Lan Wei
A Dataset and Benchmarks for Deep Learning-Based Optical Microrobot Pose and Depth Perception
May 23, 2025Abstract:Optical microrobots, manipulated via optical tweezers (OT), have broad applications in biomedicine. However, reliable pose and depth perception remain fundamental challenges due to the transparent or low-contrast nature of the microrobots, as well as the noisy and dynamic conditions of the microscale environments in which they operate. An open dataset is crucial for enabling reproducible research, facilitating benchmarking, and accelerating the development of perception models tailored to microscale challenges. Standardised evaluation enables consistent comparison across algorithms, ensuring objective benchmarking and facilitating reproducible research. Here, we introduce the OpTical MicroRobot dataset (OTMR), the first publicly available dataset designed to support microrobot perception under the optical microscope. OTMR contains 232,881 images spanning 18 microrobot types and 176 distinct poses. We benchmarked the performance of eight deep learning models, including architectures derived via neural architecture search (NAS), on two key tasks: pose classification and depth regression. Results indicated that Vision Transformer (ViT) achieve the highest accuracy in pose classification, while depth regression benefits from deeper architectures. Additionally, increasing the size of the training dataset leads to substantial improvements across both tasks, highlighting OTMR's potential as a foundational resource for robust and generalisable microrobot perception in complex microscale environments.
Coarse-to-Fine Learning for Multi-Pipette Localisation in Robot-Assisted In Vivo Patch-Clamp
Mar 31, 2025



Abstract:In vivo image-guided multi-pipette patch-clamp is essential for studying cellular interactions and network dynamics in neuroscience. However, current procedures mainly rely on manual expertise, which limits accessibility and scalability. Robotic automation presents a promising solution, but achieving precise real-time detection of multiple pipettes remains a challenge. Existing methods focus on ex vivo experiments or single pipette use, making them inadequate for in vivo multi-pipette scenarios. To address these challenges, we propose a heatmap-augmented coarse-to-fine learning technique to facilitate multi-pipette real-time localisation for robot-assisted in vivo patch-clamp. More specifically, we introduce a Generative Adversarial Network (GAN)-based module to remove background noise and enhance pipette visibility. We then introduce a two-stage Transformer model that starts with predicting the coarse heatmap of the pipette tips, followed by the fine-grained coordination regression module for precise tip localisation. To ensure robust training, we use the Hungarian algorithm for optimal matching between the predicted and actual locations of tips. Experimental results demonstrate that our method achieved > 98% accuracy within 10 {\mu}m, and > 89% accuracy within 5 {\mu}m for the localisation of multi-pipette tips. The average MSE is 2.52 {\mu}m.
Boundary-aware Transformers for Skin Lesion Segmentation
Oct 08, 2021



Abstract:Skin lesion segmentation from dermoscopy images is of great importance for improving the quantitative analysis of skin cancer. However, the automatic segmentation of melanoma is a very challenging task owing to the large variation of melanoma and ambiguous boundaries of lesion areas. While convolutional neutral networks (CNNs) have achieved remarkable progress in this task, most of existing solutions are still incapable of effectively capturing global dependencies to counteract the inductive bias caused by limited receptive fields. Recently, transformers have been proposed as a promising tool for global context modeling by employing a powerful global attention mechanism, but one of their main shortcomings when applied to segmentation tasks is that they cannot effectively extract sufficient local details to tackle ambiguous boundaries. We propose a novel boundary-aware transformer (BAT) to comprehensively address the challenges of automatic skin lesion segmentation. Specifically, we integrate a new boundary-wise attention gate (BAG) into transformers to enable the whole network to not only effectively model global long-range dependencies via transformers but also, simultaneously, capture more local details by making full use of boundary-wise prior knowledge. Particularly, the auxiliary supervision of BAG is capable of assisting transformers to learn position embedding as it provides much spatial information. We conducted extensive experiments to evaluate the proposed BAT and experiments corroborate its effectiveness, consistently outperforming state-of-the-art methods in two famous datasets.
OSTSC: Over Sampling for Time Series Classification in R
Nov 27, 2017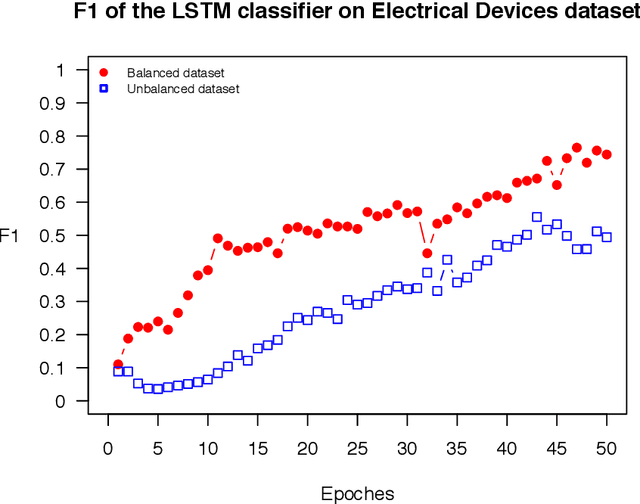
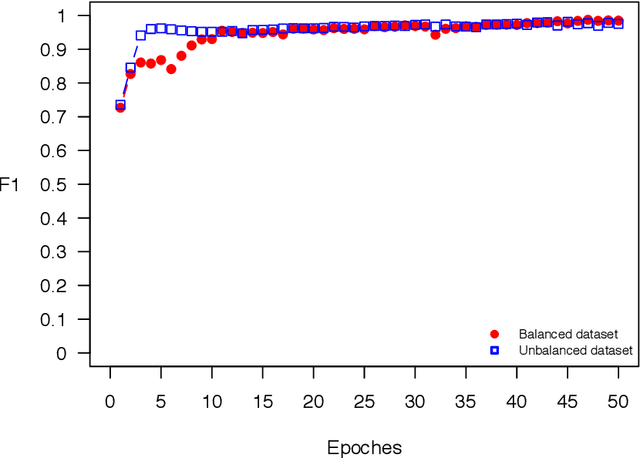
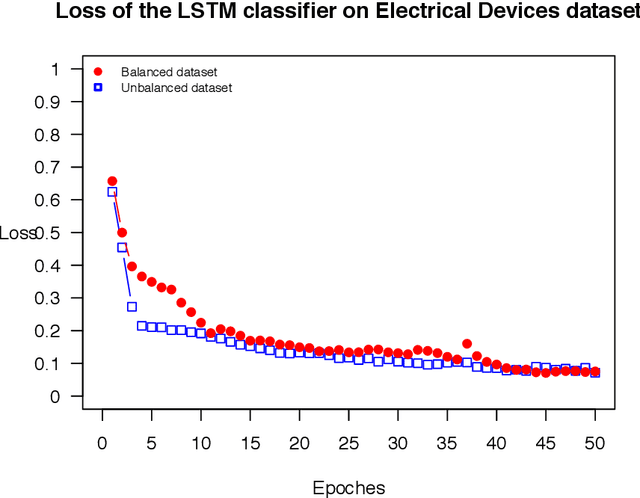
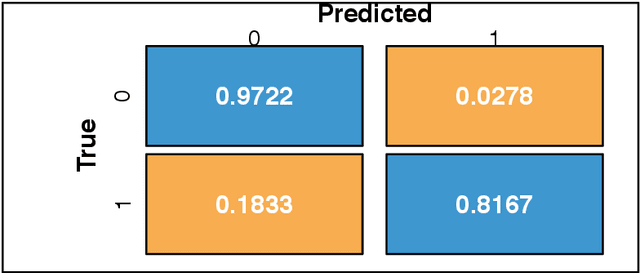
Abstract:The OSTSC package is a powerful oversampling approach for classifying univariant, but multinomial time series data in R. This article provides a brief overview of the oversampling methodology implemented by the package. A tutorial of the OSTSC package is provided. We begin by providing three test cases for the user to quickly validate the functionality in the package. To demonstrate the performance impact of OSTSC, we then provide two medium size imbalanced time series datasets. Each example applies a TensorFlow implementation of a Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) classifier - a type of a Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) classifier - to imbalanced time series. The classifier performance is compared with and without oversampling. Finally, larger versions of these two datasets are evaluated to demonstrate the scalability of the package. The examples demonstrate that the OSTSC package improves the performance of RNN classifiers applied to highly imbalanced time series data. In particular, OSTSC is observed to increase the AUC of LSTM from 0.543 to 0.784 on a high frequency trading dataset consisting of 30,000 time series observations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge