Latha Pemula
SPot-the-Difference Self-Supervised Pre-training for Anomaly Detection and Segmentation
Jul 28, 2022



Abstract:Visual anomaly detection is commonly used in industrial quality inspection. In this paper, we present a new dataset as well as a new self-supervised learning method for ImageNet pre-training to improve anomaly detection and segmentation in 1-class and 2-class 5/10/high-shot training setups. We release the Visual Anomaly (VisA) Dataset consisting of 10,821 high-resolution color images (9,621 normal and 1,200 anomalous samples) covering 12 objects in 3 domains, making it the largest industrial anomaly detection dataset to date. Both image and pixel-level labels are provided. We also propose a new self-supervised framework - SPot-the-difference (SPD) - which can regularize contrastive self-supervised pre-training, such as SimSiam, MoCo and SimCLR, to be more suitable for anomaly detection tasks. Our experiments on VisA and MVTec-AD dataset show that SPD consistently improves these contrastive pre-training baselines and even the supervised pre-training. For example, SPD improves Area Under the Precision-Recall curve (AU-PR) for anomaly segmentation by 5.9% and 6.8% over SimSiam and supervised pre-training respectively in the 2-class high-shot regime. We open-source the project at http://github.com/amazon-research/spot-diff .
Towards Total Recall in Industrial Anomaly Detection
Jun 15, 2021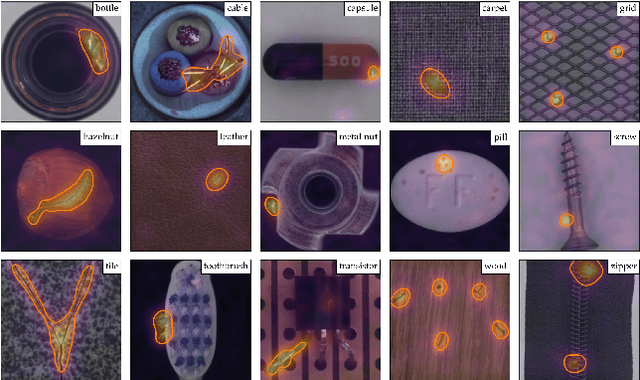
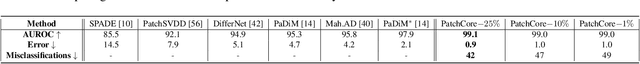
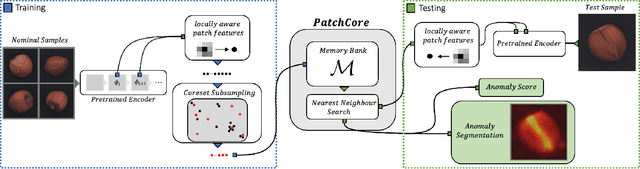
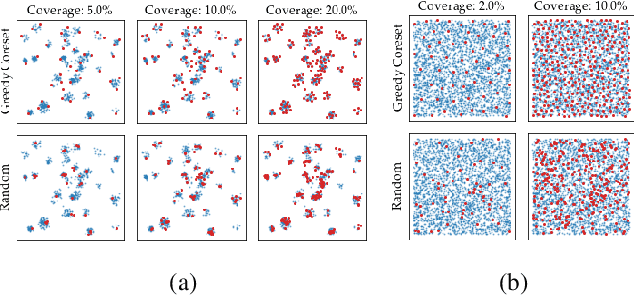
Abstract:Being able to spot defective parts is a critical component in large-scale industrial manufacturing. A particular challenge that we address in this work is the cold-start problem: fit a model using nominal (non-defective) example images only. While handcrafted solutions per class are possible, the goal is to build systems that work well simultaneously on many different tasks automatically. The best peforming approaches combine embeddings from ImageNet models with an outlier detection model. In this paper, we extend on this line of work and propose PatchCore, which uses a maximally representative memory bank of nominal patch-features. PatchCore offers competitive inference times while achieving state-of-the-art performance for both detection and localization. On the standard dataset MVTec AD, PatchCore achieves an image-level anomaly detection AUROC score of $99.1\%$, more than halving the error compared to the next best competitor. We further report competitive results on two additional datasets and also find competitive results in the few samples regime.
Radio Transformer Networks: Attention Models for Learning to Synchronize in Wireless Systems
May 03, 2016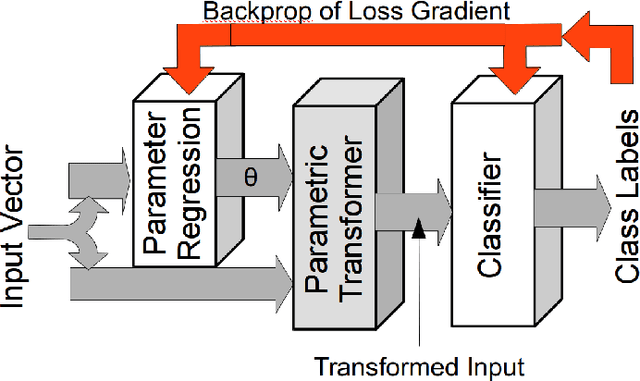
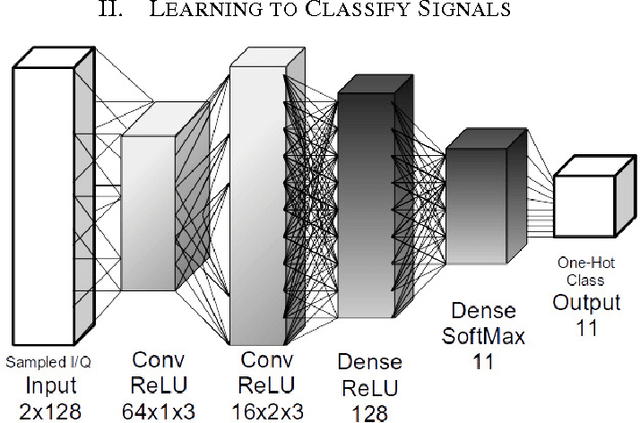
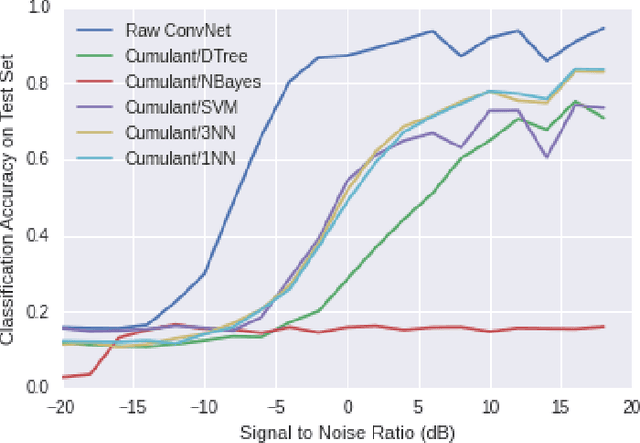
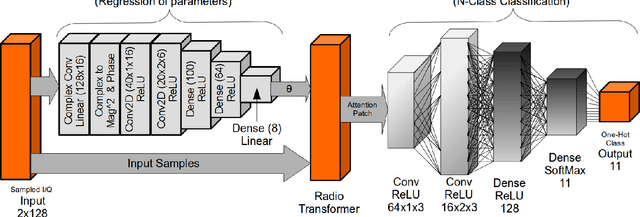
Abstract:We introduce learned attention models into the radio machine learning domain for the task of modulation recognition by leveraging spatial transformer networks and introducing new radio domain appropriate transformations. This attention model allows the network to learn a localization network capable of synchronizing and normalizing a radio signal blindly with zero knowledge of the signals structure based on optimization of the network for classification accuracy, sparse representation, and regularization. Using this architecture we are able to outperform our prior results in accuracy vs signal to noise ratio against an identical system without attention, however we believe such an attention model has implication far beyond the task of modulation recognition.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge