Leqi Zou
MegaScale: Scaling Large Language Model Training to More Than 10,000 GPUs
Feb 23, 2024



Abstract:We present the design, implementation and engineering experience in building and deploying MegaScale, a production system for training large language models (LLMs) at the scale of more than 10,000 GPUs. Training LLMs at this scale brings unprecedented challenges to training efficiency and stability. We take a full-stack approach that co-designs the algorithmic and system components across model block and optimizer design, computation and communication overlapping, operator optimization, data pipeline, and network performance tuning. Maintaining high efficiency throughout the training process (i.e., stability) is an important consideration in production given the long extent of LLM training jobs. Many hard stability issues only emerge at large scale, and in-depth observability is the key to address them. We develop a set of diagnosis tools to monitor system components and events deep in the stack, identify root causes, and derive effective techniques to achieve fault tolerance and mitigate stragglers. MegaScale achieves 55.2% Model FLOPs Utilization (MFU) when training a 175B LLM model on 12,288 GPUs, improving the MFU by 1.34x compared to Megatron-LM. We share our operational experience in identifying and fixing failures and stragglers. We hope by articulating the problems and sharing our experience from a systems perspective, this work can inspire future LLM systems research.
Monolith: Real Time Recommendation System With Collisionless Embedding Table
Sep 27, 2022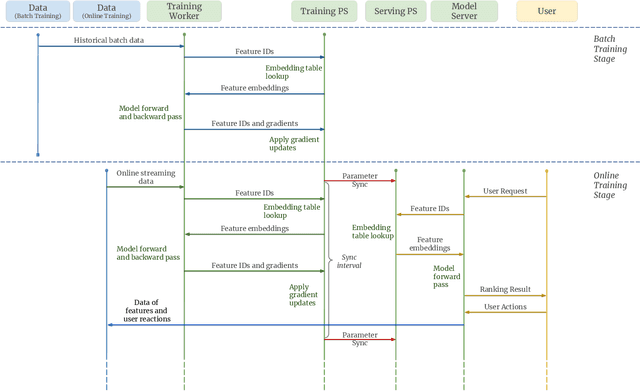
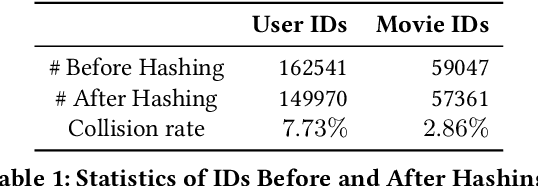
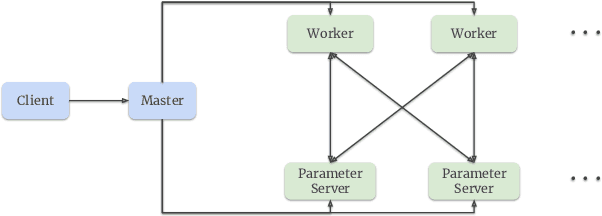
Abstract:Building a scalable and real-time recommendation system is vital for many businesses driven by time-sensitive customer feedback, such as short-videos ranking or online ads. Despite the ubiquitous adoption of production-scale deep learning frameworks like TensorFlow or PyTorch, these general-purpose frameworks fall short of business demands in recommendation scenarios for various reasons: on one hand, tweaking systems based on static parameters and dense computations for recommendation with dynamic and sparse features is detrimental to model quality; on the other hand, such frameworks are designed with batch-training stage and serving stage completely separated, preventing the model from interacting with customer feedback in real-time. These issues led us to reexamine traditional approaches and explore radically different design choices. In this paper, we present Monolith, a system tailored for online training. Our design has been driven by observations of our application workloads and production environment that reflects a marked departure from other recommendations systems. Our contributions are manifold: first, we crafted a collisionless embedding table with optimizations such as expirable embeddings and frequency filtering to reduce its memory footprint; second, we provide an production-ready online training architecture with high fault-tolerance; finally, we proved that system reliability could be traded-off for real-time learning. Monolith has successfully landed in the BytePlus Recommend product.
CowClip: Reducing CTR Prediction Model Training Time from 12 hours to 10 minutes on 1 GPU
Apr 22, 2022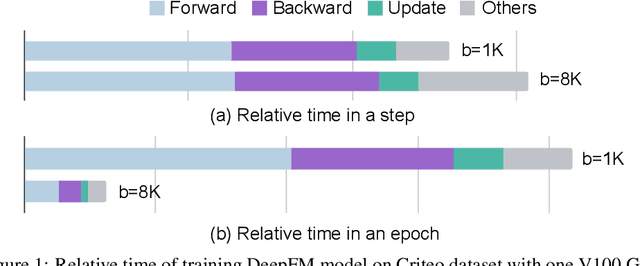
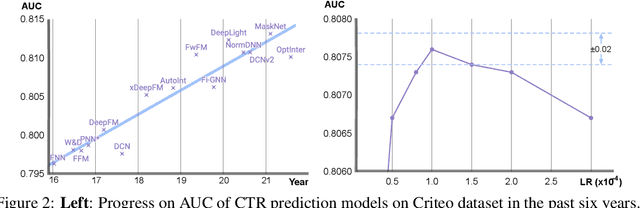
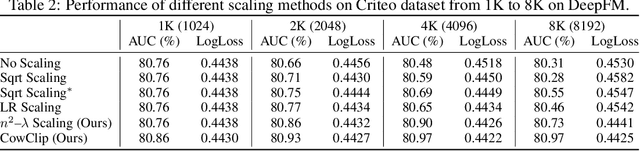
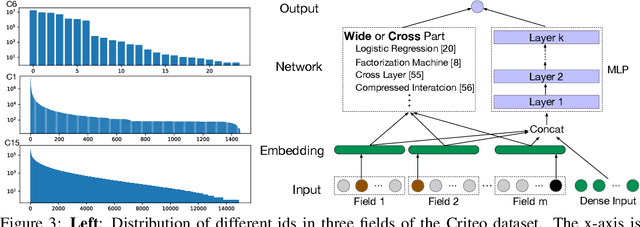
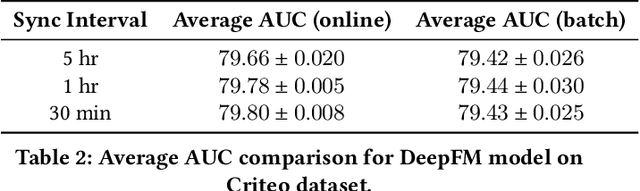
Abstract:The click-through rate (CTR) prediction task is to predict whether a user will click on the recommended item. As mind-boggling amounts of data are produced online daily, accelerating CTR prediction model training is critical to ensuring an up-to-date model and reducing the training cost. One approach to increase the training speed is to apply large batch training. However, as shown in computer vision and natural language processing tasks, training with a large batch easily suffers from the loss of accuracy. Our experiments show that previous scaling rules fail in the training of CTR prediction neural networks. To tackle this problem, we first theoretically show that different frequencies of ids make it challenging to scale hyperparameters when scaling the batch size. To stabilize the training process in a large batch size setting, we develop the adaptive Column-wise Clipping (CowClip). It enables an easy and effective scaling rule for the embeddings, which keeps the learning rate unchanged and scales the L2 loss. We conduct extensive experiments with four CTR prediction networks on two real-world datasets and successfully scaled 128 times the original batch size without accuracy loss. In particular, for CTR prediction model DeepFM training on the Criteo dataset, our optimization framework enlarges the batch size from 1K to 128K with over 0.1% AUC improvement and reduces training time from 12 hours to 10 minutes on a single V100 GPU. Our code locates at https://github.com/bytedance/LargeBatchCTR.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge