Marc Schmidt
Generating peak-aware pseudo-measurements for low-voltage feeders using metadata of distribution system operators
Sep 29, 2024


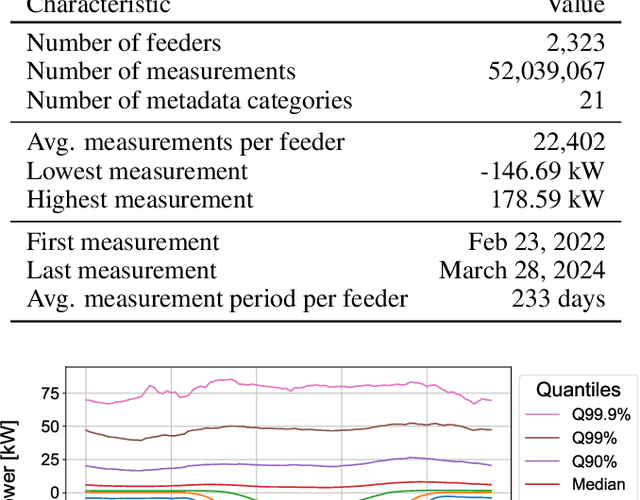
Abstract:Distribution system operators (DSOs) must cope with new challenges such as the reconstruction of distribution grids along climate neutrality pathways or the ability to manage and control consumption and generation in the grid. In order to meet the challenges, measurements within the distribution grid often form the basis for DSOs. Hence, it is an urgent problem that measurement devices are not installed in many low-voltage (LV) grids. In order to overcome this problem, we present an approach to estimate pseudo-measurements for non-measured LV feeders based on the metadata of the respective feeder using regression models. The feeder metadata comprise information about the number of grid connection points, the installed power of consumers and producers, and billing data in the downstream LV grid. Additionally, we use weather data, calendar data and timestamp information as model features. The existing measurements are used as model target. We extensively evaluate the estimated pseudo-measurements on a large real-world dataset with 2,323 LV feeders characterized by both consumption and feed-in. For this purpose, we introduce peak metrics inspired by the BigDEAL challenge for the peak magnitude, timing and shape for both consumption and feed-in. As regression models, we use XGBoost, a multilayer perceptron (MLP) and a linear regression (LR). We observe that XGBoost and MLP outperform the LR. Furthermore, the results show that the approach adapts to different weather, calendar and timestamp conditions and produces realistic load curves based on the feeder metadata. In the future, the approach can be adapted to other grid levels like substation transformers and can supplement research fields like load modeling, state estimation and LV load forecasting.
Multi-view Tracking, Re-ID, and Social Network Analysis of a Flock of Visually Similar Birds in an Outdoor Aviary
Dec 01, 2022Abstract:The ability to capture detailed interactions among individuals in a social group is foundational to our study of animal behavior and neuroscience. Recent advances in deep learning and computer vision are driving rapid progress in methods that can record the actions and interactions of multiple individuals simultaneously. Many social species, such as birds, however, live deeply embedded in a three-dimensional world. This world introduces additional perceptual challenges such as occlusions, orientation-dependent appearance, large variation in apparent size, and poor sensor coverage for 3D reconstruction, that are not encountered by applications studying animals that move and interact only on 2D planes. Here we introduce a system for studying the behavioral dynamics of a group of songbirds as they move throughout a 3D aviary. We study the complexities that arise when tracking a group of closely interacting animals in three dimensions and introduce a novel dataset for evaluating multi-view trackers. Finally, we analyze captured ethogram data and demonstrate that social context affects the distribution of sequential interactions between birds in the aviary.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge