Lingyi Wang
Knowledge-Driven 3D Semantic Spectrum Map: KE-VQ-Transformer Based UAV Semantic Communication and Map Completion
Dec 24, 2025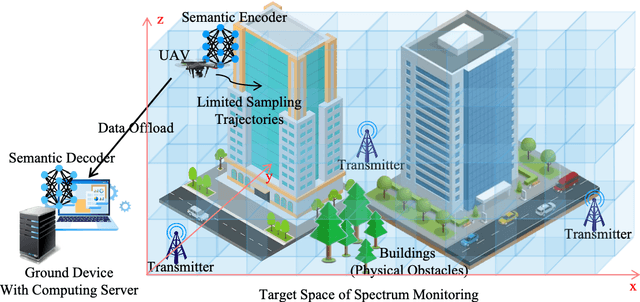
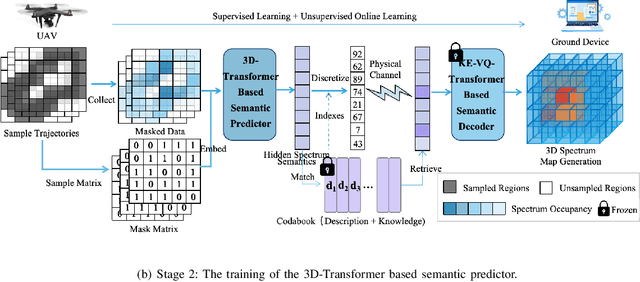
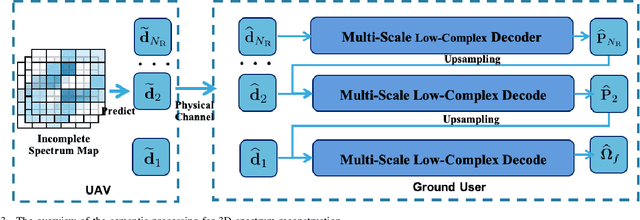
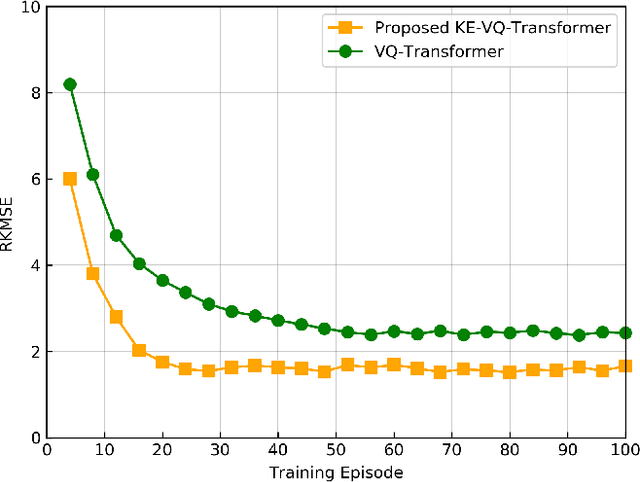
Abstract:Artificial intelligence (AI)-native three-dimensional (3D) spectrum maps are crucial in spectrum monitoring for intelligent communication networks. However, it is challenging to obtain and transmit 3D spectrum maps in a spectrum-efficient, computation-efficient, and AI-driven manner, especially under complex communication environments and sparse sampling data. In this paper, we consider practical air-to-ground semantic communications for spectrum map completion, where the unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) measures the spectrum at spatial points and extracts the spectrum semantics, which are then utilized to complete spectrum maps at the ground device. Since statistical machine learning can easily be misled by superficial data correlations with the lack of interpretability, we propose a novel knowledge-enhanced semantic spectrum map completion framework with two expert knowledge-driven constraints from physical signal propagation models. This framework can capture the real-world physics and avoid getting stuck in the mindset of superficial data distributions. Furthermore, a knowledge-enhanced vector-quantized Transformer (KE-VQ-Transformer) based multi-scale low-complex intelligent completion approach is proposed, where the sparse window is applied to avoid ultra-large 3D attention computation, and the multi-scale design improves the completion performance. The knowledge-enhanced mean square error (KMSE) and root KMSE (RKMSE) are introduced as novel metrics for semantic spectrum map completion that jointly consider the numerical precision and physical consistency with the signal propagation model, based on which a joint offline and online training method is developed with supervised and unsupervised knowledge loss. The simulation demonstrates that our proposed scheme outperforms the state-of-the-art benchmark schemes in terms of RKMSE.
Knowledge Graph-Based Explainable and Generalized Zero-Shot Semantic Communications
Jul 03, 2025Abstract:Data-driven semantic communication is based on superficial statistical patterns, thereby lacking interpretability and generalization, especially for applications with the presence of unseen data. To address these challenges, we propose a novel knowledge graph-enhanced zero-shot semantic communication (KGZS-SC) network. Guided by the structured semantic information from a knowledge graph-based semantic knowledge base (KG-SKB), our scheme provides generalized semantic representations and enables reasoning for unseen cases. Specifically, the KG-SKB aligns the semantic features in a shared category semantics embedding space and enhances the generalization ability of the transmitter through aligned semantic features, thus reducing communication overhead by selectively transmitting compact visual semantics. At the receiver, zero-shot learning (ZSL) is leveraged to enable direct classification for unseen cases without the demand for retraining or additional computational overhead, thereby enhancing the adaptability and efficiency of the classification process in dynamic or resource-constrained environments. The simulation results conducted on the APY datasets show that the proposed KGZS-SC network exhibits robust generalization and significantly outperforms existing SC frameworks in classifying unseen categories across a range of SNR levels.
World Model-Based Learning for Long-Term Age of Information Minimization in Vehicular Networks
May 03, 2025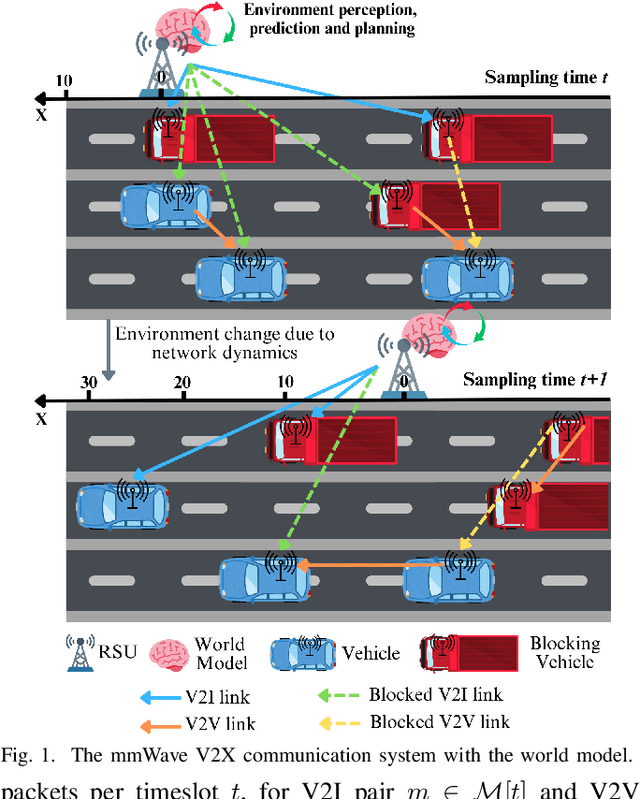
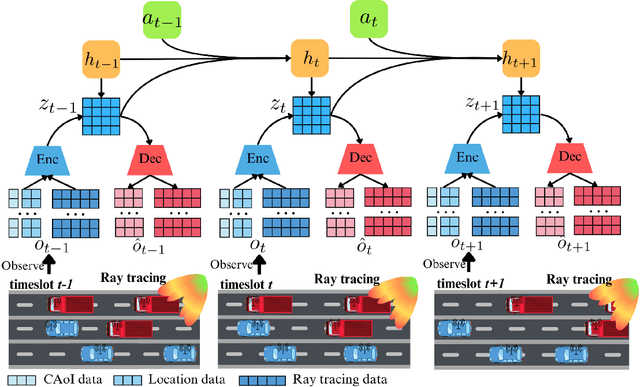
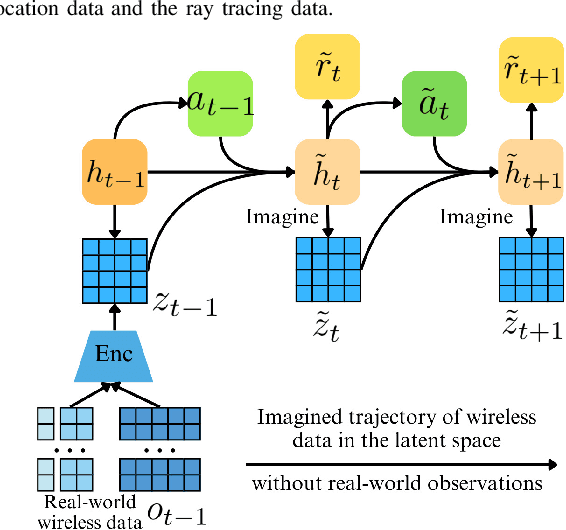
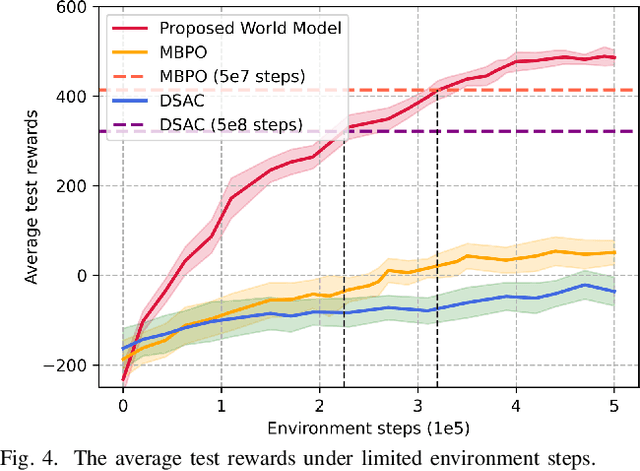
Abstract:Traditional reinforcement learning (RL)-based learning approaches for wireless networks rely on expensive trial-and-error mechanisms and real-time feedback based on extensive environment interactions, which leads to low data efficiency and short-sighted policies. These limitations become particularly problematic in complex, dynamic networks with high uncertainty and long-term planning requirements. To address these limitations, in this paper, a novel world model-based learning framework is proposed to minimize packet-completeness-aware age of information (CAoI) in a vehicular network. Particularly, a challenging representative scenario is considered pertaining to a millimeter-wave (mmWave) vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication network, which is characterized by high mobility, frequent signal blockages, and extremely short coherence time. Then, a world model framework is proposed to jointly learn a dynamic model of the mmWave V2X environment and use it to imagine trajectories for learning how to perform link scheduling. In particular, the long-term policy is learned in differentiable imagined trajectories instead of environment interactions. Moreover, owing to its imagination abilities, the world model can jointly predict time-varying wireless data and optimize link scheduling in real-world wireless and V2X networks. Thus, during intervals without actual observations, the world model remains capable of making efficient decisions. Extensive experiments are performed on a realistic simulator based on Sionna that integrates physics-based end-to-end channel modeling, ray-tracing, and scene geometries with material properties. Simulation results show that the proposed world model achieves a significant improvement in data efficiency, and achieves 26% improvement and 16% improvement in CAoI, respectively, compared to the model-based RL (MBRL) method and the model-free RL (MFRL) method.
DMWM: Dual-Mind World Model with Long-Term Imagination
Feb 11, 2025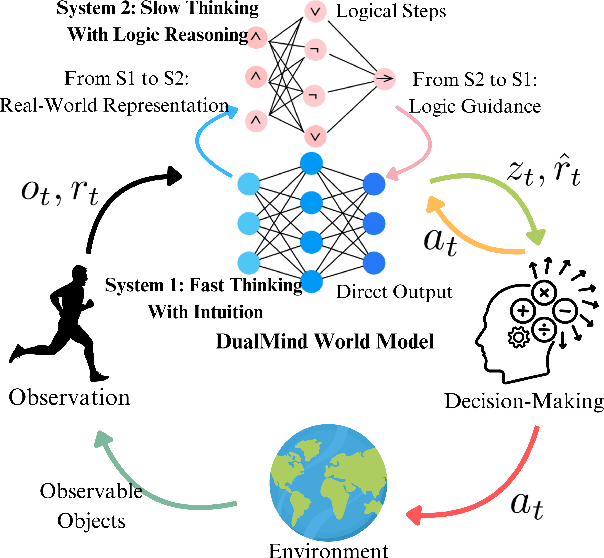
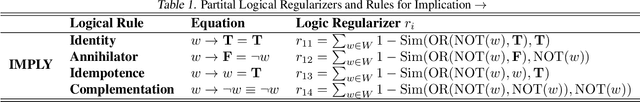
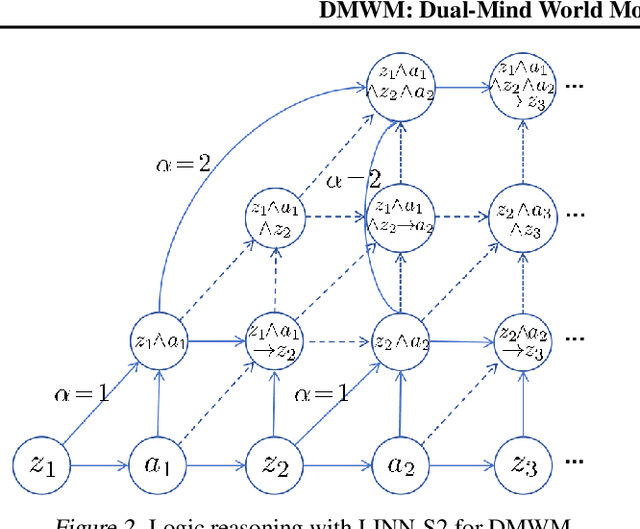
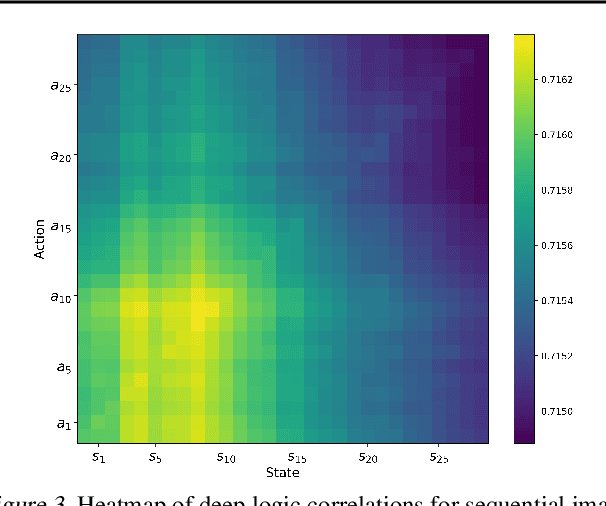
Abstract:Imagination in world models is crucial for enabling agents to learn long-horizon policy in a sample-efficient manner. Existing recurrent state-space model (RSSM)-based world models depend on single-step statistical inference to capture the environment dynamics, and, hence, they are unable to perform long-term imagination tasks due to the accumulation of prediction errors. Inspired by the dual-process theory of human cognition, we propose a novel dual-mind world model (DMWM) framework that integrates logical reasoning to enable imagination with logical consistency. DMWM is composed of two components: an RSSM-based System 1 (RSSM-S1) component that handles state transitions in an intuitive manner and a logic-integrated neural network-based System 2 (LINN-S2) component that guides the imagination process through hierarchical deep logical reasoning. The inter-system feedback mechanism is designed to ensure that the imagination process follows the logical rules of the real environment. The proposed framework is evaluated on benchmark tasks that require long-term planning from the DMControl suite. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that the proposed framework yields significant improvements in terms of logical coherence, trial efficiency, data efficiency and long-term imagination over the state-of-the-art world models.
IRS-Enhanced Secure Semantic Communication Networks: Cross-Layer and Context-Awared Resource Allocation
Nov 04, 2024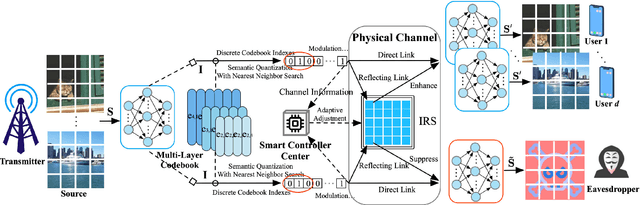
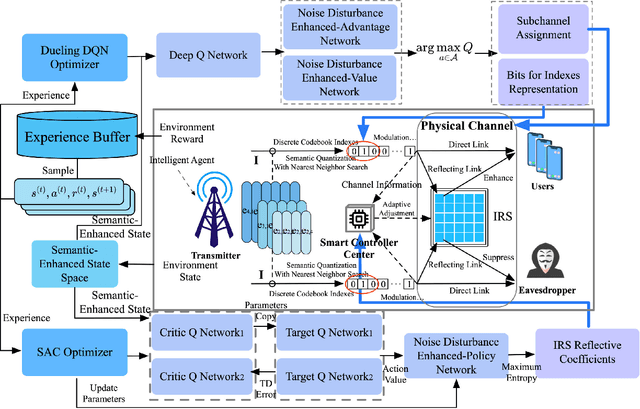
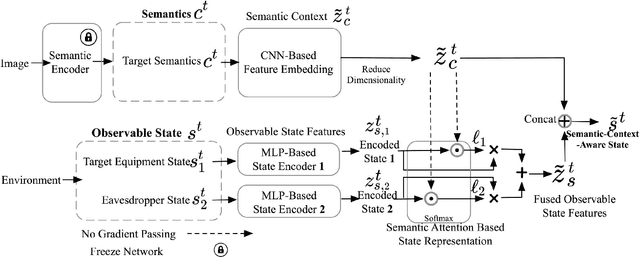
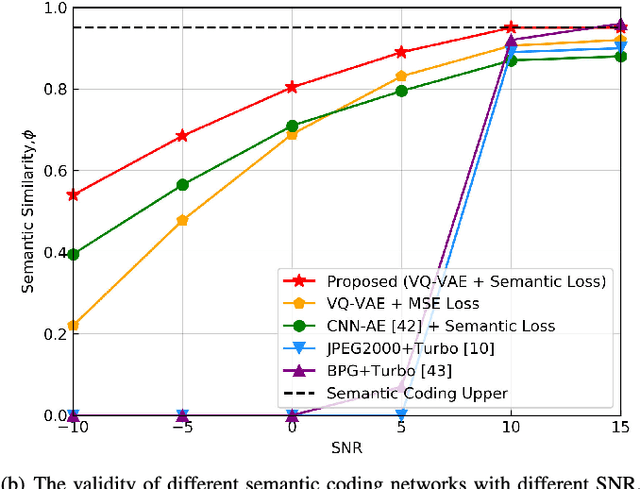
Abstract:Learning-task oriented semantic communication is pivotal in optimizing transmission efficiency by extracting and conveying essential semantics tailored to specific tasks, such as image reconstruction and classification. Nevertheless, the challenge of eavesdropping poses a formidable threat to semantic privacy due to the open nature of wireless communications. In this paper, intelligent reflective surface (IRS)-enhanced secure semantic communication (IRS-SSC) is proposed to guarantee the physical layer security from a task-oriented semantic perspective. Specifically, a multi-layer codebook is exploited to discretize continuous semantic features and describe semantics with different numbers of bits, thereby meeting the need for hierarchical semantic representation and further enhancing the transmission efficiency. Novel semantic security metrics, i.e., secure semantic rate (S-SR) and secure semantic spectrum efficiency (S-SSE), are defined to map the task-oriented security requirements at the application layer into the physical layer. To achieve artificial intelligence (AI)-native secure communication, we propose a noise disturbance enhanced hybrid deep reinforcement learning (NdeHDRL)-based resource allocation scheme. This scheme dynamically maximizes the S-SSE by jointly optimizing the bits for semantic representations, reflective coefficients of the IRS, and the subchannel assignment. Moreover, we propose a novel semantic context awared state space (SCA-SS) to fusion the high-dimensional semantic space and the observable system state space, which enables the agent to perceive semantic context and solves the dimensional catastrophe problem. Simulation results demonstrate the efficiency of our proposed schemes in both enhancing the security performance and the S-SSE compared to several benchmark schemes.
Adaptive Resource Allocation for Semantic Communication Networks
Dec 02, 2023Abstract:Semantic communication, recognized as a promising technology for future intelligent applications, has received widespread research attention. Despite the potential of semantic communication to enhance transmission reliability, especially in low signal-to-noise (SNR) environments, the critical issue of resource allocation and compatibility in the dynamic wireless environment remains largely unexplored. In this paper, we propose an adaptive semantic resource allocation paradigm with semantic-bit quantization (SBQ) compatibly for existing wireless communications, where the inaccurate environment perception introduced by the additional mapping relationship between semantic metrics and transmission metrics is solved. In order to investigate the performance of semantic communication networks, the quality of service for semantic communication (SC-QoS), including the semantic quantization efficiency (SQE) and transmission latency, is proposed for the first time. A problem of maximizing the overall effective SC-QoS is formulated by jointly optimizing the transmit beamforming of the base station, the bits for semantic representation, the subchannel assignment, and the bandwidth resource allocation. To address the non-convex formulated problem, an intelligent resource allocation scheme is proposed based on a hybrid deep reinforcement learning (DRL) algorithm, where the intelligent agent can perceive both semantic tasks and dynamic wireless environments. Simulation results demonstrate that our design can effectively combat semantic noise and achieve superior performance in wireless communications compared to several benchmark schemes. Furthermore, compared to mapping-guided paradigm based resource allocation schemes, our proposed adaptive scheme can achieve up to 13% performance improvement in terms of SC-QoS.
Hybrid Hierarchical DRL Enabled Resource Allocation for Secure Transmission in Multi-IRS-Assisted Sensing-Enhanced Spectrum Sharing Networks
Dec 02, 2023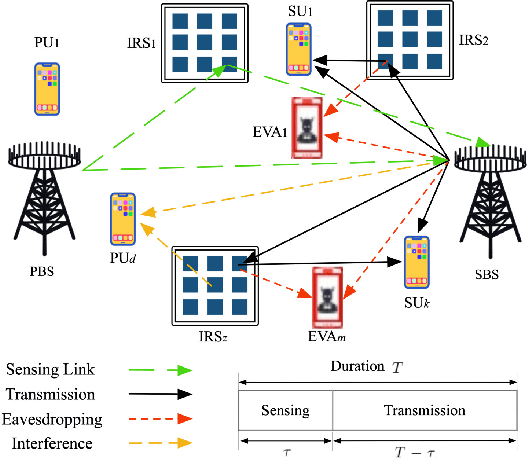
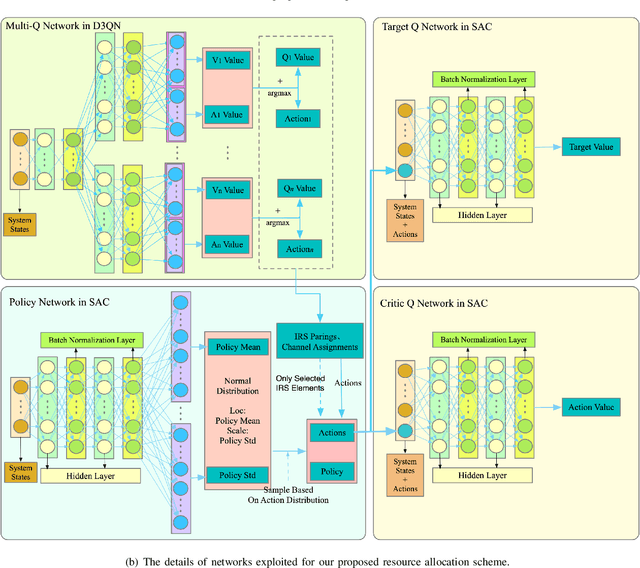
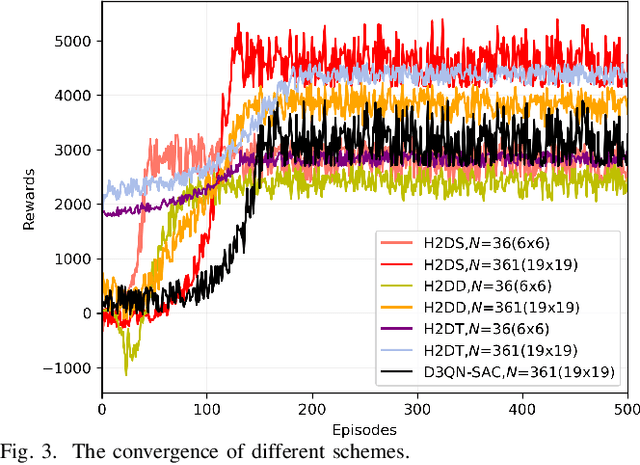
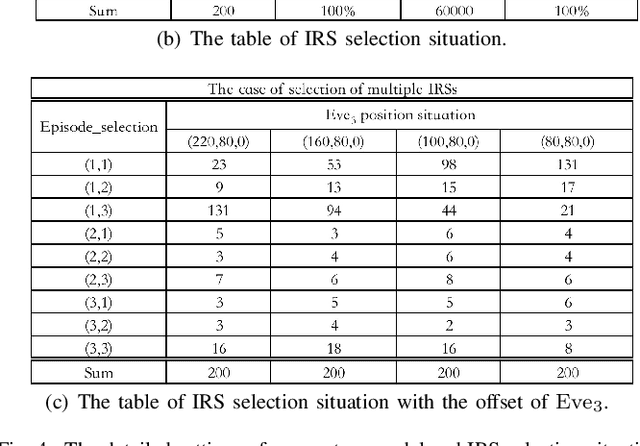
Abstract:Secure communications are of paramount importance in spectrum sharing networks due to the allocation and sharing characteristics of spectrum resources. To further explore the potential of intelligent reflective surfaces (IRSs) in enhancing spectrum sharing and secure transmission performance, a multiple intelligent reflection surface (multi-IRS)-assisted sensing-enhanced wideband spectrum sharing network is investigated by considering physical layer security techniques. An intelligent resource allocation scheme based on double deep Q networks (D3QN) algorithm and soft Actor-Critic (SAC) algorithm is proposed to maximize the secure transmission rate of the secondary network by jointly optimizing IRS pairings, subchannel assignment, transmit beamforming of the secondary base station, reflection coefficients of IRSs and the sensing time. To tackle the sparse reward problem caused by a significant amount of reflection elements of multiple IRSs, the method of hierarchical reinforcement learning is exploited. An alternative optimization (AO)-based conventional mathematical scheme is introduced to verify the computational complexity advantage of our proposed intelligent scheme. Simulation results demonstrate the efficiency of our proposed intelligent scheme as well as the superiority of multi-IRS design in enhancing secrecy rate and spectrum utilization. It is shown that inappropriate deployment of IRSs can reduce the security performance with the presence of multiple eavesdroppers (Eves), and the arrangement of IRSs deserves further consideration.
Graph Neural Network-Based Scheduling for Multi-UAV-Enabled Communications in D2D Networks
Feb 15, 2022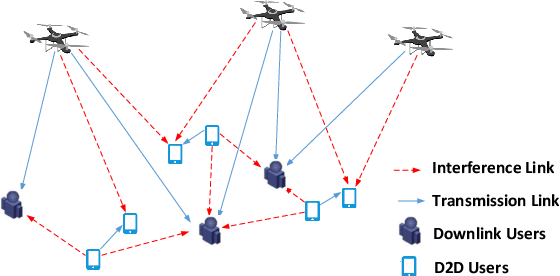
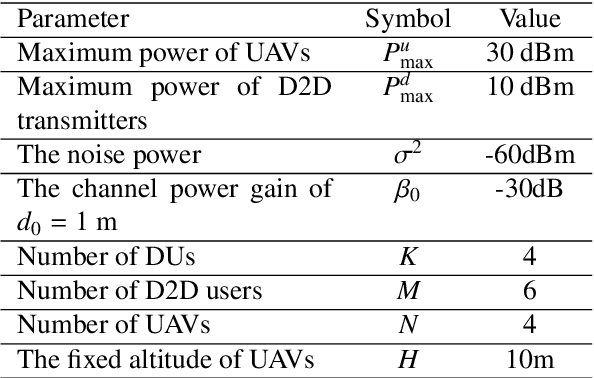
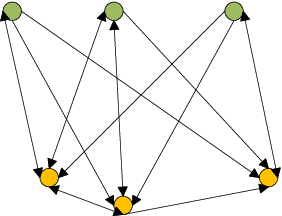
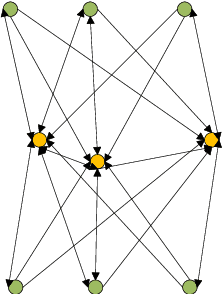
Abstract:In this paper, we jointly design the power control and position dispatch for Multi-unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV)-enabled communication in device-to-device (D2D) networks. Our objective is to maximize the total transmission rate of downlink users (DUs). Meanwhile, the quality of service (QoS) of all D2D users must be satisfied. We comprehensively considered the interference among D2D communications and downlink transmissions. The original problem is strongly non-convex, which requires high computational complexity for traditional optimization methods. And to make matters worse, the results are not necessarily globally optimal. In this paper, we propose a novel graph neural networks (GNN) based approach that can map the considered system into a specific graph structure and achieve the optimal solution in a low complexity manner. Particularly, we first construct a GNN-based model for the proposed network, in which the transmission links and interference links are formulated as vertexes and edges, respectively. Then, by taking the channel state information and the coordinates of ground users as the inputs, as well as the location of UAVs and the transmission power of all transmitters as outputs, we obtain the mapping from inputs to outputs through training the parameters of GNN. Simulation results verified that the way to maximize the total transmission rate of DUs can be extracted effectively via the training on samples. Moreover, it also shows that the performance of proposed GNN-based method is better than that of traditional means.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge