Luis Roldao
3DGS-Calib: 3D Gaussian Splatting for Multimodal SpatioTemporal Calibration
Mar 18, 2024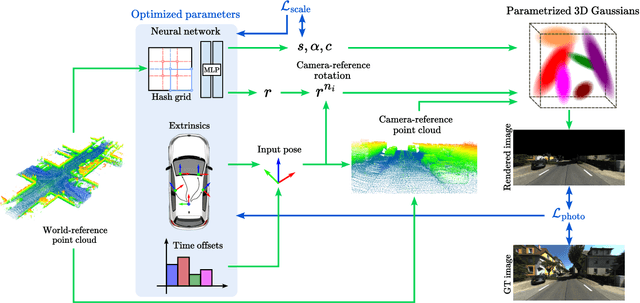
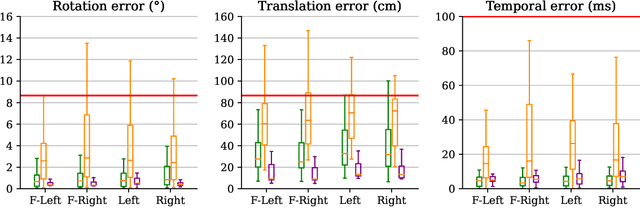
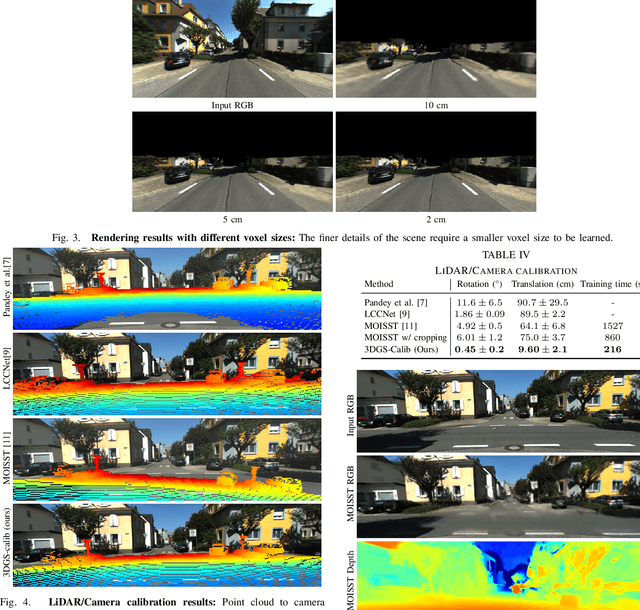
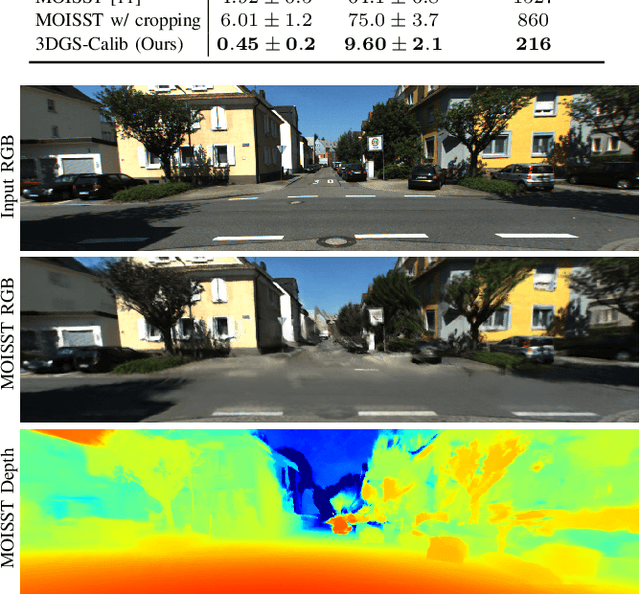
Abstract:Reliable multimodal sensor fusion algorithms require accurate spatiotemporal calibration. Recently, targetless calibration techniques based on implicit neural representations have proven to provide precise and robust results. Nevertheless, such methods are inherently slow to train given the high computational overhead caused by the large number of sampled points required for volume rendering. With the recent introduction of 3D Gaussian Splatting as a faster alternative to implicit representation methods, we propose to leverage this new rendering approach to achieve faster multi-sensor calibration. We introduce 3DGS-Calib, a new calibration method that relies on the speed and rendering accuracy of 3D Gaussian Splatting to achieve multimodal spatiotemporal calibration that is accurate, robust, and with a substantial speed-up compared to methods relying on implicit neural representations. We demonstrate the superiority of our proposal with experimental results on sequences from KITTI-360, a widely used driving dataset.
SWAG: Splatting in the Wild images with Appearance-conditioned Gaussians
Mar 15, 2024



Abstract:Implicit neural representation methods have shown impressive advancements in learning 3D scenes from unstructured in-the-wild photo collections but are still limited by the large computational cost of volumetric rendering. More recently, 3D Gaussian Splatting emerged as a much faster alternative with superior rendering quality and training efficiency, especially for small-scale and object-centric scenarios. Nevertheless, this technique suffers from poor performance on unstructured in-the-wild data. To tackle this, we extend over 3D Gaussian Splatting to handle unstructured image collections. We achieve this by modeling appearance to seize photometric variations in the rendered images. Additionally, we introduce a new mechanism to train transient Gaussians to handle the presence of scene occluders in an unsupervised manner. Experiments on diverse photo collection scenes and multi-pass acquisition of outdoor landmarks show the effectiveness of our method over prior works achieving state-of-the-art results with improved efficiency.
3D Semantic Scene Completion: a Survey
Mar 12, 2021



Abstract:Semantic Scene Completion (SSC) aims to jointly estimate the complete geometry and semantics of a scene, assuming partial sparse input. In the last years following the multiplication of large-scale 3D datasets, SSC has gained significant momentum in the research community because it holds unresolved challenges. Specifically, SSC lies in the ambiguous completion of large unobserved areas and the weak supervision signal of the ground truth. This led to a substantially increasing number of papers on the matter. This survey aims to identify, compare and analyze the techniques providing a critical analysis of the SSC literature on both methods and datasets. Throughout the paper, we provide an in-depth analysis of the existing works covering all choices made by the authors while highlighting the remaining avenues of research. SSC performance of the SoA on the most popular datasets is also evaluated and analyzed.
Real-time Dynamic Object Detection for Autonomous Driving using Prior 3D-Maps
Sep 28, 2018
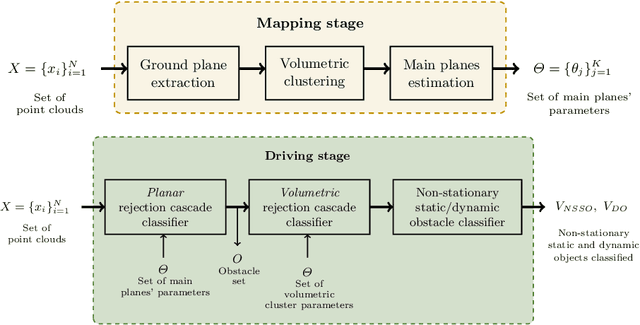


Abstract:Lidar has become an essential sensor for autonomous driving as it provides reliable depth estimation. Lidar is also the primary sensor used in building 3D maps which can be used even in the case of low-cost systems which do not use Lidar. Computation on Lidar point clouds is intensive as it requires processing of millions of points per second. Additionally there are many subsequent tasks such as clustering, detection, tracking and classification which makes real-time execution challenging. In this paper, we discuss real-time dynamic object detection algorithms which leverages previously mapped Lidar point clouds to reduce processing. The prior 3D maps provide a static background model and we formulate dynamic object detection as a background subtraction problem. Computation and modeling challenges in the mapping and online execution pipeline are described. We propose a rejection cascade architecture to subtract road regions and other 3D regions separately. We implemented an initial version of our proposed algorithm and evaluated the accuracy on CARLA simulator.
A Statistical Update of Grid Representations from Range Sensors
Jul 23, 2018



Abstract:In a wide range of robotic applications, being able to create a 3D model of the surrounding environment is a key feature for autonomous tasks. In this research report, we present a statistical model to perform 3D reconstructions of the environment from range sensors using an occupancy grid. To do so, we take into account all the available information obtained from the sensor, considering the distances traversed by the rays in each cell and seeking to reduce reconstruction errors caused by discretization. The approach has been validated qualitatively using the KITTI dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge