Lang Zhou
Department of Pathology & Clinical Bioinformatics, Erasmus University Medical Center Rotterdam, Department of Computer Science, Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam
ReViP: Reducing False Completion in Vision-Language-Action Models with Vision-Proprioception Rebalance
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models have advanced robotic manipulation by combining vision, language, and proprioception to predict actions. However, previous methods fuse proprioceptive signals directly with VLM-encoded vision-language features, resulting in state-dominant bias and false completions despite visible execution failures. We attribute this to modality imbalance, where policies over-rely on internal state while underusing visual evidence. To address this, we present ReViP, a novel VLA framework with Vision-Proprioception Rebalance to enhance visual grounding and robustness under perturbations. The key insight is to introduce auxiliary task-aware environment priors to adaptively modulate the coupling between semantic perception and proprioceptive dynamics. Specifically, we use an external VLM as a task-stage observer to extract real-time task-centric visual cues from visual observations, which drive a Vision-Proprioception Feature-wise Linear Modulation to enhance environmental awareness and reduce state-driven errors. Moreover, to evaluate false completion, we propose the first False-Completion Benchmark Suite built on LIBERO with controlled settings such as Object-Drop. Extensive experiments show that ReViP effectively reduces false-completion rates and improves success rates over strong VLA baselines on our suite, with gains extending to LIBERO, RoboTwin 2.0, and real-world evaluations.
Multilingual BERT language model for medical tasks: Evaluation on domain-specific adaptation and cross-linguality
Oct 31, 2025Abstract:In multilingual healthcare applications, the availability of domain-specific natural language processing(NLP) tools is limited, especially for low-resource languages. Although multilingual bidirectional encoder representations from transformers (BERT) offers a promising motivation to mitigate the language gap, the medical NLP tasks in low-resource languages are still underexplored. Therefore, this study investigates how further pre-training on domain-specific corpora affects model performance on medical tasks, focusing on three languages: Dutch, Romanian and Spanish. In terms of further pre-training, we conducted four experiments to create medical domain models. Then, these models were fine-tuned on three downstream tasks: Automated patient screening in Dutch clinical notes, named entity recognition in Romanian and Spanish clinical notes. Results show that domain adaptation significantly enhanced task performance. Furthermore, further differentiation of domains, e.g. clinical and general biomedical domains, resulted in diverse performances. The clinical domain-adapted model outperformed the more general biomedical domain-adapted model. Moreover, we observed evidence of cross-lingual transferability. Moreover, we also conducted further investigations to explore potential reasons contributing to these performance differences. These findings highlight the feasibility of domain adaptation and cross-lingual ability in medical NLP. Within the low-resource language settings, these findings can provide meaningful guidance for developing multilingual medical NLP systems to mitigate the lack of training data and thereby improve the model performance.
Cross-Lingual Consistency: A Novel Inference Framework for Advancing Reasoning in Large Language Models
Apr 02, 2025Abstract:Chain-of-thought (CoT) has emerged as a critical mechanism for enhancing reasoning capabilities in large language models (LLMs), with self-consistency demonstrating notable promise in boosting performance. However, inherent linguistic biases in multilingual training corpora frequently cause semantic drift and logical inconsistencies, especially in sub-10B parameter LLMs handling complex inference tasks. To overcome these constraints, we propose the Cross-Lingual Consistency (CLC) framework, an innovative inference paradigm that integrates multilingual reasoning paths through majority voting to elevate LLMs' reasoning capabilities. Empirical evaluations on the CMATH dataset reveal CLC's superiority over the conventional self-consistency method, delivering 9.5%, 6.5%, and 6.0% absolute accuracy gains for DeepSeek-Math-7B-Instruct, Qwen2.5-Math-7B-Instruct, and Gemma2-9B-Instruct respectively. Expanding CLC's linguistic scope to 11 diverse languages implies two synergistic benefits: 1) neutralizing linguistic biases in multilingual training corpora through multilingual ensemble voting, 2) escaping monolingual reasoning traps by exploring the broader multilingual solution space. This dual benefits empirically enables more globally optimal reasoning paths compared to monolingual self-consistency baselines, as evidenced by the 4.1%-18.5% accuracy gains using Gemma2-9B-Instruct on the MGSM dataset.
Mars Rover Localization Based on A2G Obstacle Distribution Pattern Matching
Oct 07, 2022Abstract:Rover localization is one of the perquisites for large scale rover exploration. In NASA's Mars 2020 mission, the Ingenuity helicopter is carried together with the rover, which is capable of obtaining high-resolution imagery of Mars terrain, and it is possible to perform localization based on aerial-to-ground (A2G) imagery correspondence. However, considering the low-texture nature of the Mars terrain, and large perspective changes between UAV and rover imagery, traditional image matching methods will struggle to obtain valid image correspondence. In this paper we propose a novel pipeline for Mars rover localization. An algorithm combing image-based rock detection and rock distribution pattern matching is used to acquire A2G imagery correspondence, thus establishing the rover position in a UAV-generated ground map. Feasibility of this method is evaluated on sample data from a Mars analogue environment. The proposed method can serve as a reliable assist in future Mars missions.
Deep Double-Side Learning Ensemble Model for Few-Shot Parkinson Speech Recognition
Jun 20, 2020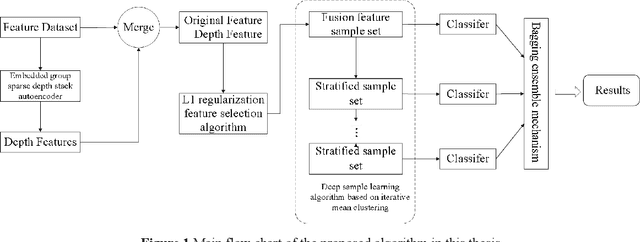

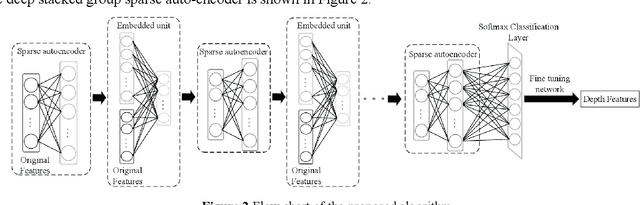

Abstract:Diagnosis and therapeutic effect assessment of Parkinson disease based on voice data are very important,but its few-shot learning problem is challenging.Although deep learning is good at automatic feature extraction, it suffers from few-shot learning problem. Therefore, the general effective method is first conduct feature extraction based on prior knowledge, and then carry out feature reduction for subsequent classification. However, there are two major problems: 1) Structural information among speech features has not been mined and new features of higher quality have not been reconstructed. 2) Structural information between data samples has not been mined and new samples with higher quality have not been reconstructed. To solve these two problems, based on the existing Parkinson speech feature data set, a deep double-side learning ensemble model is designed in this paper that can reconstruct speech features and samples deeply and simultaneously. As to feature reconstruction, an embedded deep stacked group sparse auto-encoder is designed in this paper to conduct nonlinear feature transformation, so as to acquire new high-level deep features, and then the deep features are fused with original speech features by L1 regularization feature selection method. As to speech sample reconstruction, a deep sample learning algorithm is designed in this paper based on iterative mean clustering to conduct samples transformation, so as to obtain new high-level deep samples. Finally, the bagging ensemble learning mode is adopted to fuse the deep feature learning algorithm and the deep samples learning algorithm together, thereby constructing a deep double-side learning ensemble model. At the end of this paper, two representative speech datasets of Parkinson's disease were used for verification. The experimental results show that the proposed algorithm are effective.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge