Luo Zhong
Learning Text-Image Joint Embedding for Efficient Cross-Modal Retrieval with Deep Feature Engineering
Oct 22, 2021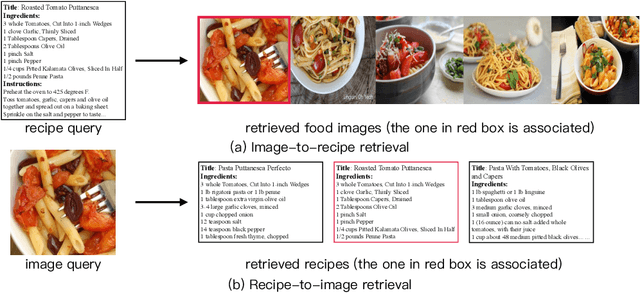
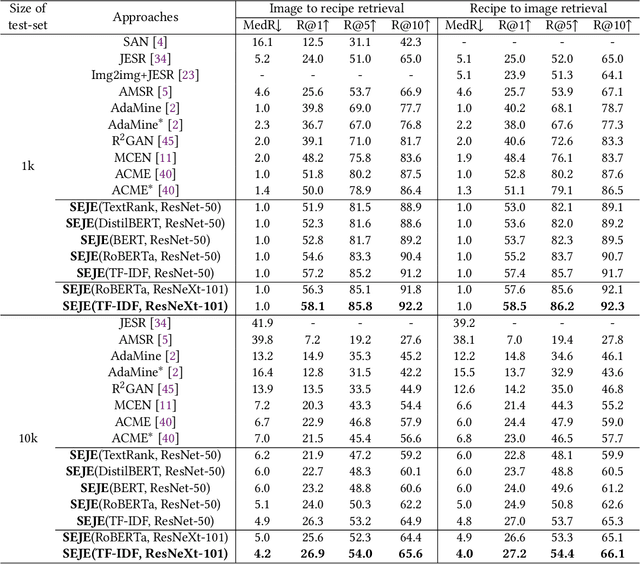
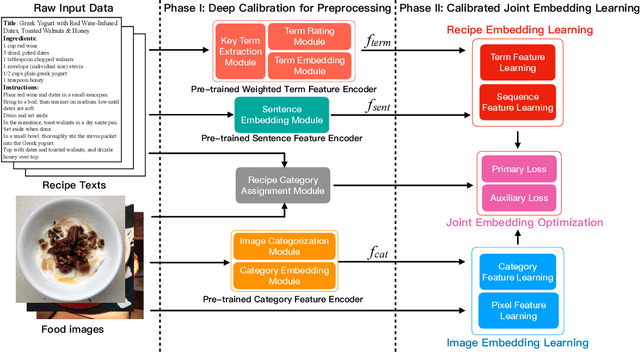
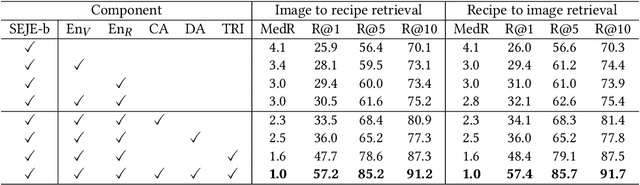
Abstract:This paper introduces a two-phase deep feature engineering framework for efficient learning of semantics enhanced joint embedding, which clearly separates the deep feature engineering in data preprocessing from training the text-image joint embedding model. We use the Recipe1M dataset for the technical description and empirical validation. In preprocessing, we perform deep feature engineering by combining deep feature engineering with semantic context features derived from raw text-image input data. We leverage LSTM to identify key terms, deep NLP models from the BERT family, TextRank, or TF-IDF to produce ranking scores for key terms before generating the vector representation for each key term by using word2vec. We leverage wideResNet50 and word2vec to extract and encode the image category semantics of food images to help semantic alignment of the learned recipe and image embeddings in the joint latent space. In joint embedding learning, we perform deep feature engineering by optimizing the batch-hard triplet loss function with soft-margin and double negative sampling, taking into account also the category-based alignment loss and discriminator-based alignment loss. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our SEJE approach with deep feature engineering significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art approaches.
Visual-aware Attention Dual-stream Decoder for Video Captioning
Oct 16, 2021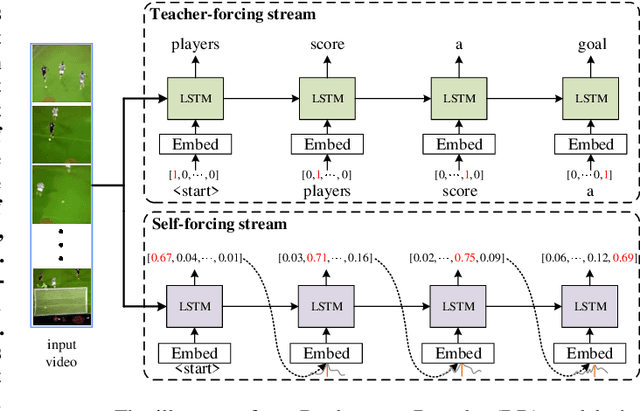
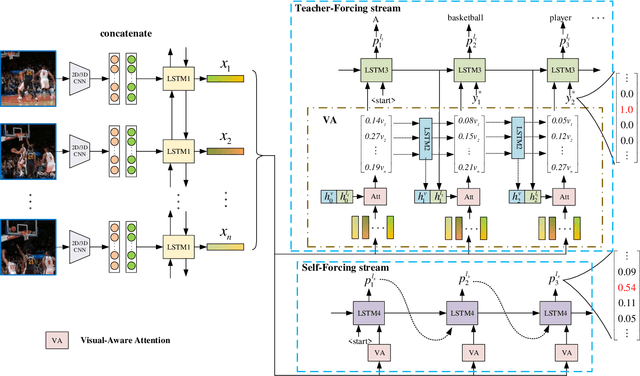
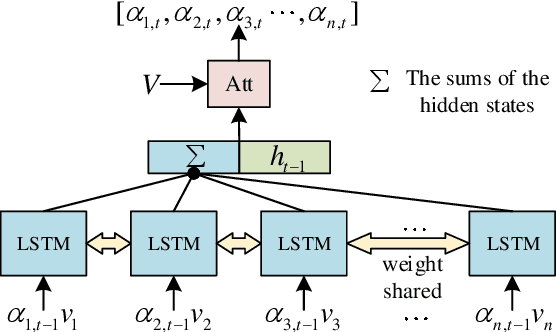
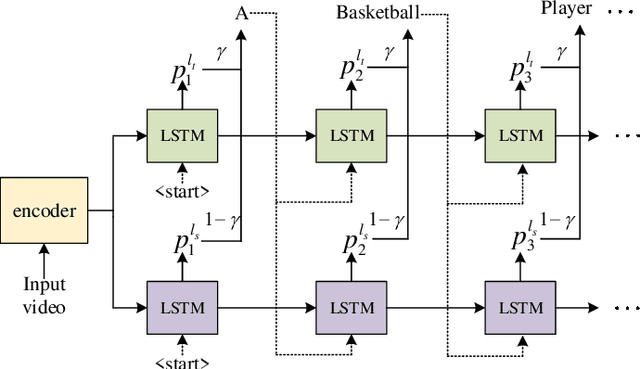
Abstract:Video captioning is a challenging task that captures different visual parts and describes them in sentences, for it requires visual and linguistic coherence. The attention mechanism in the current video captioning method learns to assign weight to each frame, promoting the decoder dynamically. This may not explicitly model the correlation and the temporal coherence of the visual features extracted in the sequence frames.To generate semantically coherent sentences, we propose a new Visual-aware Attention (VA) model, which concatenates dynamic changes of temporal sequence frames with the words at the previous moment, as the input of attention mechanism to extract sequence features.In addition, the prevalent approaches widely use the teacher-forcing (TF) learning during training, where the next token is generated conditioned on the previous ground-truth tokens. The semantic information in the previously generated tokens is lost. Therefore, we design a self-forcing (SF) stream that takes the semantic information in the probability distribution of the previous token as input to enhance the current token.The Dual-stream Decoder (DD) architecture unifies the TF and SF streams, generating sentences to promote the annotated captioning for both streams.Meanwhile, with the Dual-stream Decoder utilized, the exposure bias problem is alleviated, caused by the discrepancy between the training and testing in the TF learning.The effectiveness of the proposed Visual-aware Attention Dual-stream Decoder (VADD) is demonstrated through the result of experimental studies on Microsoft video description (MSVD) corpus and MSR-Video to text (MSR-VTT) datasets.
Learning Joint Embedding with Modality Alignments for Cross-Modal Retrieval of Recipes and Food Images
Aug 18, 2021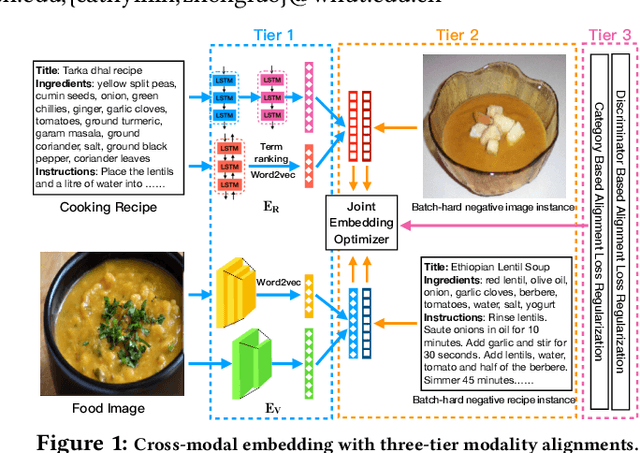
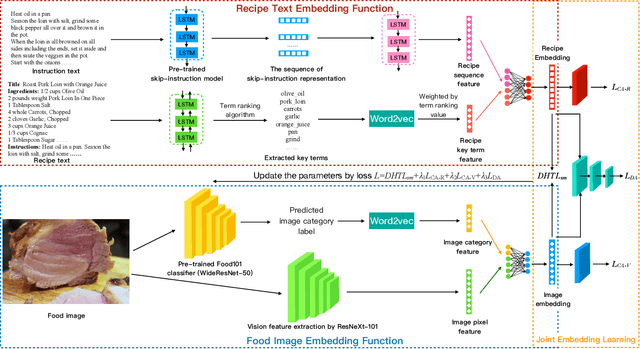
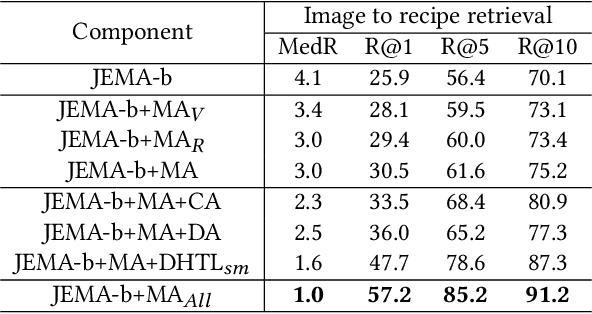

Abstract:This paper presents a three-tier modality alignment approach to learning text-image joint embedding, coined as JEMA, for cross-modal retrieval of cooking recipes and food images. The first tier improves recipe text embedding by optimizing the LSTM networks with term extraction and ranking enhanced sequence patterns, and optimizes the image embedding by combining the ResNeXt-101 image encoder with the category embedding using wideResNet-50 with word2vec. The second tier modality alignment optimizes the textual-visual joint embedding loss function using a double batch-hard triplet loss with soft-margin optimization. The third modality alignment incorporates two types of cross-modality alignments as the auxiliary loss regularizations to further reduce the alignment errors in the joint learning of the two modality-specific embedding functions. The category-based cross-modal alignment aims to align the image category with the recipe category as a loss regularization to the joint embedding. The cross-modal discriminator-based alignment aims to add the visual-textual embedding distribution alignment to further regularize the joint embedding loss. Extensive experiments with the one-million recipes benchmark dataset Recipe1M demonstrate that the proposed JEMA approach outperforms the state-of-the-art cross-modal embedding methods for both image-to-recipe and recipe-to-image retrievals.
Efficient Deep Feature Calibration for Cross-Modal Joint Embedding Learning
Aug 08, 2021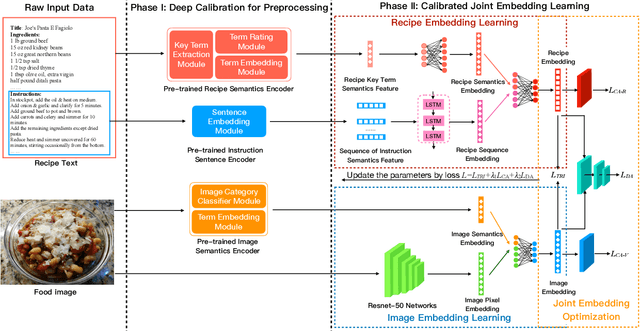
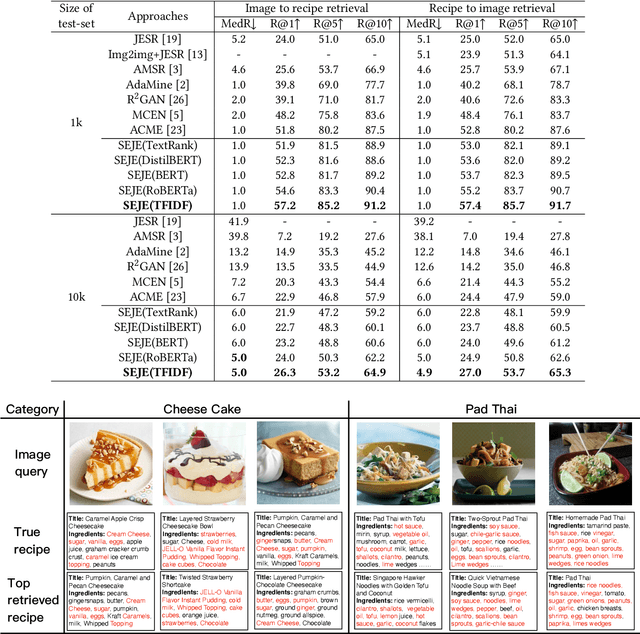

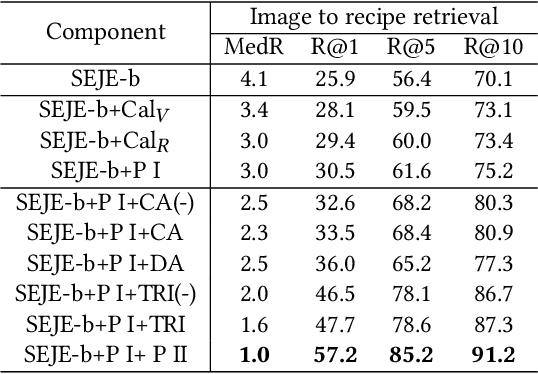
Abstract:This paper introduces a two-phase deep feature calibration framework for efficient learning of semantics enhanced text-image cross-modal joint embedding, which clearly separates the deep feature calibration in data preprocessing from training the joint embedding model. We use the Recipe1M dataset for the technical description and empirical validation. In preprocessing, we perform deep feature calibration by combining deep feature engineering with semantic context features derived from raw text-image input data. We leverage LSTM to identify key terms, NLP methods to produce ranking scores for key terms before generating the key term feature. We leverage wideResNet50 to extract and encode the image category semantics to help semantic alignment of the learned recipe and image embeddings in the joint latent space. In joint embedding learning, we perform deep feature calibration by optimizing the batch-hard triplet loss function with soft-margin and double negative sampling, also utilizing the category-based alignment loss and discriminator-based alignment loss. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our SEJE approach with the deep feature calibration significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art approaches.
Learning TFIDF Enhanced Joint Embedding for Recipe-Image Cross-Modal Retrieval Service
Aug 02, 2021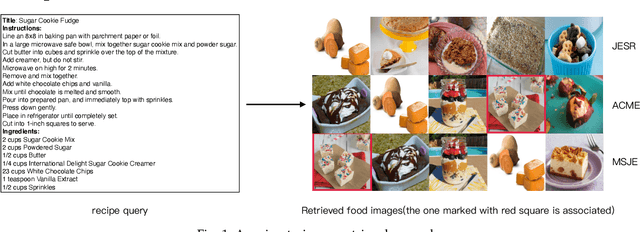

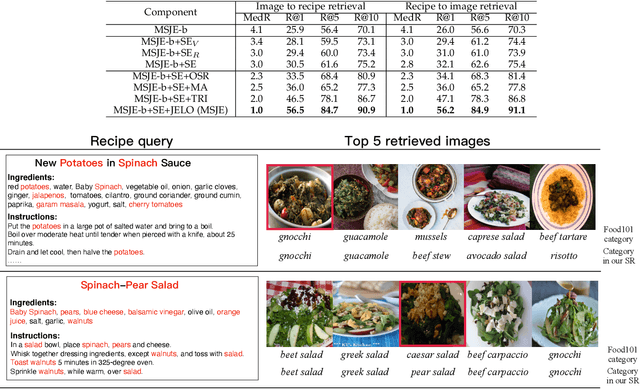
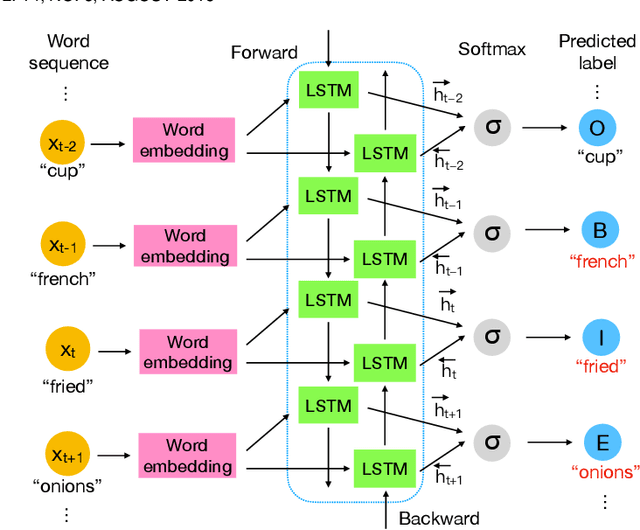
Abstract:It is widely acknowledged that learning joint embeddings of recipes with images is challenging due to the diverse composition and deformation of ingredients in cooking procedures. We present a Multi-modal Semantics enhanced Joint Embedding approach (MSJE) for learning a common feature space between the two modalities (text and image), with the ultimate goal of providing high-performance cross-modal retrieval services. Our MSJE approach has three unique features. First, we extract the TFIDF feature from the title, ingredients and cooking instructions of recipes. By determining the significance of word sequences through combining LSTM learned features with their TFIDF features, we encode a recipe into a TFIDF weighted vector for capturing significant key terms and how such key terms are used in the corresponding cooking instructions. Second, we combine the recipe TFIDF feature with the recipe sequence feature extracted through two-stage LSTM networks, which is effective in capturing the unique relationship between a recipe and its associated image(s). Third, we further incorporate TFIDF enhanced category semantics to improve the mapping of image modality and to regulate the similarity loss function during the iterative learning of cross-modal joint embedding. Experiments on the benchmark dataset Recipe1M show the proposed approach outperforms the state-of-the-art approaches.
Image-to-Video Person Re-Identification by Reusing Cross-modal Embeddings
Oct 22, 2018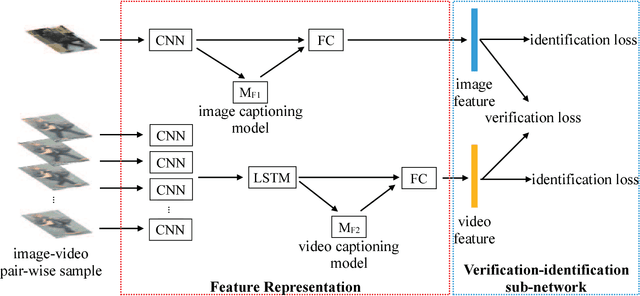
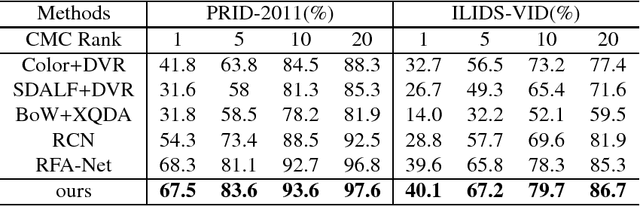
Abstract:Image-to-video person re-identification identifies a target person by a probe image from quantities of pedestrian videos captured by non-overlapping cameras. Despite the great progress achieved,it's still challenging to match in the multimodal scenario,i.e. between image and video. Currently,state-of-the-art approaches mainly focus on the task-specific data,neglecting the extra information on the different but related tasks. In this paper,we propose an end-to-end neural network framework for image-to-video person reidentification by leveraging cross-modal embeddings learned from extra information.Concretely speaking,cross-modal embeddings from image captioning and video captioning models are reused to help learned features be projected into a coordinated space,where similarity can be directly computed. Besides,training steps from fixed model reuse approach are integrated into our framework,which can incorporate beneficial information and eventually make the target networks independent of existing models. Apart from that,our proposed framework resorts to CNNs and LSTMs for extracting visual and spatiotemporal features,and combines the strengths of identification and verification model to improve the discriminative ability of the learned feature. The experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our framework on narrowing down the gap between heterogeneous data and obtaining observable improvement in image-to-video person re-identification.
Using Sentiment Representation Learning to Enhance Gender Classification for User Profiling
Oct 09, 2018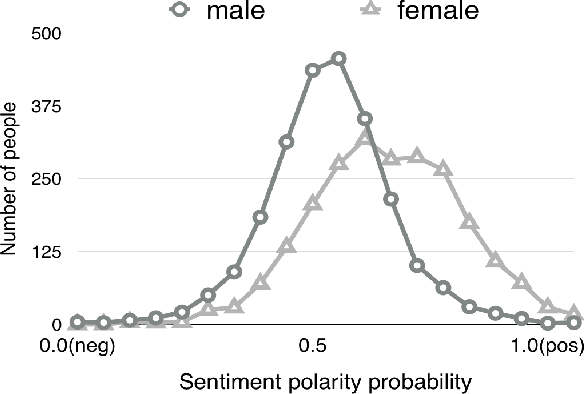
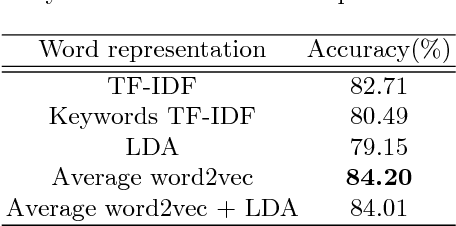
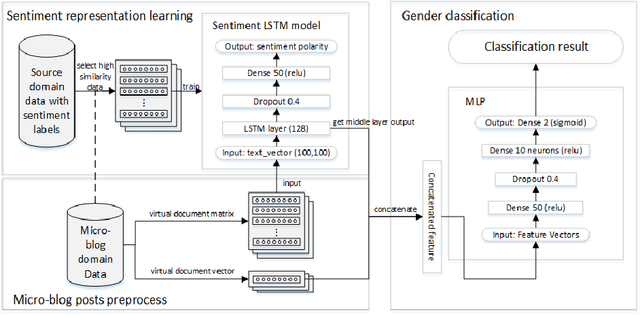
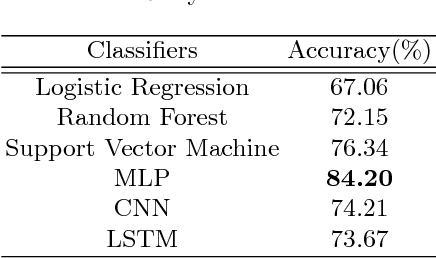
Abstract:User profiling means exploiting the technology of machine learning to predict attributes of users, such as demographic attributes, hobby attributes, preference attributes, etc. It's a powerful data support of precision marketing. Existing methods mainly study network behavior, personal preferences, post texts to build user profile. Through our data analysis of micro-blog, we find that females show more positive and have richer emotions than males in online social platform. This difference is very conducive to the distinction between genders. Therefore, we argue that sentiment context is important as well for user profiling.This paper focuses on exploiting microblog user posts to predict one of the demographic labels: gender. We propose a Sentiment Representation Learning based Multi-Layer Perceptron(SRL-MLP) model to classify gender. First we build a sentiment polarity classifier in advance by training Long Short-Term Memory(LSTM) model on e-commerce review corpus. Next we transfer sentiment representation to a basic MLP network. Last we conduct experiments on gender classification by sentiment representation. Experimental results show that our approach can improve gender classification accuracy by 5.53\%, from 84.20\% to 89.73\%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge