Majdi Hassan
Amortized Sampling with Transferable Normalizing Flows
Aug 25, 2025Abstract:Efficient equilibrium sampling of molecular conformations remains a core challenge in computational chemistry and statistical inference. Classical approaches such as molecular dynamics or Markov chain Monte Carlo inherently lack amortization; the computational cost of sampling must be paid in-full for each system of interest. The widespread success of generative models has inspired interest into overcoming this limitation through learning sampling algorithms. Despite performing on par with conventional methods when trained on a single system, learned samplers have so far demonstrated limited ability to transfer across systems. We prove that deep learning enables the design of scalable and transferable samplers by introducing Prose, a 280 million parameter all-atom transferable normalizing flow trained on a corpus of peptide molecular dynamics trajectories up to 8 residues in length. Prose draws zero-shot uncorrelated proposal samples for arbitrary peptide systems, achieving the previously intractable transferability across sequence length, whilst retaining the efficient likelihood evaluation of normalizing flows. Through extensive empirical evaluation we demonstrate the efficacy of Prose as a proposal for a variety of sampling algorithms, finding a simple importance sampling-based finetuning procedure to achieve superior performance to established methods such as sequential Monte Carlo on unseen tetrapeptides. We open-source the Prose codebase, model weights, and training dataset, to further stimulate research into amortized sampling methods and finetuning objectives.
ET-Flow: Equivariant Flow-Matching for Molecular Conformer Generation
Oct 29, 2024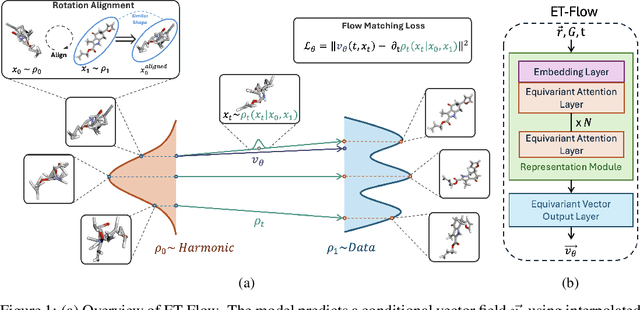
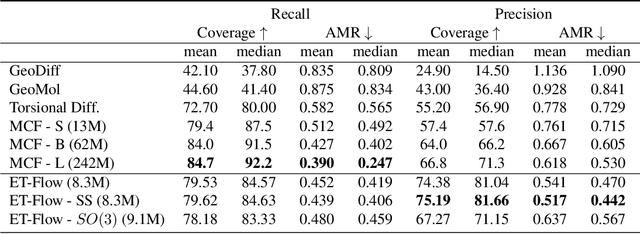
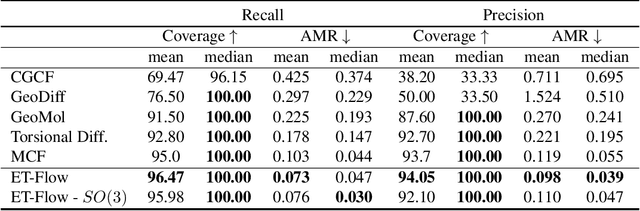
Abstract:Predicting low-energy molecular conformations given a molecular graph is an important but challenging task in computational drug discovery. Existing state-of-the-art approaches either resort to large scale transformer-based models that diffuse over conformer fields, or use computationally expensive methods to generate initial structures and diffuse over torsion angles. In this work, we introduce Equivariant Transformer Flow (ET-Flow). We showcase that a well-designed flow matching approach with equivariance and harmonic prior alleviates the need for complex internal geometry calculations and large architectures, contrary to the prevailing methods in the field. Our approach results in a straightforward and scalable method that directly operates on all-atom coordinates with minimal assumptions. With the advantages of equivariance and flow matching, ET-Flow significantly increases the precision and physical validity of the generated conformers, while being a lighter model and faster at inference. Code is available https://github.com/shenoynikhil/ETFlow.
Biomedical Knowledge Graph Refinement and Completion using Graph Representation Learning and Top-K Similarity Measure
Dec 18, 2020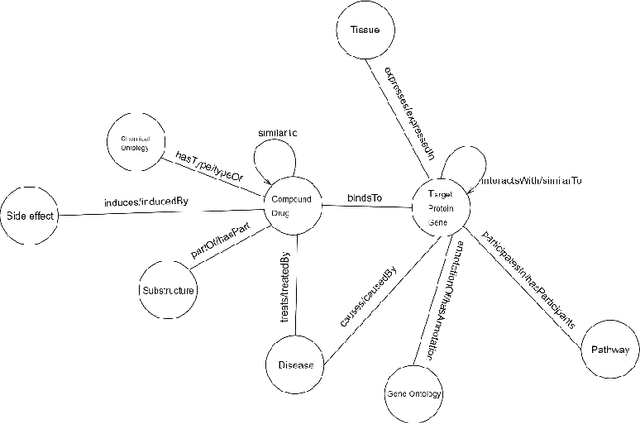
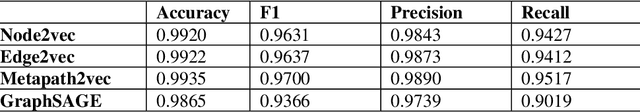
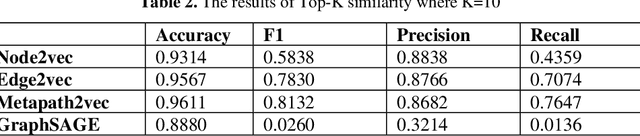
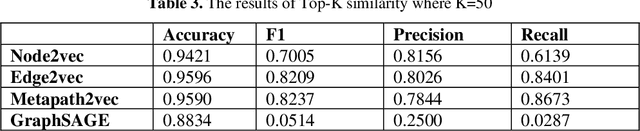
Abstract:Knowledge Graphs have been one of the fundamental methods for integrating heterogeneous data sources. Integrating heterogeneous data sources is crucial, especially in the biomedical domain, where central data-driven tasks such as drug discovery rely on incorporating information from different biomedical databases. These databases contain various biological entities and relations such as proteins (PDB), genes (Gene Ontology), drugs (DrugBank), diseases (DDB), and protein-protein interactions (BioGRID). The process of semantically integrating heterogeneous biomedical databases is often riddled with imperfections. The quality of data-driven drug discovery relies on the accuracy of the mining methods used and the data's quality as well. Thus, having complete and refined biomedical knowledge graphs is central to achieving more accurate drug discovery outcomes. Here we propose using the latest graph representation learning and embedding models to refine and complete biomedical knowledge graphs. This preliminary work demonstrates learning discrete representations of the integrated biomedical knowledge graph Chem2Bio2RD [3]. We perform a knowledge graph completion and refinement task using a simple top-K cosine similarity measure between the learned embedding vectors to predict missing links between drugs and targets present in the data. We show that this simple procedure can be used alternatively to binary classifiers in link prediction.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge