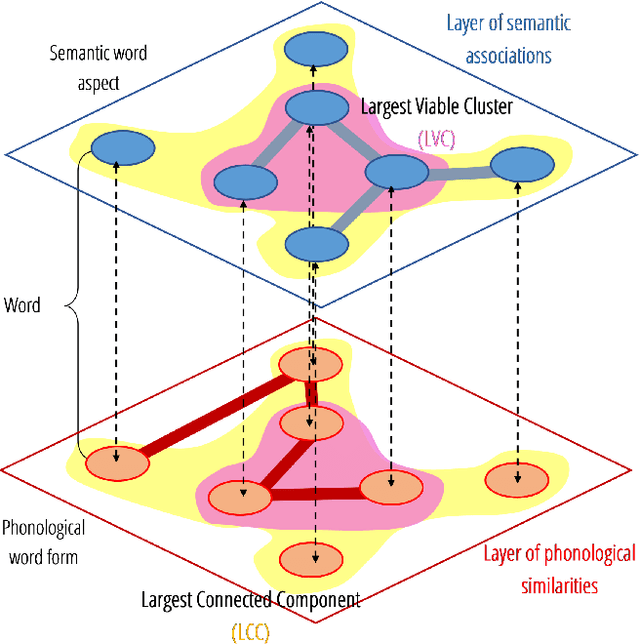
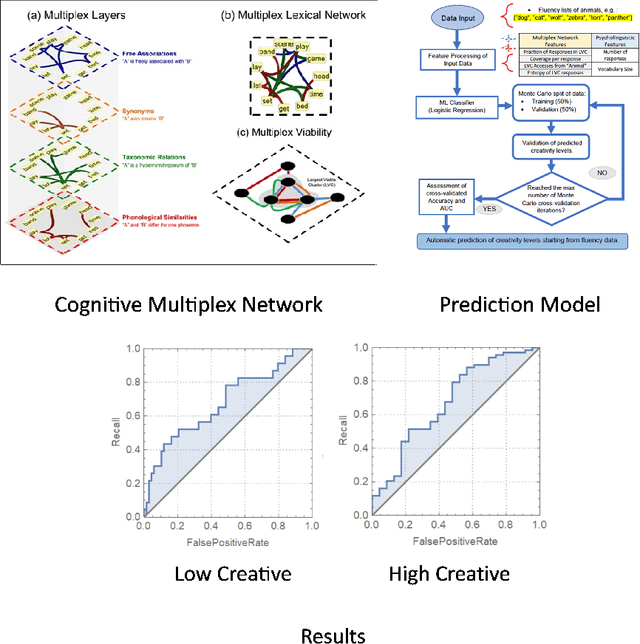
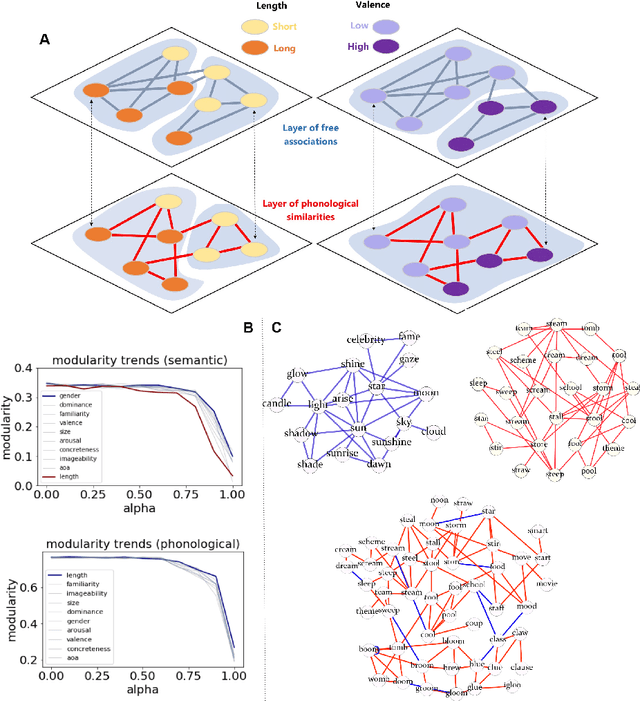
Abstract:The mental lexicon is a complex cognitive system representing information about the words/concepts that one knows. Decades of psychological experiments have shown that conceptual associations across multiple, interactive cognitive levels can greatly influence word acquisition, storage, and processing. How can semantic, phonological, syntactic, and other types of conceptual associations be mapped within a coherent mathematical framework to study how the mental lexicon works? We here review cognitive multilayer networks as a promising quantitative and interpretative framework for investigating the mental lexicon. Cognitive multilayer networks can map multiple types of information at once, thus capturing how different layers of associations might co-exist within the mental lexicon and influence cognitive processing. This review starts with a gentle introduction to the structure and formalism of multilayer networks. We then discuss quantitative mechanisms of psychological phenomena that could not be observed in single-layer networks and were only unveiled by combining multiple layers of the lexicon: (i) multiplex viability highlights language kernels and facilitative effects of knowledge processing in healthy and clinical populations; (ii) multilayer community detection enables contextual meaning reconstruction depending on psycholinguistic features; (iii) layer analysis can mediate latent interactions of mediation, suppression and facilitation for lexical access. By outlining novel quantitative perspectives where multilayer networks can shed light on cognitive knowledge representations, also in next-generation brain/mind models, we discuss key limitations and promising directions for cutting-edge future research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge