Martin Eigel
Learning Transient Convective Heat Transfer with Geometry Aware World Models
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Partial differential equation (PDE) simulations are fundamental to engineering and physics but are often computationally prohibitive for real-time applications. While generative AI offers a promising avenue for surrogate modeling, standard video generation architectures lack the specific control and data compatibility required for physical simulations. This paper introduces a geometry aware world model architecture, derived from a video generation architecture (LongVideoGAN), designed to learn transient physics. We introduce two key architecture elements: (1) a twofold conditioning mechanism incorporating global physical parameters and local geometric masks, and (2) an architectural adaptation to support arbitrary channel dimensions, moving beyond standard RGB constraints. We evaluate this approach on a 2D transient computational fluid dynamics (CFD) problem involving convective heat transfer from buoyancy-driven flow coupled to a heat flow in a solid structure. We demonstrate that the conditioned model successfully reproduces complex temporal dynamics and spatial correlations of the training data. Furthermore, we assess the model's generalization capabilities on unseen geometric configurations, highlighting both its potential for controlled simulation synthesis and current limitations in spatial precision for out-of-distribution samples.
A tensor network formalism for neuro-symbolic AI
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:The unification of neural and symbolic approaches to artificial intelligence remains a central open challenge. In this work, we introduce a tensor network formalism, which captures sparsity principles originating in the different approaches in tensor decompositions. In particular, we describe a basis encoding scheme for functions and model neural decompositions as tensor decompositions. The proposed formalism can be applied to represent logical formulas and probability distributions as structured tensor decompositions. This unified treatment identifies tensor network contractions as a fundamental inference class and formulates efficiently scaling reasoning algorithms, originating from probability theory and propositional logic, as contraction message passing schemes. The framework enables the definition and training of hybrid logical and probabilistic models, which we call Hybrid Logic Network. The theoretical concepts are accompanied by the python library tnreason, which enables the implementation and practical use of the proposed architectures.
Approximation and learning with compositional tensor trains
Dec 19, 2025Abstract:We introduce compositional tensor trains (CTTs) for the approximation of multivariate functions, a class of models obtained by composing low-rank functions in the tensor-train format. This format can encode standard approximation tools, such as (sparse) polynomials, deep neural networks (DNNs) with fixed width, or tensor networks with arbitrary permutation of the inputs, or more general affine coordinate transformations, with similar complexities. This format can be viewed as a DNN with width exponential in the input dimension and structured weights matrices. Compared to DNNs, this format enables controlled compression at the layer level using efficient tensor algebra. On the optimization side, we derive a layerwise algorithm inspired by natural gradient descent, allowing to exploit efficient low-rank tensor algebra. This relies on low-rank estimations of Gram matrices, and tensor structured random sketching. Viewing the format as a discrete dynamical system, we also derive an optimization algorithm inspired by numerical methods in optimal control. Numerical experiments on regression tasks demonstrate the expressivity of the new format and the relevance of the proposed optimization algorithms. Overall, CTTs combine the expressivity of compositional models with the algorithmic efficiency of tensor algebra, offering a scalable alternative to standard deep neural networks.
Multi-level Neural Networks for high-dimensional parametric obstacle problems
Apr 07, 2025Abstract:A new method to solve computationally challenging (random) parametric obstacle problems is developed and analyzed, where the parameters can influence the related partial differential equation (PDE) and determine the position and surface structure of the obstacle. As governing equation, a stationary elliptic diffusion problem is assumed. The high-dimensional solution of the obstacle problem is approximated by a specifically constructed convolutional neural network (CNN). This novel algorithm is inspired by a finite element constrained multigrid algorithm to represent the parameter to solution map. This has two benefits: First, it allows for efficient practical computations since multi-level data is used as an explicit output of the NN thanks to an appropriate data preprocessing. This improves the efficacy of the training process and subsequently leads to small errors in the natural energy norm. Second, the comparison of the CNN to a multigrid algorithm provides means to carry out a complete a priori convergence and complexity analysis of the proposed NN architecture. Numerical experiments illustrate a state-of-the-art performance for this challenging problem.
Sampling from Boltzmann densities with physics informed low-rank formats
Dec 10, 2024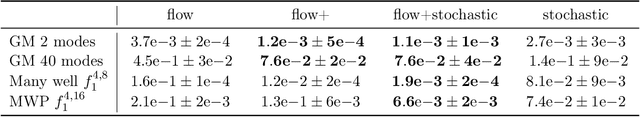
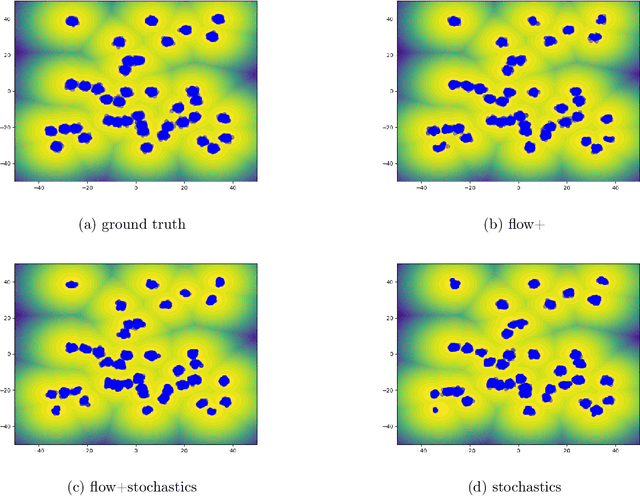
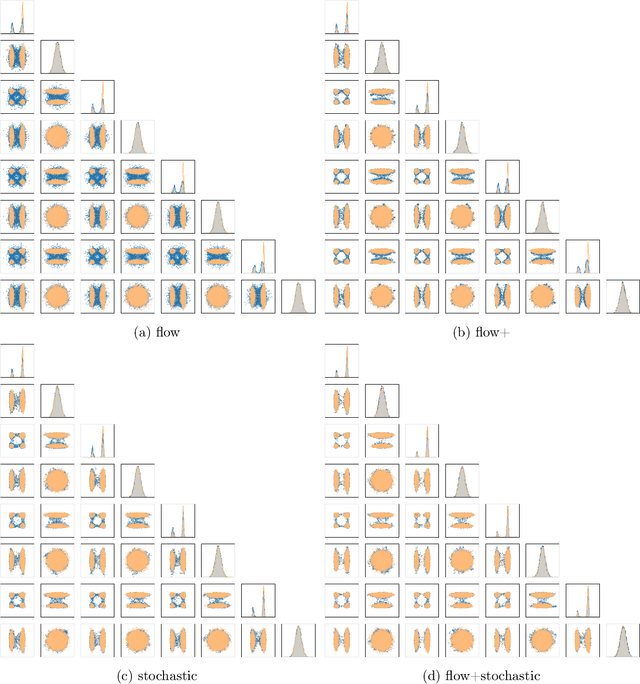
Abstract:Our method proposes the efficient generation of samples from an unnormalized Boltzmann density by solving the underlying continuity equation in the low-rank tensor train (TT) format. It is based on the annealing path commonly used in MCMC literature, which is given by the linear interpolation in the space of energies. Inspired by Sequential Monte Carlo, we alternate between deterministic time steps from the TT representation of the flow field and stochastic steps, which include Langevin and resampling steps. These adjust the relative weights of the different modes of the target distribution and anneal to the correct path distribution. We showcase the efficiency of our method on multiple numerical examples.
Multilevel CNNs for Parametric PDEs based on Adaptive Finite Elements
Aug 20, 2024



Abstract:A neural network architecture is presented that exploits the multilevel properties of high-dimensional parameter-dependent partial differential equations, enabling an efficient approximation of parameter-to-solution maps, rivaling best-in-class methods such as low-rank tensor regression in terms of accuracy and complexity. The neural network is trained with data on adaptively refined finite element meshes, thus reducing data complexity significantly. Error control is achieved by using a reliable finite element a posteriori error estimator, which is also provided as input to the neural network. The proposed U-Net architecture with CNN layers mimics a classical finite element multigrid algorithm. It can be shown that the CNN efficiently approximates all operations required by the solver, including the evaluation of the residual-based error estimator. In the CNN, a culling mask set-up according to the local corrections due to refinement on each mesh level reduces the overall complexity, allowing the network optimization with localized fine-scale finite element data. A complete convergence and complexity analysis is carried out for the adaptive multilevel scheme, which differs in several aspects from previous non-adaptive multilevel CNN. Moreover, numerical experiments with common benchmark problems from Uncertainty Quantification illustrate the practical performance of the architecture.
Adaptive Multilevel Neural Networks for Parametric PDEs with Error Estimation
Mar 19, 2024Abstract:To solve high-dimensional parameter-dependent partial differential equations (pPDEs), a neural network architecture is presented. It is constructed to map parameters of the model data to corresponding finite element solutions. To improve training efficiency and to enable control of the approximation error, the network mimics an adaptive finite element method (AFEM). It outputs a coarse grid solution and a series of corrections as produced in an AFEM, allowing a tracking of the error decay over successive layers of the network. The observed errors are measured by a reliable residual based a posteriori error estimator, enabling the reduction to only few parameters for the approximation in the output of the network. This leads to a problem adapted representation of the solution on locally refined grids. Furthermore, each solution of the AFEM is discretized in a hierarchical basis. For the architecture, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) are chosen. The hierarchical basis then allows to handle sparse images for finely discretized meshes. Additionally, as corrections on finer levels decrease in amplitude, i.e., importance for the overall approximation, the accuracy of the network approximation is allowed to decrease successively. This can either be incorporated in the number of generated high fidelity samples used for training or the size of the network components responsible for the fine grid outputs. The architecture is described and preliminary numerical examples are presented.
Generative Modelling with Tensor Train approximations of Hamilton--Jacobi--Bellman equations
Feb 23, 2024Abstract:Sampling from probability densities is a common challenge in fields such as Uncertainty Quantification (UQ) and Generative Modelling (GM). In GM in particular, the use of reverse-time diffusion processes depending on the log-densities of Ornstein-Uhlenbeck forward processes are a popular sampling tool. In Berner et al. [2022] the authors point out that these log-densities can be obtained by solution of a \textit{Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman} (HJB) equation known from stochastic optimal control. While this HJB equation is usually treated with indirect methods such as policy iteration and unsupervised training of black-box architectures like Neural Networks, we propose instead to solve the HJB equation by direct time integration, using compressed polynomials represented in the Tensor Train (TT) format for spatial discretization. Crucially, this method is sample-free, agnostic to normalization constants and can avoid the curse of dimensionality due to the TT compression. We provide a complete derivation of the HJB equation's action on Tensor Train polynomials and demonstrate the performance of the proposed time-step-, rank- and degree-adaptive integration method on a nonlinear sampling task in 20 dimensions.
Functional SDE approximation inspired by a deep operator network architecture
Feb 05, 2024Abstract:A novel approach to approximate solutions of Stochastic Differential Equations (SDEs) by Deep Neural Networks is derived and analysed. The architecture is inspired by the notion of Deep Operator Networks (DeepONets), which is based on operator learning in function spaces in terms of a reduced basis also represented in the network. In our setting, we make use of a polynomial chaos expansion (PCE) of stochastic processes and call the corresponding architecture SDEONet. The PCE has been used extensively in the area of uncertainty quantification (UQ) with parametric partial differential equations. This however is not the case with SDE, where classical sampling methods dominate and functional approaches are seen rarely. A main challenge with truncated PCEs occurs due to the drastic growth of the number of components with respect to the maximum polynomial degree and the number of basis elements. The proposed SDEONet architecture aims to alleviate the issue of exponential complexity by learning an optimal sparse truncation of the Wiener chaos expansion. A complete convergence and complexity analysis is presented, making use of recent Neural Network approximation results. Numerical experiments illustrate the promising performance of the suggested approach in 1D and higher dimensions.
Approximating Langevin Monte Carlo with ResNet-like Neural Network architectures
Nov 06, 2023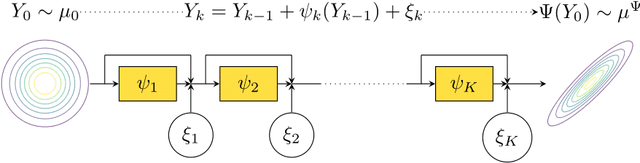
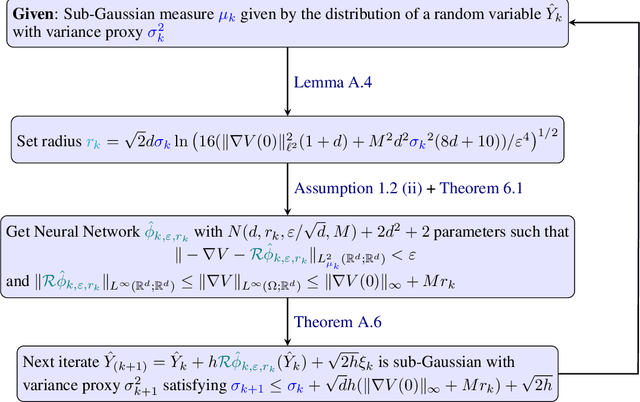
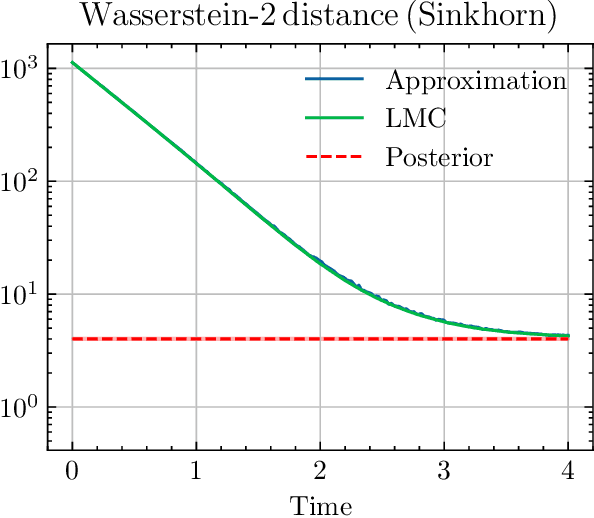
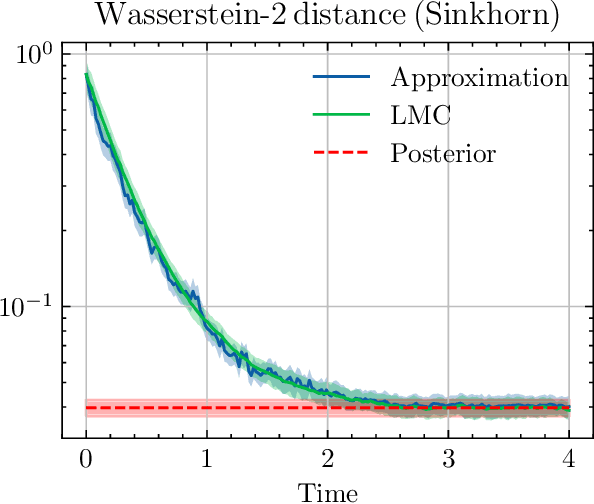
Abstract:We sample from a given target distribution by constructing a neural network which maps samples from a simple reference, e.g. the standard normal distribution, to samples from the target. To that end, we propose using a neural network architecture inspired by the Langevin Monte Carlo (LMC) algorithm. Based on LMC perturbation results, we show approximation rates of the proposed architecture for smooth, log-concave target distributions measured in the Wasserstein-$2$ distance. The analysis heavily relies on the notion of sub-Gaussianity of the intermediate measures of the perturbed LMC process. In particular, we derive bounds on the growth of the intermediate variance proxies under different assumptions on the perturbations. Moreover, we propose an architecture similar to deep residual neural networks and derive expressivity results for approximating the sample to target distribution map.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge