Lingxi Guo
Fast and Interpretable 2D Homography Decomposition: Similarity-Kernel-Similarity and Affine-Core-Affine Transformations
Feb 28, 2024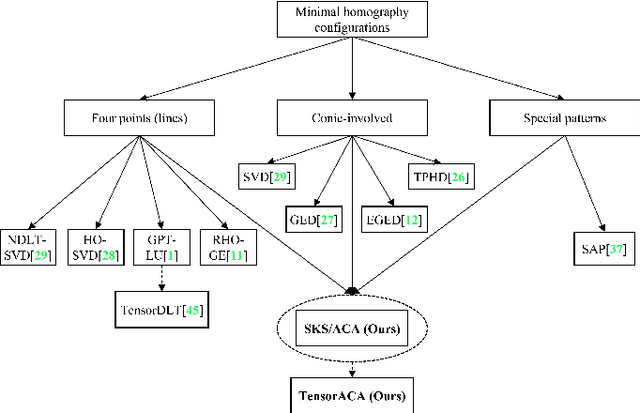
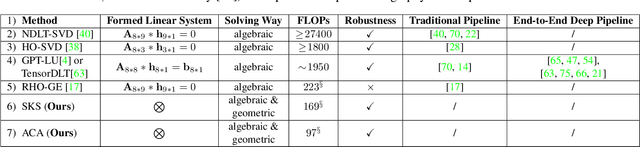
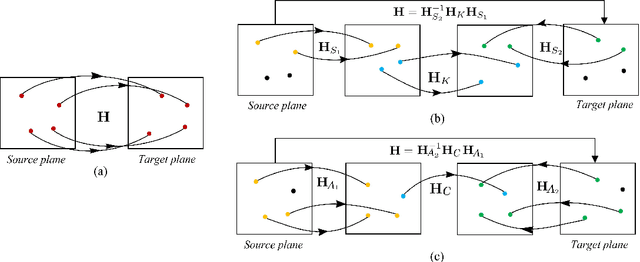
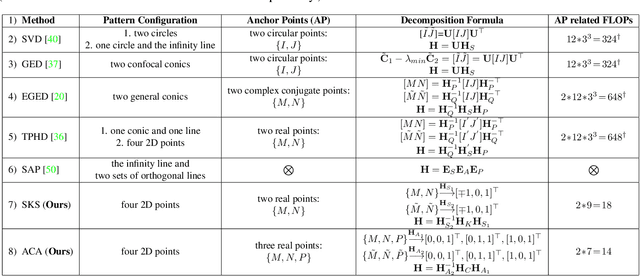
Abstract:In this paper, we present two fast and interpretable decomposition methods for 2D homography, which are named Similarity-Kernel-Similarity (SKS) and Affine-Core-Affine (ACA) transformations respectively. Under the minimal $4$-point configuration, the first and the last similarity transformations in SKS are computed by two anchor points on target and source planes, respectively. Then, the other two point correspondences can be exploited to compute the middle kernel transformation with only four parameters. Furthermore, ACA uses three anchor points to compute the first and the last affine transformations, followed by computation of the middle core transformation utilizing the other one point correspondence. ACA can compute a homography up to a scale with only $85$ floating-point operations (FLOPs), without even any division operations. Therefore, as a plug-in module, ACA facilitates the traditional feature-based Random Sample Consensus (RANSAC) pipeline, as well as deep homography pipelines estimating $4$-point offsets. In addition to the advantages of geometric parameterization and computational efficiency, SKS and ACA can express each element of homography by a polynomial of input coordinates ($7$th degree to $9$th degree), extend the existing essential Similarity-Affine-Projective (SAP) decomposition and calculate 2D affine transformations in a unified way. Source codes are released in https://github.com/cscvlab/SKS-Homography.
A Structure Feature Algorithm for Multi-modal Forearm Registration
Nov 10, 2021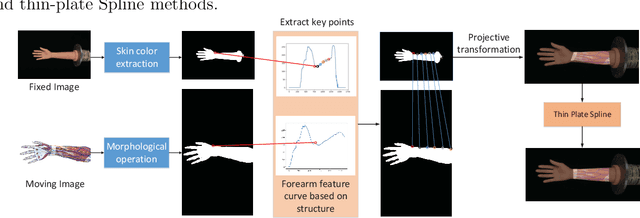
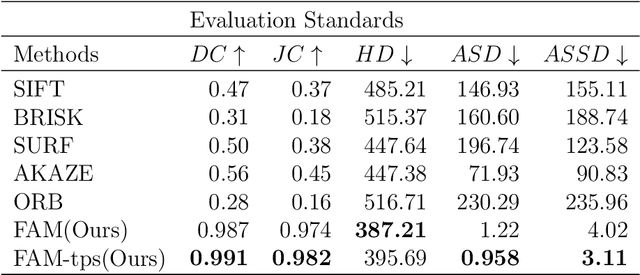
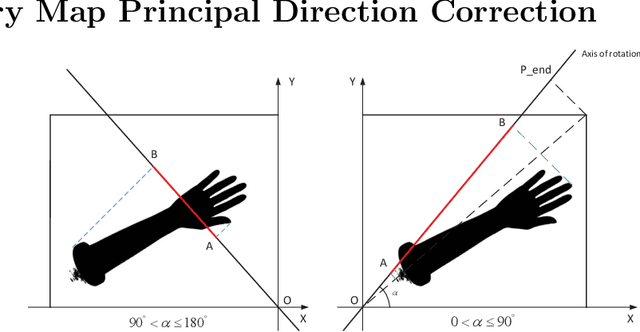
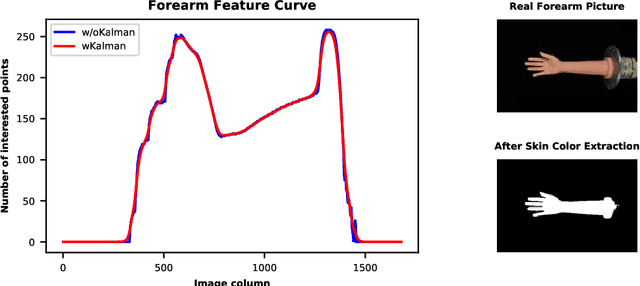
Abstract:Augmented reality technology based on image registration is becoming increasingly popular for the convenience of pre-surgery preparation and medical education. This paper focuses on the registration of forearm images and digital anatomical models. Due to the difference in texture features of forearm multi-modal images, this paper proposes a forearm feature representation curve (FFRC) based on structure compliant multi-modal image registration framework (FAM) for the forearm.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge