Martin Thoma
Comparative evaluation of instrument segmentation and tracking methods in minimally invasive surgery
May 07, 2018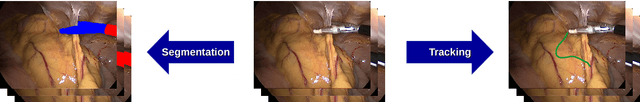
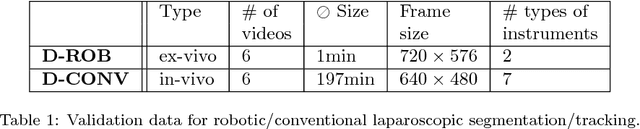
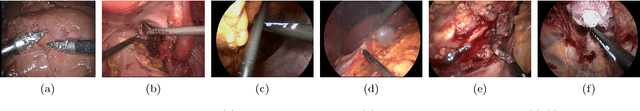
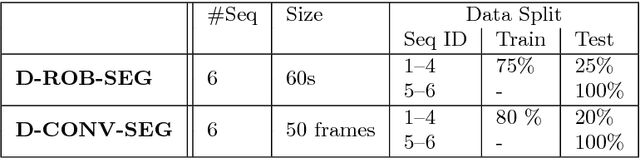
Abstract:Intraoperative segmentation and tracking of minimally invasive instruments is a prerequisite for computer- and robotic-assisted surgery. Since additional hardware like tracking systems or the robot encoders are cumbersome and lack accuracy, surgical vision is evolving as promising techniques to segment and track the instruments using only the endoscopic images. However, what is missing so far are common image data sets for consistent evaluation and benchmarking of algorithms against each other. The paper presents a comparative validation study of different vision-based methods for instrument segmentation and tracking in the context of robotic as well as conventional laparoscopic surgery. The contribution of the paper is twofold: we introduce a comprehensive validation data set that was provided to the study participants and present the results of the comparative validation study. Based on the results of the validation study, we arrive at the conclusion that modern deep learning approaches outperform other methods in instrument segmentation tasks, but the results are still not perfect. Furthermore, we show that merging results from different methods actually significantly increases accuracy in comparison to the best stand-alone method. On the other hand, the results of the instrument tracking task show that this is still an open challenge, especially during challenging scenarios in conventional laparoscopic surgery.
The WiLI benchmark dataset for written language identification
Jan 23, 2018



Abstract:This paper describes the WiLI-2018 benchmark dataset for monolingual written natural language identification. WiLI-2018 is a publicly available, free of charge dataset of short text extracts from Wikipedia. It contains 1000 paragraphs of 235 languages, totaling in 23500 paragraphs. WiLI is a classification dataset: Given an unknown paragraph written in one dominant language, it has to be decided which language it is.
Analysis and Optimization of Convolutional Neural Network Architectures
Jul 31, 2017



Abstract:Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) dominate various computer vision tasks since Alex Krizhevsky showed that they can be trained effectively and reduced the top-5 error from 26.2 % to 15.3 % on the ImageNet large scale visual recognition challenge. Many aspects of CNNs are examined in various publications, but literature about the analysis and construction of neural network architectures is rare. This work is one step to close this gap. A comprehensive overview over existing techniques for CNN analysis and topology construction is provided. A novel way to visualize classification errors with confusion matrices was developed. Based on this method, hierarchical classifiers are described and evaluated. Additionally, some results are confirmed and quantified for CIFAR-100. For example, the positive impact of smaller batch sizes, averaging ensembles, data augmentation and test-time transformations on the accuracy. Other results, such as the positive impact of learned color transformation on the test accuracy could not be confirmed. A model which has only one million learned parameters for an input size of 32x32x3 and 100 classes and which beats the state of the art on the benchmark dataset Asirra, GTSRB, HASYv2 and STL-10 was developed.
The HASYv2 dataset
Jan 29, 2017



Abstract:This paper describes the HASYv2 dataset. HASY is a publicly available, free of charge dataset of single symbols similar to MNIST. It contains 168233 instances of 369 classes. HASY contains two challenges: A classification challenge with 10 pre-defined folds for 10-fold cross-validation and a verification challenge.
A Survey of Semantic Segmentation
May 11, 2016



Abstract:This survey gives an overview over different techniques used for pixel-level semantic segmentation. Metrics and datasets for the evaluation of segmentation algorithms and traditional approaches for segmentation such as unsupervised methods, Decision Forests and SVMs are described and pointers to the relevant papers are given. Recently published approaches with convolutional neural networks are mentioned and typical problematic situations for segmentation algorithms are examined. A taxonomy of segmentation algorithms is given.
Creativity in Machine Learning
Jan 12, 2016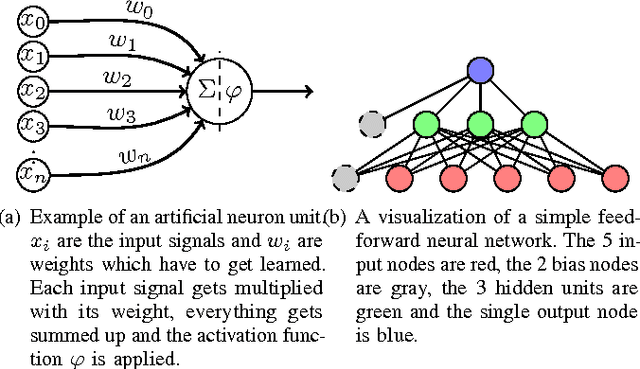



Abstract:Recent machine learning techniques can be modified to produce creative results. Those results did not exist before; it is not a trivial combination of the data which was fed into the machine learning system. The obtained results come in multiple forms: As images, as text and as audio. This paper gives a high level overview of how they are created and gives some examples. It is meant to be a summary of the current work and give people who are new to machine learning some starting points.
On-line Recognition of Handwritten Mathematical Symbols
Nov 29, 2015



Abstract:Finding the name of an unknown symbol is often hard, but writing the symbol is easy. This bachelor's thesis presents multiple systems that use the pen trajectory to classify handwritten symbols. Five preprocessing steps, one data augmentation algorithm, five features and five variants for multilayer Perceptron training were evaluated using 166898 recordings which were collected with two crowdsourcing projects. The evaluation results of these 21 experiments were used to create an optimized recognizer which has a TOP1 error of less than 17.5% and a TOP3 error of 4.0%. This is an improvement of 18.5% for the TOP1 error and 29.7% for the TOP3 error.
Über die Klassifizierung von Knoten in dynamischen Netzwerken mit Inhalt
Nov 23, 2015Abstract:This paper explains the DYCOS-Algorithm as it was introduced in by Aggarwal and Li in 2011. It operates on graphs whichs nodes are partially labeled and automatically adds missing labels to nodes. To do so, the DYCOS algorithm makes use of the structure of the graph as well as content which is assigned to the node. Aggarwal and Li measured in an experimental analysis that DYCOS adds the missing labels to a Graph with 19396 nodes of which 14814 are labeled and another Graph with 806635 nodes of which 18999 are labeld on one core of an Intel Xeon 2.5 GHz CPU with 32 G RAM within less than a minute. Additionally, extensions of the DYCOS algorithm are proposed. ----- In dieser Arbeit wird der DYCOS-Algorithmus, wie er 2011 von Aggarwal und Li vorgestellt wurde, erkl\"art. Er arbeitet auf Graphen, deren Knoten teilweise mit Beschriftungen versehen sind und erg\"anzt automatisch Beschriftungen f\"ur Knoten, die bisher noch keine Beschriftung haben. Dieser Vorgang wird "Klassifizierung" genannt. Dazu verwendet er die Struktur des Graphen sowie textuelle Informationen, die den Knoten zugeordnet sind. Die von Aggarwal und Li beschriebene experimentelle Analyse ergab, dass er auch auf dynamischen Graphen mit 19396 bzw. 806635 Knoten, von denen nur 14814 bzw. 18999 beschriftet waren, innerhalb von weniger als einer Minute auf einem Kern einer Intel Xeon 2.5 GHz CPU mit 32 G RAM ausgef\"uhrt werden kann. Zus\"atzlich wird die Ver\"offentlichung von Aggarwal und Li kritisch er\"ortert und und es werden m\"ogliche Erweiterungen des DYCOS-Algorithmus vorgeschlagen.
Pixel-wise Segmentation of Street with Neural Networks
Nov 02, 2015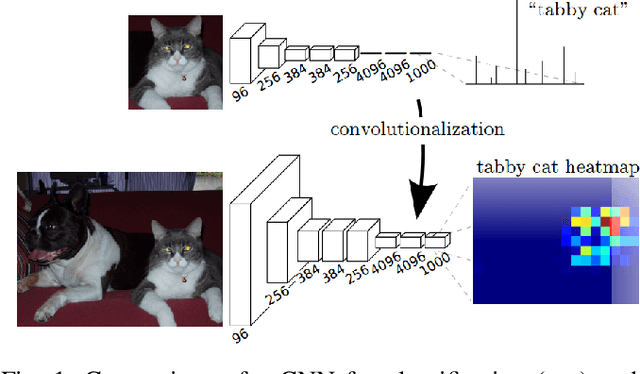



Abstract:Pixel-wise street segmentation of photographs taken from a drivers perspective is important for self-driving cars and can also support other object recognition tasks. A framework called SST was developed to examine the accuracy and execution time of different neural networks. The best neural network achieved an $F_1$-score of 89.5% with a simple feedforward neural network which trained to solve a regression task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge