Marco Scutari
DAG Learning from Zero-Inflated Count Data Using Continuous Optimization
Dec 18, 2025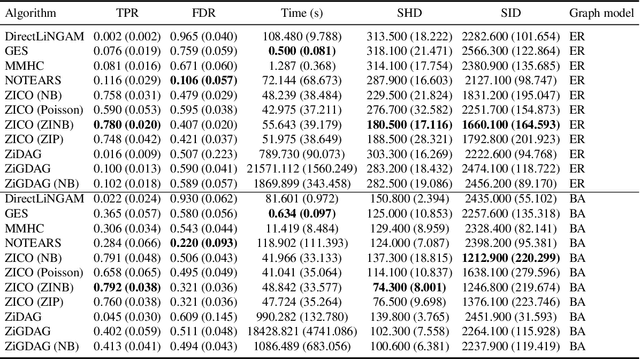
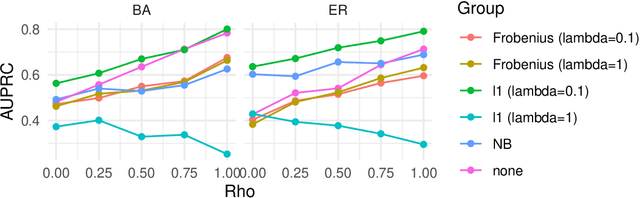
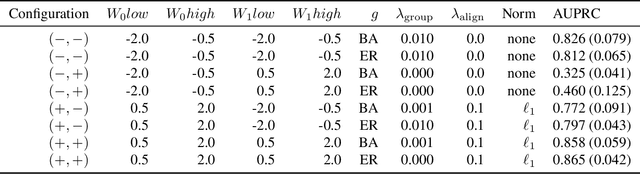
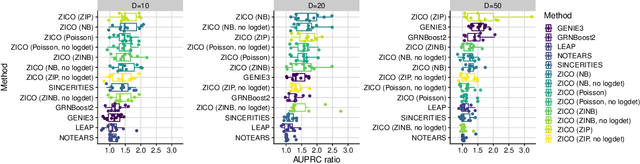
Abstract:We address network structure learning from zero-inflated count data by casting each node as a zero-inflated generalized linear model and optimizing a smooth, score-based objective under a directed acyclic graph constraint. Our Zero-Inflated Continuous Optimization (ZICO) approach uses node-wise likelihoods with canonical links and enforces acyclicity through a differentiable surrogate constraint combined with sparsity regularization. ZICO achieves superior performance with faster runtimes on simulated data. It also performs comparably to or better than common algorithms for reverse engineering gene regulatory networks. ZICO is fully vectorized and mini-batched, enabling learning on larger variable sets with practical runtimes in a wide range of domains.
Causal Discovery on Higher-Order Interactions
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:Causal discovery combines data with knowledge provided by experts to learn the DAG representing the causal relationships between a given set of variables. When data are scarce, bagging is used to measure our confidence in an average DAG obtained by aggregating bootstrapped DAGs. However, the aggregation step has received little attention from the specialized literature: the average DAG is constructed using only the confidence in the individual edges of the bootstrapped DAGs, thus disregarding complex higher-order edge structures. In this paper, we introduce a novel theoretical framework based on higher-order structures and describe a new DAG aggregation algorithm. We perform a simulation study, discussing the advantages and limitations of the proposed approach. Our proposal is both computationally efficient and effective, outperforming state-of-the-art solutions, especially in low sample size regimes and under high dimensionality settings.
Practical Causal Evaluation Metrics for Biological Networks
Nov 16, 2025Abstract:Estimating causal networks from biological data is a critical step in systems biology. When evaluating the inferred network, assessing the networks based on their intervention effects is particularly important for downstream probabilistic reasoning and the identification of potential drug targets. In the context of gene regulatory network inference, biological databases are often used as reference sources. These databases typically describe relationships in a qualitative rather than quantitative manner. However, few evaluation metrics have been developed that take this qualitative nature into account. To address this, we developed a metric, the sign-augmented Structural Intervention Distance (sSID), and a weighted sSID that incorporates the net effects of the intervention. Through simulations and analyses of real transcriptomic datasets, we found that our proposed metrics could identify a different algorithm as optimal compared to conventional metrics, and the network selected by sSID had a superior performance in the classification task of clinical covariates using transcriptomic data. This suggests that sSID can distinguish networks that are structurally correct but functionally incorrect, highlighting its potential as a more biologically meaningful and practical evaluation metric.
Technical Insights and Legal Considerations for Advancing Federated Learning in Bioinformatics
Mar 12, 2025



Abstract:Federated learning leverages data across institutions to improve clinical discovery while complying with data-sharing restrictions and protecting patient privacy. As the evolution of biobanks in genetics and systems biology has proved, accessing more extensive and varied data pools leads to a faster and more robust exploration and translation of results. More widespread use of federated learning may have the same impact in bioinformatics, allowing access to many combinations of genotypic, phenotypic and environmental information that are undercovered or not included in existing biobanks. This paper reviews the methodological, infrastructural and legal issues that academic and clinical institutions must address before implementing it. Finally, we provide recommendations for the reliable use of federated learning and its effective translation into clinical practice.
Benchmarking Constraint-Based Bayesian Structure Learning Algorithms: Role of Network Topology
Jan 02, 2025



Abstract:Modeling the associations between real world entities from their multivariate cross-sectional profiles can provide cues into the concerted working of these entities as a system. Several techniques have been proposed for deciphering these associations including constraint-based Bayesian structure learning (BSL) algorithms that model them as directed acyclic graphs. Benchmarking these algorithms have typically focused on assessing the variation in performance measures such as sensitivity as a function of the dimensionality represented by the number of nodes in the DAG, and sample size. The present study elucidates the importance of network topology in benchmarking exercises. More specifically, it investigates variations in sensitivity across distinct network topologies while constraining the nodes, edges, and sample-size to be identical, eliminating these as potential confounders. Sensitivity of three popular constraint-based BSL algorithms (Peter-Clarke, Grow-Shrink, Incremental Association Markov Blanket) in learning the network structure from multivariate cross-sectional profiles sampled from network models with sub-linear, linear, and super-linear DAG topologies generated using preferential attachment is investigated. Results across linear and nonlinear models revealed statistically significant $(\alpha=0.05)$ decrease in sensitivity estimates from sub-linear to super-linear topology constitutively across the three algorithms. These results are demonstrated on networks with nodes $(N_{nods}=48,64)$, noise strengths $(\sigma =3,6)$ and sample size $(N = 2^{10})$. The findings elucidate the importance of accommodating the network topology in constraint-based BSL benchmarking exercises.
Entropy and the Kullback-Leibler Divergence for Bayesian Networks: Computational Complexity and Efficient Implementation
Nov 29, 2023Abstract:Bayesian networks (BNs) are a foundational model in machine learning and causal inference. Their graphical structure can handle high-dimensional problems, divide-and-conquering them into a sparse collection of smaller ones; underlies Judea Pearl's causality; and determines their explainability and interpretability. Despite their popularity, there are few resources in the literature on how to compute Shannon's entropy and the Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence for BNs under their most common distributional assumptions. In this paper, we provide computationally efficient algorithms for both by leveraging BNs' graphical structure, and we illustrate them with a complete set of numerical examples. In the process, we show it is possible to reduce the computational complexity of KL from cubic to quadratic for Gaussian BNs.
Towards a Transportable Causal Network Model Based on Observational Healthcare Data
Nov 20, 2023


Abstract:Over the last decades, many prognostic models based on artificial intelligence techniques have been used to provide detailed predictions in healthcare. Unfortunately, the real-world observational data used to train and validate these models are almost always affected by biases that can strongly impact the outcomes validity: two examples are values missing not-at-random and selection bias. Addressing them is a key element in achieving transportability and in studying the causal relationships that are critical in clinical decision making, going beyond simpler statistical approaches based on probabilistic association. In this context, we propose a novel approach that combines selection diagrams, missingness graphs, causal discovery and prior knowledge into a single graphical model to estimate the cardiovascular risk of adolescent and young females who survived breast cancer. We learn this model from data comprising two different cohorts of patients. The resulting causal network model is validated by expert clinicians in terms of risk assessment, accuracy and explainability, and provides a prognostic model that outperforms competing machine learning methods.
Learning Bayesian Networks with Heterogeneous Agronomic Data Sets via Mixed-Effect Models and Hierarchical Clustering
Aug 29, 2023Abstract:Research involving diverse but related data sets, where associations between covariates and outcomes may vary, is prevalent in various fields including agronomic studies. In these scenarios, hierarchical models, also known as multilevel models, are frequently employed to assimilate information from different data sets while accommodating their distinct characteristics. However, their structure extend beyond simple heterogeneity, as variables often form complex networks of causal relationships. Bayesian networks (BNs) provide a powerful framework for modelling such relationships using directed acyclic graphs to illustrate the connections between variables. This study introduces a novel approach that integrates random effects into BN learning. Rooted in linear mixed-effects models, this approach is particularly well-suited for handling hierarchical data. Results from a real-world agronomic trial suggest that employing this approach enhances structural learning, leading to the discovery of new connections and the improvement of improved model specification. Furthermore, we observe a reduction in prediction errors from 28% to 17%. By extending the applicability of BNs to complex data set structures, this approach contributes to the effective utilisation of BNs for hierarchical agronomic data. This, in turn, enhances their value as decision-support tools in the field.
Analyzing Complex Systems with Cascades Using Continuous-Time Bayesian Networks
Aug 21, 2023



Abstract:Interacting systems of events may exhibit cascading behavior where events tend to be temporally clustered. While the cascades themselves may be obvious from the data, it is important to understand which states of the system trigger them. For this purpose, we propose a modeling framework based on continuous-time Bayesian networks (CTBNs) to analyze cascading behavior in complex systems. This framework allows us to describe how events propagate through the system and to identify likely sentry states, that is, system states that may lead to imminent cascading behavior. Moreover, CTBNs have a simple graphical representation and provide interpretable outputs, both of which are important when communicating with domain experts. We also develop new methods for knowledge extraction from CTBNs and we apply the proposed methodology to a data set of alarms in a large industrial system.
Risk Assessment of Lymph Node Metastases in Endometrial Cancer Patients: A Causal Approach
May 17, 2023



Abstract:Assessing the pre-operative risk of lymph node metastases in endometrial cancer patients is a complex and challenging task. In principle, machine learning and deep learning models are flexible and expressive enough to capture the dynamics of clinical risk assessment. However, in this setting we are limited to observational data with quality issues, missing values, small sample size and high dimensionality: we cannot reliably learn such models from limited observational data with these sources of bias. Instead, we choose to learn a causal Bayesian network to mitigate the issues above and to leverage the prior knowledge on endometrial cancer available from clinicians and physicians. We introduce a causal discovery algorithm for causal Bayesian networks based on bootstrap resampling, as opposed to the single imputation used in related works. Moreover, we include a context variable to evaluate whether selection bias results in learning spurious associations. Finally, we discuss the strengths and limitations of our findings in light of the presence of missing data that may be missing-not-at-random, which is common in real-world clinical settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge