Liqing Cui
When Gradient Descent Meets Derivative-Free Optimization: A Match Made in Black-Box Scenario
May 17, 2023Abstract:Large pre-trained language models (PLMs) have garnered significant attention for their versatility and potential for solving a wide spectrum of natural language processing (NLP) tasks. However, the cost of running these PLMs may be prohibitive. Furthermore, PLMs may not be open-sourced due to commercial considerations and potential risks of misuse, such as GPT-3. The parameters and gradients of PLMs are unavailable in this scenario. To solve the issue, black-box tuning has been proposed, which utilizes derivative-free optimization (DFO), instead of gradient descent, for training task-specific continuous prompts. However, these gradient-free methods still exhibit a significant gap compared to gradient-based methods. In this paper, we introduce gradient descent into black-box tuning scenario through knowledge distillation. Furthermore, we propose a novel method GDFO, which integrates gradient descent and derivative-free optimization to optimize task-specific continuous prompts in a harmonized manner. Experimental results show that GDFO can achieve significant performance gains over previous state-of-the-art methods.
Identifying Emotion from Natural Walking
Sep 10, 2015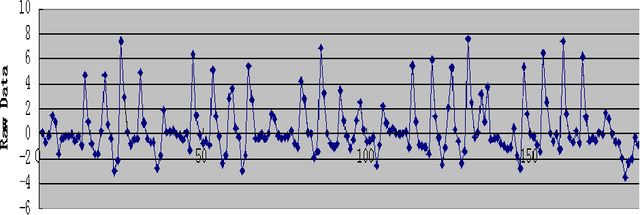
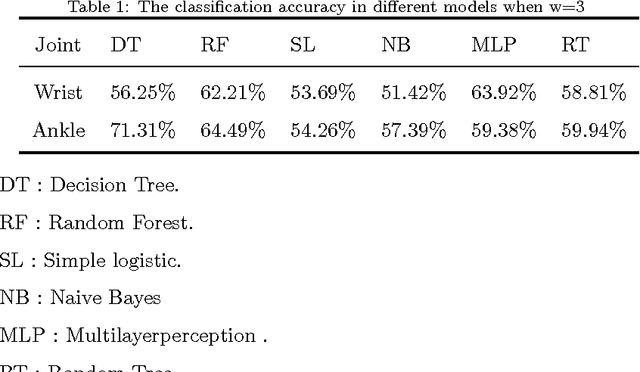
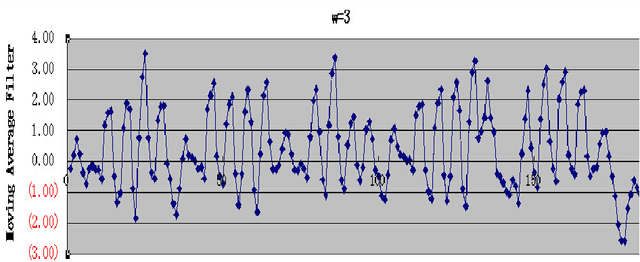
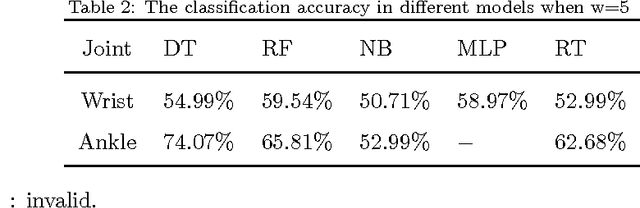
Abstract:Emotion identification from gait aims to automatically determine persons affective state, it has attracted a great deal of interests and offered immense potential value in action tendency, health care, psychological detection and human-computer(robot) interaction.In this paper, we propose a new method of identifying emotion from natural walking, and analyze the relevance between the traits of walking and affective states. After obtaining the pure acceleration data of wrist and ankle, we set a moving average filter window with different sizes w, then extract 114 features including time-domain, frequency-domain, power and distribution features from each data slice, and run principal component analysis (PCA) to reduce dimension. In experiments, we train SVM, Decision Tree, multilayerperception, Random Tree and Random Forest classification models, and compare the classification accuracy on data of wrist and ankle with respect to different w. The performance of emotion identification on acceleration data of ankle is better than wrist.Comparing different classification models' results, SVM has best accuracy of identifying anger and happy could achieve 90:31% and 89:76% respectively, and identification ratio of anger-happy is 87:10%.The anger-neutral-happy classification reaches 85%-78%-78%.The results show that it is capable of identifying personal emotional states through the gait of walking.
Recognition of Emotions using Kinects
Aug 04, 2015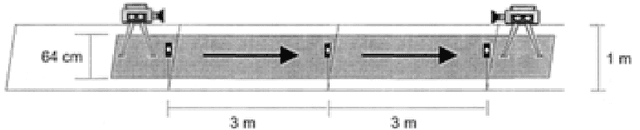
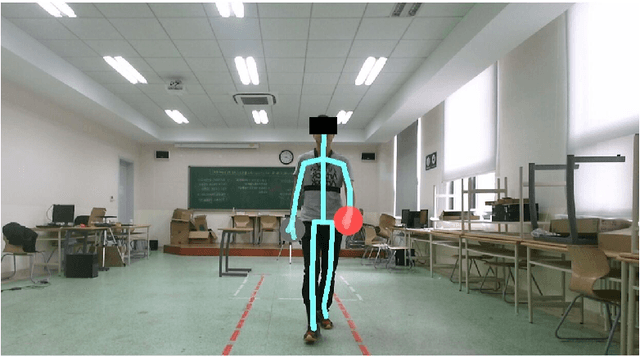

Abstract:Psychological studies indicate that emotional states are expressed in the way people walk and the human gait is investigated in terms of its ability to reveal a person's emotional state. And Microsoft Kinect is a rapidly developing, inexpensive, portable and no-marker motion capture system. This paper gives a new referable method to do emotion recognition, by using Microsoft Kinect to do gait pattern analysis, which has not been reported. $59$ subjects are recruited in this study and their gait patterns are record by two Kinect cameras. Significant joints selecting, Coordinate system transforming, Slider window gauss filter, Differential operation, and Data segmentation are used in data preprocessing. Feature extracting is based on Fourier transformation. By using the NaiveBayes, RandomForests, libSVM and SMO classification, the recognition rate of natural and unnatural emotions can reach above 70%.It is concluded that using the Kinect system can be a new method in recognition of emotions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge