Lu Zheng
LiNR: Model Based Neural Retrieval on GPUs at LinkedIn
Jul 18, 2024



Abstract:This paper introduces LiNR, LinkedIn's large-scale, GPU-based retrieval system. LiNR supports a billion-sized index on GPU models. We discuss our experiences and challenges in creating scalable, differentiable search indexes using TensorFlow and PyTorch at production scale. In LiNR, both items and model weights are integrated into the model binary. Viewing index construction as a form of model training, we describe scaling our system for large indexes, incorporating full scans and efficient filtering. A key focus is on enabling attribute-based pre-filtering for exhaustive GPU searches, addressing the common challenge of post-filtering in KNN searches that often reduces system quality. We further provide multi-embedding retrieval algorithms and strategies for tackling cold start issues in retrieval. Our advancements in supporting larger indexes through quantization are also discussed. We believe LiNR represents one of the industry's first Live-updated model-based retrieval indexes. Applied to out-of-network post recommendations on LinkedIn Feed, LiNR has contributed to a 3% relative increase in professional daily active users. We envisage LiNR as a step towards integrating retrieval and ranking into a single GPU model, simplifying complex infrastructures and enabling end-to-end optimization of the entire differentiable infrastructure through gradient descent.
Multi-institutional Validation of Two-Streamed Deep Learning Method for Automated Delineation of Esophageal Gross Tumor Volume using planning-CT and FDG-PETCT
Oct 11, 2021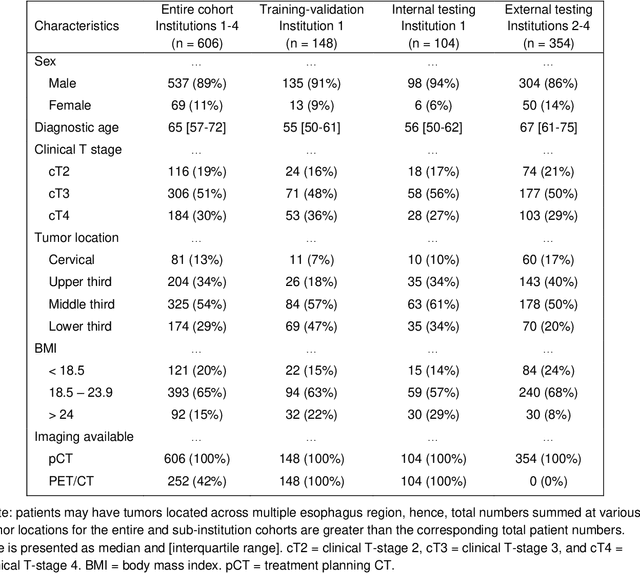
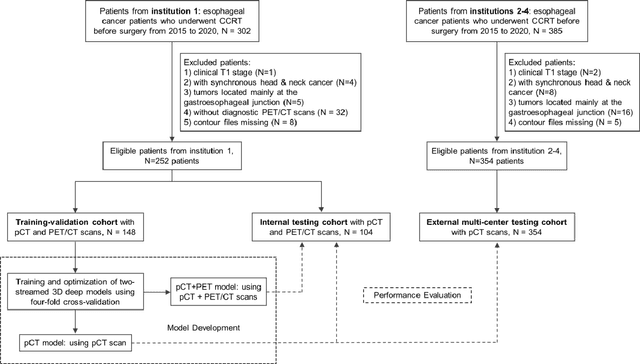
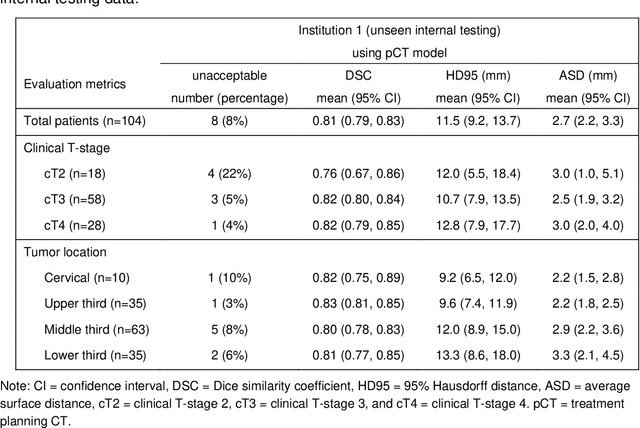
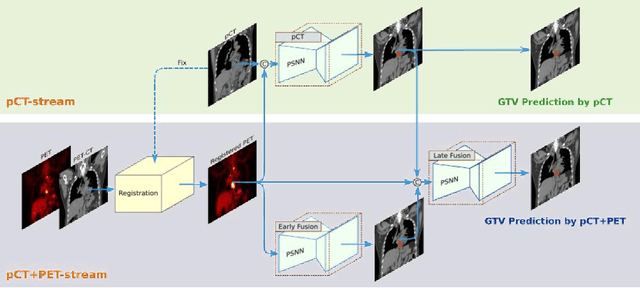
Abstract:Background: The current clinical workflow for esophageal gross tumor volume (GTV) contouring relies on manual delineation of high labor-costs and interuser variability. Purpose: To validate the clinical applicability of a deep learning (DL) multi-modality esophageal GTV contouring model, developed at 1 institution whereas tested at multiple ones. Methods and Materials: We collected 606 esophageal cancer patients from four institutions. 252 institution-1 patients had a treatment planning-CT (pCT) and a pair of diagnostic FDG-PETCT; 354 patients from other 3 institutions had only pCT. A two-streamed DL model for GTV segmentation was developed using pCT and PETCT scans of a 148 patient institution-1 subset. This built model had the flexibility of segmenting GTVs via only pCT or pCT+PETCT combined. For independent evaluation, the rest 104 institution-1 patients behaved as unseen internal testing, and 354 institutions 2-4 patients were used for external testing. We evaluated manual revision degrees by human experts to assess the contour-editing effort. The performance of the deep model was compared against 4 radiation oncologists in a multiuser study with 20 random external patients. Contouring accuracy and time were recorded for the pre-and post-DL assisted delineation process. Results: Our model achieved high segmentation accuracy in internal testing (mean Dice score: 0.81 using pCT and 0.83 using pCT+PET) and generalized well to external evaluation (mean DSC: 0.80). Expert assessment showed that the predicted contours of 88% patients need only minor or no revision. In multi-user evaluation, with the assistance of a deep model, inter-observer variation and required contouring time were reduced by 37.6% and 48.0%, respectively. Conclusions: Deep learning predicted GTV contours were in close agreement with the ground truth and could be adopted clinically with mostly minor or no changes.
Machine learning driven synthesis of few-layered WTe2
Oct 10, 2019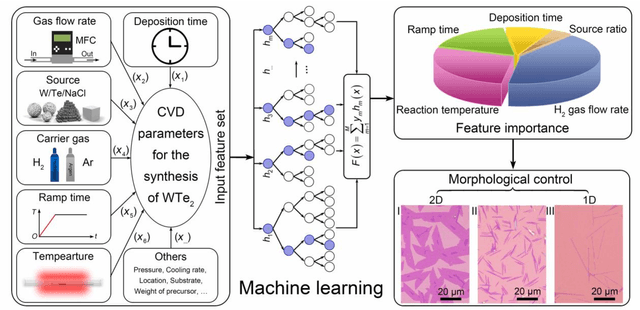
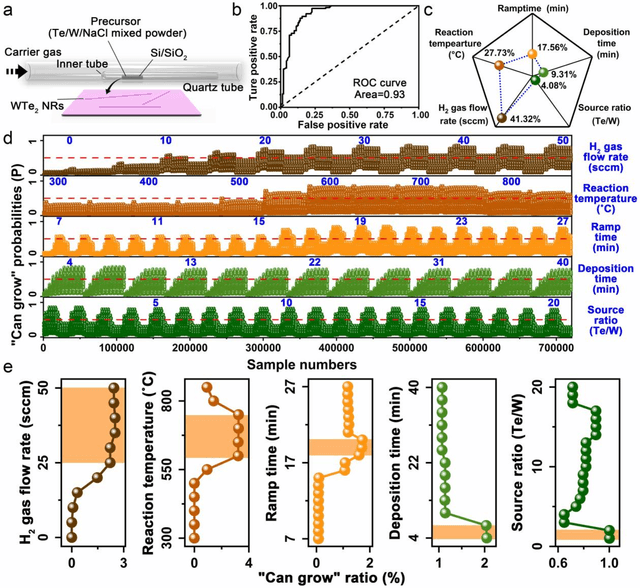
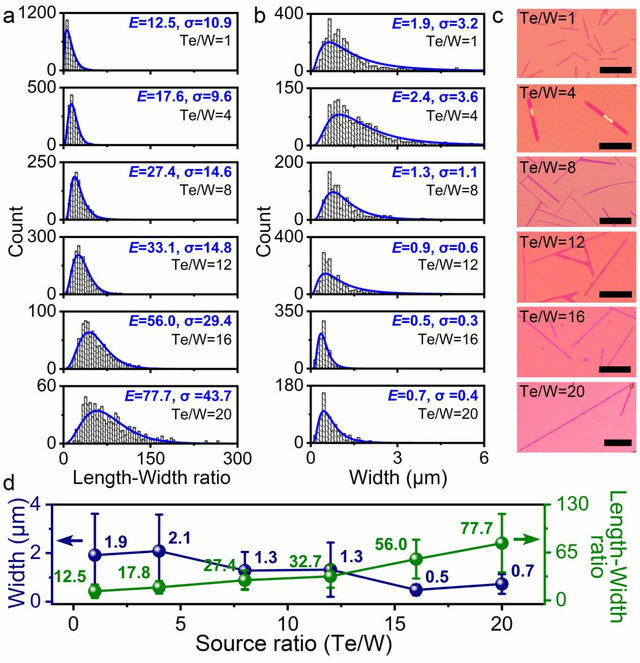
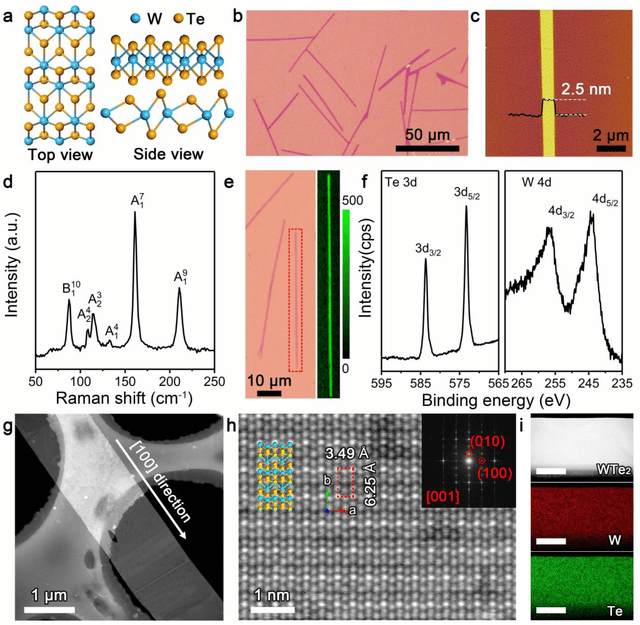
Abstract:Reducing the lateral scale of two-dimensional (2D) materials to one-dimensional (1D) has attracted substantial research interest not only to achieve competitive electronic device applications but also for the exploration of fundamental physical properties. Controllable synthesis of high-quality 1D nanoribbons (NRs) is thus highly desirable and essential for the further study. Traditional exploration of the optimal synthesis conditions of novel materials is based on the trial-and-error approach, which is time consuming, costly and laborious. Recently, machine learning (ML) has demonstrated promising capability in guiding material synthesis through effectively learning from the past data and then making recommendations. Here, we report the implementation of supervised ML for the chemical vapor deposition (CVD) synthesis of high-quality 1D few-layered WTe2 nanoribbons (NRs). The synthesis parameters of the WTe2 NRs are optimized by the trained ML model. On top of that, the growth mechanism of as-synthesized 1T' few-layered WTe2 NRs is further proposed, which may inspire the growth strategies for other 1D nanostructures. Our findings suggest that ML is a powerful and efficient approach to aid the synthesis of 1D nanostructures, opening up new opportunities for intelligent material development.
Belief Propagation by Message Passing in Junction Trees: Computing Each Message Faster Using GPU Parallelization
Feb 14, 2012



Abstract:Compiling Bayesian networks (BNs) to junction trees and performing belief propagation over them is among the most prominent approaches to computing posteriors in BNs. However, belief propagation over junction tree is known to be computationally intensive in the general case. Its complexity may increase dramatically with the connectivity and state space cardinality of Bayesian network nodes. In this paper, we address this computational challenge using GPU parallelization. We develop data structures and algorithms that extend existing junction tree techniques, and specifically develop a novel approach to computing each belief propagation message in parallel. We implement our approach on an NVIDIA GPU and test it using BNs from several applications. Experimentally, we study how junction tree parameters affect parallelization opportunities and hence the performance of our algorithm. We achieve speedups ranging from 0.68 to 9.18 for the BNs studied.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge