Laifeng Hu
FastMap: Fast Queries Initialization Based Vectorized HD Map Reconstruction Framework
Mar 07, 2025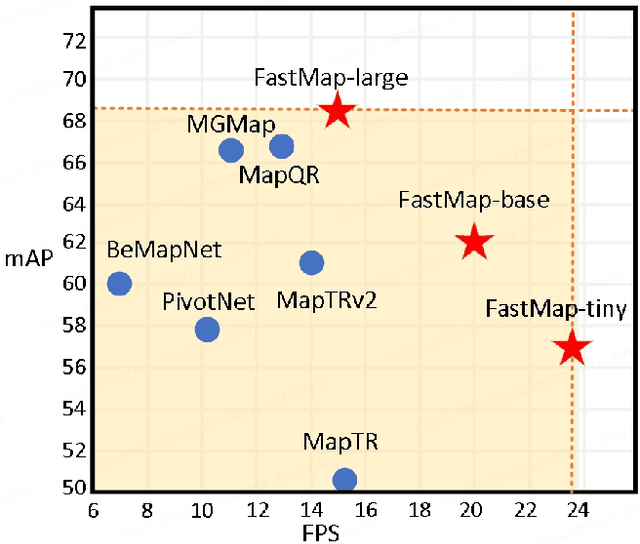
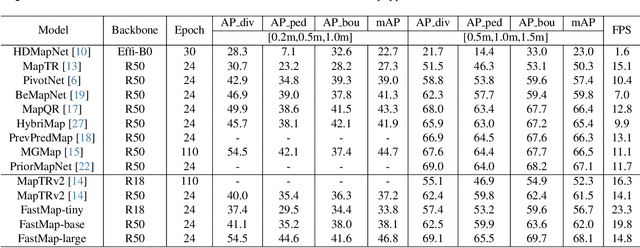
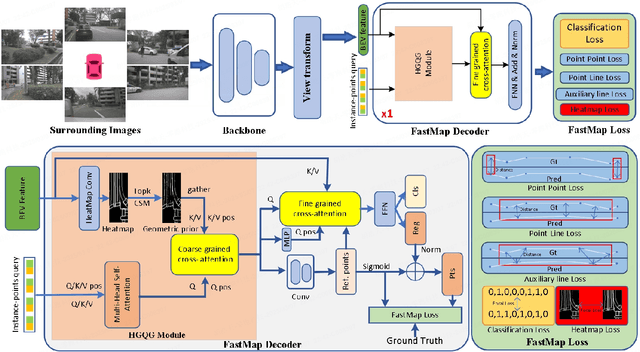
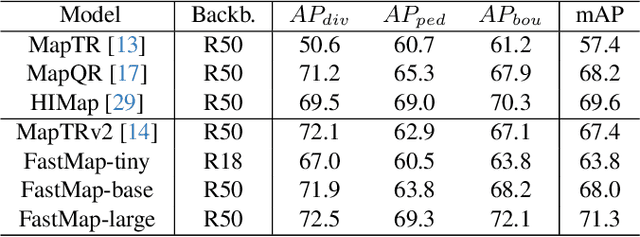
Abstract:Reconstruction of high-definition maps is a crucial task in perceiving the autonomous driving environment, as its accuracy directly impacts the reliability of prediction and planning capabilities in downstream modules. Current vectorized map reconstruction methods based on the DETR framework encounter limitations due to the redundancy in the decoder structure, necessitating the stacking of six decoder layers to maintain performance, which significantly hampers computational efficiency. To tackle this issue, we introduce FastMap, an innovative framework designed to reduce decoder redundancy in existing approaches. FastMap optimizes the decoder architecture by employing a single-layer, two-stage transformer that achieves multilevel representation capabilities. Our framework eliminates the conventional practice of randomly initializing queries and instead incorporates a heatmap-guided query generation module during the decoding phase, which effectively maps image features into structured query vectors using learnable positional encoding. Additionally, we propose a geometry-constrained point-to-line loss mechanism for FastMap, which adeptly addresses the challenge of distinguishing highly homogeneous features that often arise in traditional point-to-point loss computations. Extensive experiments demonstrate that FastMap achieves state-of-the-art performance in both nuScenes and Argoverse2 datasets, with its decoder operating 3.2 faster than the baseline. Code and more demos are available at https://github.com/hht1996ok/FastMap.
ADMap: Anti-disturbance framework for reconstructing online vectorized HD map
Jan 24, 2024



Abstract:In the field of autonomous driving, online high-definition (HD) map reconstruction is crucial for planning tasks. Recent research has developed several high-performance HD map reconstruction models to meet this necessity. However, the point sequences within the instance vectors may be jittery or jagged due to prediction bias, which can impact subsequent tasks. Therefore, this paper proposes the Anti-disturbance Map reconstruction framework (ADMap). To mitigate point-order jitter, the framework consists of three modules: Multi-Scale Perception Neck, Instance Interactive Attention (IIA), and Vector Direction Difference Loss (VDDL). By exploring the point-order relationships between and within instances in a cascading manner, the model can monitor the point-order prediction process more effectively. ADMap achieves state-of-the-art performance on the nuScenes and Argoverse2 datasets. Extensive results demonstrate its ability to produce stable and reliable map elements in complex and changing driving scenarios. Code and more demos are available at https://github.com/hht1996ok/ADMap.
EA-BEV: Edge-aware Bird' s-Eye-View Projector for 3D Object Detection
Apr 18, 2023



Abstract:In recent years, great progress has been made in the Lift-Splat-Shot-based (LSS-based) 3D object detection method, which converts features of 2D camera view and 3D lidar view to Bird's-Eye-View (BEV) for feature fusion. However, inaccurate depth estimation (e.g. the 'depth jump' problem) is an obstacle to develop LSS-based methods. To alleviate the 'depth jump' problem, we proposed Edge-Aware Bird's-Eye-View (EA-BEV) projector. By coupling proposed edge-aware depth fusion module and depth estimate module, the proposed EA-BEV projector solves the problem and enforces refined supervision on depth. Besides, we propose sparse depth supervision and gradient edge depth supervision, for constraining learning on global depth and local marginal depth information. Our EA-BEV projector is a plug-and-play module for any LSS-based 3D object detection models, and effectively improves the baseline performance. We demonstrate the effectiveness on the nuScenes benchmark. On the nuScenes 3D object detection validation dataset, our proposed EA-BEV projector can boost several state-of-the-art LLS-based baselines on nuScenes 3D object detection benchmark and nuScenes BEV map segmentation benchmark with negligible increment of inference time.
GAM : Gradient Attention Module of Optimization for Point Clouds Analysis
Mar 21, 2023Abstract:In point cloud analysis tasks, the existing local feature aggregation descriptors (LFAD) are unable to fully utilize information in the neighborhood of central points. Previous methods rely solely on Euclidean distance to constrain the local aggregation process, which can be easily affected by abnormal points and cannot adequately fit with the original geometry of the point cloud. We believe that fine-grained geometric information (FGGI) is significant for the aggregation of local features. Therefore, we propose a gradient-based local attention module, termed as Gradient Attention Module (GAM), to address the aforementioned problem. Our proposed GAM simplifies the process that extracts gradient information in the neighborhood and uses the Zenith Angle matrix and Azimuth Angle matrix as explicit representation, which accelerates the module by 35X. Comprehensive experiments were conducted on five benchmark datasets to demonstrate the effectiveness and generalization capability of the proposed GAM for 3D point cloud analysis. Especially on S3DIS dataset, GAM achieves the best performance among current point-based models with mIoU/OA/mAcc of 74.4%/90.6%/83.2%, respectively.
* In AAAI, 2023
DHARI Report to EPIC-Kitchens 2020 Object Detection Challenge
Jun 28, 2020



Abstract:In this report, we describe the technical details of oursubmission to the EPIC-Kitchens Object Detection Challenge.Duck filling and mix-up techniques are firstly introduced to augment the data and significantly improve the robustness of the proposed method. Then we propose GRE-FPN and Hard IoU-imbalance Sampler methods to extract more representative global object features. To bridge the gap of category imbalance, Class Balance Sampling is utilized and greatly improves the test results. Besides, some training and testing strategies are also exploited, such as Stochastic Weight Averaging and multi-scale testing. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach can significantly improve the mean Average Precision (mAP) of object detection on both the seen and unseen test sets of EPICKitchens.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge