Lilian Ngweta
Towards LLMs Robustness to Changes in Prompt Format Styles
Apr 09, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have gained popularity in recent years for their utility in various applications. However, they are sensitive to non-semantic changes in prompt formats, where small changes in the prompt format can lead to significant performance fluctuations. In the literature, this problem is commonly referred to as prompt brittleness. Previous research on prompt engineering has focused mainly on developing techniques for identifying the optimal prompt for specific tasks. Some studies have also explored the issue of prompt brittleness and proposed methods to quantify performance variations; however, no simple solution has been found to address this challenge. We propose Mixture of Formats (MOF), a simple and efficient technique for addressing prompt brittleness in LLMs by diversifying the styles used in the prompt few-shot examples. MOF was inspired by computer vision techniques that utilize diverse style datasets to prevent models from associating specific styles with the target variable. Empirical results show that our proposed technique reduces style-induced prompt brittleness in various LLMs while also enhancing overall performance across prompt variations and different datasets.
Aligners: Decoupling LLMs and Alignment
Mar 11, 2024

Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) need to be aligned with human expectations to ensure their safety and utility in most applications. Alignment is challenging, costly, and needs to be repeated for every LLM and alignment criterion. We propose to decouple LLMs and alignment by training aligner models that can be used to align any LLM for a given criteria on an as-needed basis, thus also reducing the potential negative impacts of alignment on performance. Our recipe for training the aligner models solely relies on synthetic data generated with a (prompted) LLM and can be easily adjusted for a variety of alignment criteria. We illustrate our method by training an "ethical" aligner and verify its efficacy empirically.
Simple Disentanglement of Style and Content in Visual Representations
Feb 20, 2023



Abstract:Learning visual representations with interpretable features, i.e., disentangled representations, remains a challenging problem. Existing methods demonstrate some success but are hard to apply to large-scale vision datasets like ImageNet. In this work, we propose a simple post-processing framework to disentangle content and style in learned representations from pre-trained vision models. We model the pre-trained features probabilistically as linearly entangled combinations of the latent content and style factors and develop a simple disentanglement algorithm based on the probabilistic model. We show that the method provably disentangles content and style features and verify its efficacy empirically. Our post-processed features yield significant domain generalization performance improvements when the distribution shift occurs due to style changes or style-related spurious correlations.
Attack Techniques and Threat Identification for Vulnerabilities
Jun 22, 2022
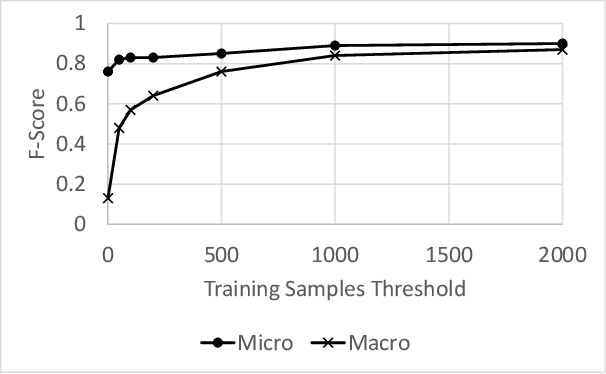
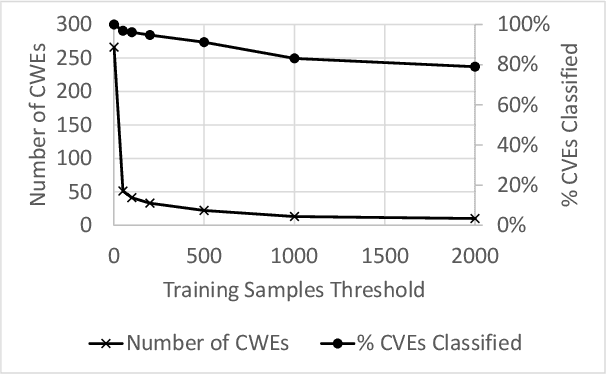
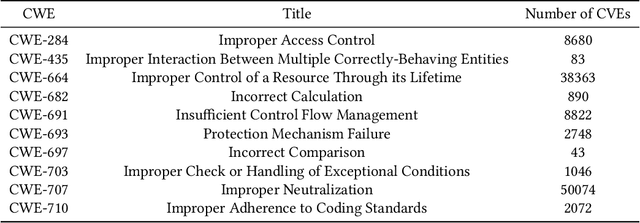
Abstract:Modern organizations struggle with insurmountable number of vulnerabilities that are discovered and reported by their network and application vulnerability scanners. Therefore, prioritization and focus become critical, to spend their limited time on the highest risk vulnerabilities. In doing this, it is important for these organizations not only to understand the technical descriptions of the vulnerabilities, but also to gain insights into attackers' perspectives. In this work, we use machine learning and natural language processing techniques, as well as several publicly available data sets to provide an explainable mapping of vulnerabilities to attack techniques and threat actors. This work provides new security intelligence, by predicting which attack techniques are most likely to be used to exploit a given vulnerability and which threat actors are most likely to conduct the exploitation. Lack of labeled data and different vocabularies make mapping vulnerabilities to attack techniques at scale a challenging problem that cannot be addressed easily using supervised or unsupervised (similarity search) learning techniques. To solve this problem, we first map the vulnerabilities to a standard set of common weaknesses, and then common weaknesses to the attack techniques. This approach yields a Mean Reciprocal Rank (MRR) of 0.95, an accuracy comparable with those reported for state-of-the-art systems. Our solution has been deployed to IBM Security X-Force Red Vulnerability Management Services, and in production since 2021. The solution helps security practitioners to assist customers to manage and prioritize their vulnerabilities, providing them with an explainable mapping of vulnerabilities to attack techniques and threat actors
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge